The design of the rear axle of the GAZ-53A and GAZ-66 vehicles is shown in Fig. 1 and 2.
To increase durability, the axles are equipped with a hypoid main gear. The driving gear is shifted downwards by 32 mm relative to the driven gear.
To prevent large deformations of the driven gear, the main gear is equipped with an adjustable stop.
The main gear and differential are mounted in a separate gearbox housing, which is freely inserted into the hole in the axle housing and secured with bolts.
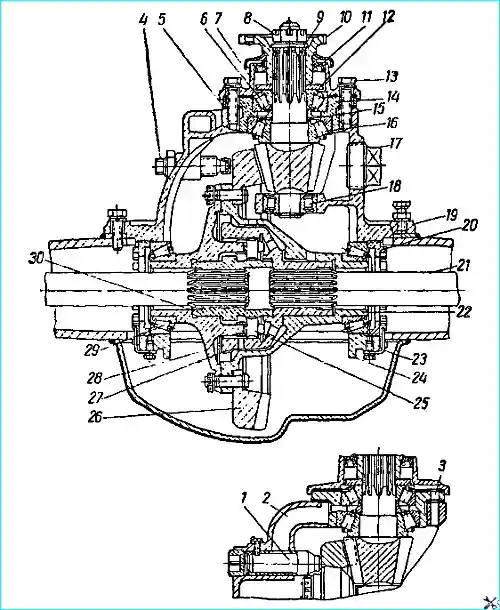
The rear axle gearboxes of the GAZ-53A and GAZ-66 vehicles differ only in the design of the differential.
The GAZ-53A vehicle uses a conventional bevel differential with four satellites, while the GAZ-66 vehicle uses a self-locking cam differential to improve cross-country ability, the design of which is shown in Fig. 63.
The separator 28 has 24 radial holes arranged in two staggered rows, into which crackers 25 are installed.
Between the rows of holes for crackers on the outer and inner surfaces of the separator, there are retaining rings that prevent the crackers from turning around their axes, and also keep them from falling out of the separator when assembling the differential.
The outer sprocket 27 is freely installed in the hole of the cup 22, and the inner sprocket 30 in the holes of the separator and the outer sprocket.
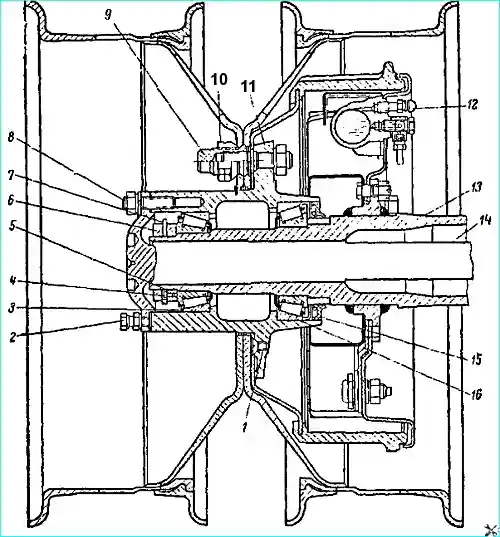
The rear axle housing of the GAZ-53A and GAZ-66 vehicles consists of two stamped halves welded along the horizontal axis of the axle.
This design ensures ease of assembly and disassembly of the unit.
The wheel journals at the ends of the GAZ-53 housing are butt-welded, and on the GAZ-66 housing they are attached to the housing using studs.
Maintenance of the rear axle
Maintenance of the rear axle during operation consists of ensuring timely replacement of lubricant, monitoring the lubricant level, checking the degree of tightening of the bolts securing the gearbox to the rear axle housing and the bolts securing the coupling of the pinion shaft bearings, checking the tightening condition of the pinion shaft bearings.
The engagement is adjusted only when installing new gears.
Rear axle malfunctions and how to eliminate them
- Causes of malfunction
How to eliminate
Increased noise from the rear axle:
- Incorrect adjustment of the engagement of the main pair of gears by contact
To reduce noise, re-adjust
- Increased lateral clearance in the engagement of the driving and driven gears as a result of wear of their teeth or bearings
Replace worn gears.
It is not necessary to adjust the position of the gears to compensate for wear, since the required contact in the engagement of the driving and driven gears is achieved only in one of their mutual positions, in which they are processed on machines
- Loosening of the bearing tightening due to wear and the ends of the parts that are tightened together with bearings
Tighten the bearings
- Excessive runout of the pinion shaft due to wear of the bearings
Tighten the bearings
- Malfunctions in the differential parts. In this case, the noise appears when turning the car (some noise when turning is acceptable)
Replace the faulty parts
- When determining the noise in the rear axle, you need to make sure that the noise comes from the axle, since a similar noise can appear when the rear wheel hub bearings are damaged.
When the nature of the road changes, the noise of the rear m remains.
The noise of a worn hub bearing is clearly audible when the car is moving at low speed and disappears with light braking.
To detect the noise of the hub bearing, each wheel should be jacked up and the condition of the bearing should be determined while the wheel is rotating.
Large radial play of the drive gear:
- Wear of the axle shaft splines (When starting the car from a standstill and with a sharp application of load while the car is moving, a knock is heard in the rear axle)
If the axle shaft is heavily worn, replace it
- Loosening of the axle shaft flange fastening nuts
Tighten the nuts
- Increased lateral clearance in the engagement of the drive and driven gears of the main transmission due to wear of the teeth
Replace worn details
- Increased lateral clearance between the teeth of the GAZ-53A differential gears or between the crackers and cams of the GAZ-66 differential due to wear of the teeth and support washers of the satellites and axle gears (or wear of the crackers and sprockets)
Replace worn parts
- Loosening of the tightening of the bolts securing the driven gear in the GAZ-5ZA satellite box (or to the separator and cup of the GAZ-66 differential)
Inspect the condition of the fasteners and, if there is no damage, tighten the bolts; tightening torque is specified below
- Bearing wear or misalignment
Make the required adjustment
Oil leakage through the seals of the drive gear and hubs, as well as along the plane of the joint between the gearbox housing and the axle housing:
- Seal wear. Wear of surfaces under oil seals on the flange of the drive pinion shaft and the hub oil seal sleeve
Replace worn oil seals flange and sleeve
- Loose tightening of the bolts securing the gearbox housings and rear axle
Tighten the bolts (torque 10-12 kgm)
- Wear of the gasket installed between the mating surfaces of the gearbox housings and rear axle
Replace the gasket
Scuffs on the teeth of the main gear gears
- Poor lubrication of the gears
If the gears are not suitable for further operation, they must be replaced.
Fill the rear axle with hypoid grease of the required quality
- Excessive shock loads
Replace gears
To troubleshoot the problem, it may be necessary to disassemble the rear axle. Depending on the nature of the problem, disassembly may be partial or complete.





