The engine consists of a crank and gas distribution mechanisms, as well as cooling, lubrication, power and control systems, and starting
With the help of a crank mechanism, the reciprocating movement of the pistons in the cylinders is converted into rotational movement of the crankshaft.
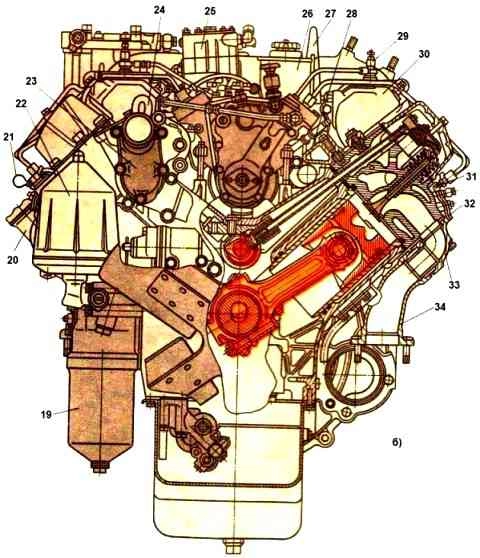
KAMAZ-740.10 engine (basic model) - cross section: 19 - full-flow oil filter; 20 - oil filler neck; 21 - oil level indicator in the engine crankcase; 22 - centrifugal oil filter; 23 - thermostat box; 24 - front eye bolt; 25 - compressor; 26 - power steering pump; 27 - rear eye bolt; 28 - left drainage pipe; 29 - torch candle; 30 - left inlet air duct; 31 - nozzle; 32 - nozzle mounting bracket; 33 - exhaust manifold pipe; 34 - exhaust manifold
The gas distribution mechanism promptly opens and closes the valves, which allow air into the cylinders and exhaust gases out of the cylinders.
The cooling system maintains the required thermal conditions of the engine.
The lubrication system supplies oil to the rubbing parts of the engine to reduce friction and wear.
The power system cleans and supplies air and fuel to the cylinders, and with the help of a regulator, it automatically regulates the flow (supply) of fuel into the combustion chamber depending on the engine load.
The diesel starting system is necessary to turn the crankshaft during startup.
Here we will describe a set of components of the KamAZ-740.10, KamAZ-7403.10 and KamAZ-7409.10 engines, and explain the operating diagram and operating principle of their mechanisms and systems.
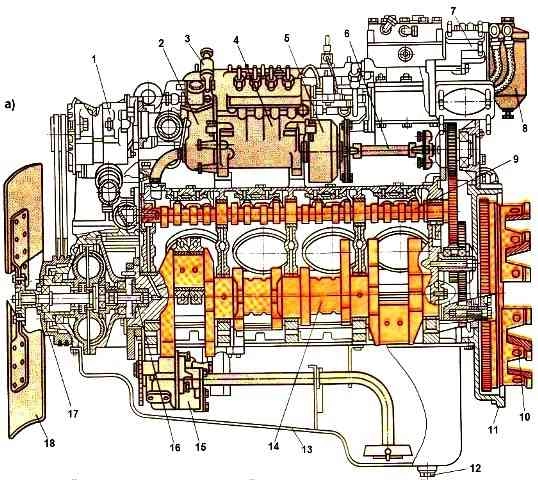
The KamAZ-740.10 engine (Fig. 1) is a four-stroke liquid-cooled diesel engine with a V-shaped arrangement of eight cylinders; is the base for all engine modifications of the brand.
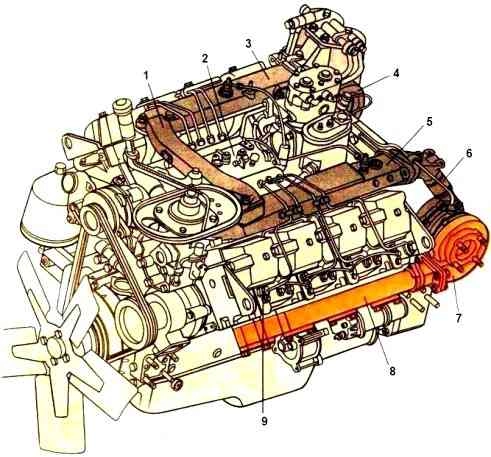
The KamA3 - 7403.10 engine (Fig. 2) has increased power due to the use of gas turbine supercharging, in which part of the energy of the exhaust gases is used to compress air and force it into the cylinders.
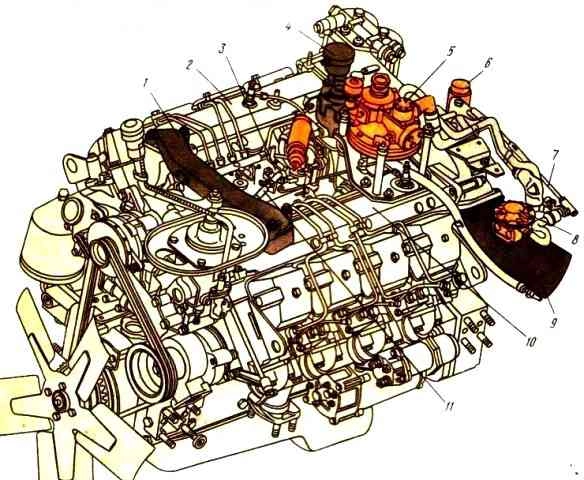
Gas-diesel 7409.10 (Fig. 3) can operate both on natural gas with its ignition by a pilot dose of diesel fuel, and on diesel fuel in diesel mode.
The main design data and parameters of the engines are given in the technical specifications (the values are given in parentheses when the engine is operating in diesel mode).
Technical characteristics of KamAZ engines
Model 740.10
- Number of measures 4
- Number of cylinders 8
Cylinder arrangement V-shaped, camber angle 90°
Cylinder operating order 1—5—4—2—6—3—7—8
The direction of rotation of the crankshaft is right
Cylinder diameter and piston stroke 120x120 mm
Working volume 10.85 l
Compression ratio 17
Rated power 154 kW
Maximum torque 637 Nm
Crankshaft rotation speed, rpm:
- - nominal 2600
- - at maximum torque (1600-1800)
- - at idle mode minimum, no more than 600
- - the same, maximum, no more than 2930
Intake valve timing:
- - opening 13° to E. m.t.
- - closing 49° after n. m.t.
Same as intake valve:
- - discovery 66° BC. m.t.
- - closing 10° after c. m.t.
Oil pressure in a warm engine, kPa:
- - at a nominal speed of 400-550
- - at a minimum speed in idle mode, at least 100
Nozzle model 33-01
High pressure fuel pump model 33-02
Model 7403.10
Number of measures 4
Number of cylinders 8
Cylinder arrangement V-shaped, camber angle 90°
Cylinder operating order 1—5—4—2—6—3—7—8
The direction of rotation of the crankshaft is right
Cylinder diameter and piston stroke 120x120 mm
Working volume 10.85 l
Compression ratio 16
Rated power, kW 191
Maximum torque, Nm 785
Crankshaft rotation speed, rpm:
- - Nominal 2600
- - at maximum torque 1600-1800
- - at idle mode minimum, no more than 600
- - the same, maximum, no more than 2930
Intake valve timing:
- - Opening 13° to E. m.t.
- - closing 49° after n. m.t.
Same as intake valve:
- - discovery 66° BC. m.t.
- - closing 10° after c. m.t.
Oil pressure in a warm engine, kPa:
- - at a nominal speed of 400-550
- - at a minimum rotation speed in idle mode, at least 100
Nozzle model 271
High pressure fuel pump model 334
Model 7409.10
Number of measures 4
Number of cylinders 8
Cylinder arrangement V-shaped, camber angle 90°
Cylinder operating order 1—5—4—2—6—3—7—8
The direction of rotation of the crankshaft is right
Cylinder diameter and piston stroke, mm 120x120
Working volume, l 10.85
Compression ratio 17
Rated power, kW 154
Maximum torque, Nm 637
Crankshaft rotation speed, rpm:
- - nominal 2550 (2600)
- - at maximum torque 1300-1800
- - at idle mode minimum, no more than 600
- - the same, maximum, no more than 2930
Intake valve timing:
- - opening 13° to E. m.t.
- - closing 49° after n. m.t.
Same as intake valve:
- - discovery 66° BC. m.t.
- - closing 10° after c. m.t.
Oil pressure in a warm engine, kPa:
- - at a nominal speed of 400-550
- - at a minimum speed in idle mode, at least 100
Nozzle model 33-01
High pressure fuel pump model 335





