Diesel timing gear D4EA
Checking the technical condition of the timing drive
Remove the top cover.
Check the timing belt (A) for damage, oil or coolant ingress
Removal and disassembly of the G4KD and G4KE cylinder block
By default, we already have the cylinder head removed

Main parameters and characteristics of YaMZ-238 engines
Power units are designed for operation at ambient temperatures from minus 60ºС to plus 50ºС, relative humidity up to 98% at a temperature of 25ºС, air dust content up to 0.4 g / m 3, as well as for movement car in mountainous conditions at an altitude of up to 4500 m above sea level and overcoming passes up to 4650 m above sea level with a corresponding decrease in power and economic indicators.

Assembling the engine of the car GAZ-66, GAZ-53
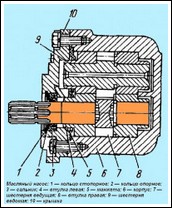
To assemble the engine, as well as to disassemble it, the engine cylinder block assembled with the clutch housing is fixed on a stand (see Fig. 1)
Before assembly, all engine parts are selected according to size, thoroughly washed, blown with compressed air and wiped with clean napkins
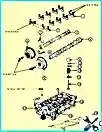
Assembly of the cylinder block of the G4KD and G4KE engine
Cylinder block
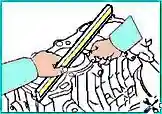
Removal and installation of the cylinder head of the 2.0 liter engine. - G4KD and 2.4 liters. – G4KE
- - it is not necessary to remove the engine to remove the cylinder head
- - to prevent damage to the paintwork of the wings of the body, it is necessary to use a special coating
- - to prevent damage to the cylinder head, before removing it, you must wait until the engine cools down
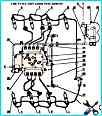
Design of the fuel system of KAMAZ 740.11-240, 740.13-260, 740.14-300 engines
The fuel supply system ensures fuel purification and uniform distribution among the engine cylinders in metered portions and at strictly defined moments in time
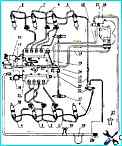
The design of the power supply of the diesel engine KAMAZ-740.30-260
The fuel supply system filters the fuel and distributes it evenly among the engine cylinders in metered portions at strictly defined moments

Characteristics of engines KAMAZ-740.50-360, KAMAZ-740.51-320
KAMA3-740.50-360, KAMA3-740.51-320 engines, designed for installation on single vehicles and truck tractors used as part of road trains, supplied to the domestic market and for export to countries with a moderate and tropical climate, as well as supplied as spare parts

Tightening torques for KAMAZ 740.11-240 diesel connections
Tightening torques for diesel connections of KamAZ vehicles
Name
Tightening conditions
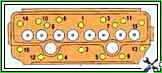
Cylinder head tightening and valve adjustment D-245E3
Checking the tightening of the cylinder head mounting bolts
Check the tightening of the cylinder head mounting bolts after the break-in period and every 40 thousand km of run on a warmed-up diesel engine in the following order:
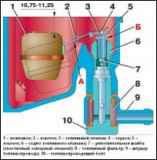
Maintenance of the K-151 carburetor
Carburetor K-151V (Fig. 1) - vertical, emulsion, two-chamber, with a falling mixture flow and sequential opening of the throttle valves
Technical characteristics of cars GAZ-66, GAZ-53
The GA3-66 vehicle is a two-axle truck, with a payload capacity of 2 tons, all-terrain, with drive on both axles. It is designed to replace the same type of GAZ-63 car produced by the plant
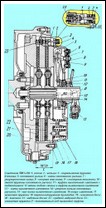
Operation of the YaMZ-238 double-disk clutch
The clutch of the YaMZ-238 model is double-disc, dry, friction type, with a peripheral arrangement of cylindrical springs
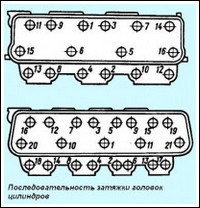
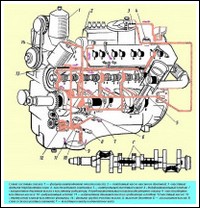
Continuation of article 2 assembly of the YaMZ-236/238 diesel engine
Installing cylinder heads, valve rocker arms and adjusting valve clearances
The cylinder head mounting studs are screwed into the right and left rows of the cylinder block, having previously lubricated the threaded holes for the studs in the block with diesel oil
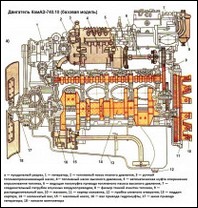
Engine KAMAZ
The engine consists of a crank and gas distribution mechanisms, as well as cooling, lubrication, power and control systems, and starting
Malfunctions of the VAZ-21114 engine
Let's consider the malfunctions that may occur during engine operation:
- - The crankshaft is not turned by the starter;
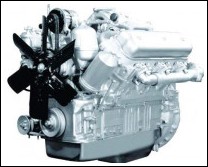
Features of the YaMZ-236/238M2 diesel engine
The YaMZ-236M2 and YaMZ-238M2 engines are six- and eight-cylinder models of the family of four-stroke diesel engines of Avtodizel OJSC

Technical characteristics of the KAMAZ 740.11-240 engine
Cylinder block, drive units and characteristics of engines KAMAZ 740.11-240, 740.13-260, 740.14-300, 740.11-3902007 RE
Technical characteristics of engines 740.11-240, 740.13-260, 740.14-300
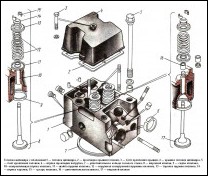
Cylinder heads Kamaz
The cylinder heads are separate for each cylinder, made of aluminum alloy. They have water cavities communicating with the same cavities of the cylinder block, inlet and outlet channels, plug-in seats and valve guides.
Page 1 of 2