You will need: the same tools as for replacing the valve stem seals, except for those that are needed directly for replacing them (tools are used only for preparatory operations),
as well as three additional containers for flushing diesel fuel with a capacity of approximately 2 liters each, a piece of hardened wire with a diameter of 0.5 mm and a length of approximately 10 cm.
Preparing the car for work. We install it on a lift or inspection pit.
Remove the timing belt (see the article replacing the timing belt).
Remove the oil separator of the ventilation system, see the article - "How to clean the engine crankcase ventilation system"

Using a 10 mm head, unscrew the bolt securing the bracket of the dipstick guide tube to the air intake bracket

Remove the tube with the dipstick from the engine sump socket.
The tube is sealed with a rubber ring.

Using an 8 mm socket, unscrew the two bolts securing the eye

Remove the eye with the bracket

Using an 8 mm socket, unscrew the twenty-four cylinder head cover mounting bolts

Using a screwdriver, pry off the cylinder head cover (using a rag under the lugs on the cover)

Remove the cylinder head cover
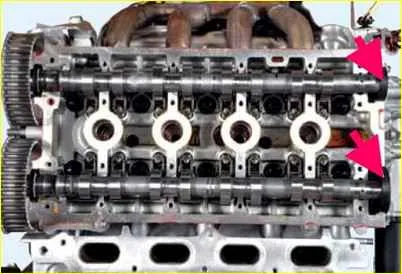
Remove two rubber-metal plugs from the cylinder head

Removing the exhaust valve shaft

Removing the intake valve shaft valves

To check the hydraulic supports, remove the lever

Remove the hydraulic compensator from the cylinder head socket
Checking the hydraulic compensators is discussed below.
To remove the pulley, lay the camshaft.
Put an 18 mm open-end wrench on the pulley mounting nut.

Insert a screwdriver through the hole in the pulley.
Leaning on the pulley hub with the blade of the screwdriver, press on the key with the rod of the screwdriver and turn it counterclockwise.
The pulley should not rotate, and the nut will unscrew.

Remove the pulley from the camshaft nose

Remove the oil seal. We also remove the oil seal from the other camshaft
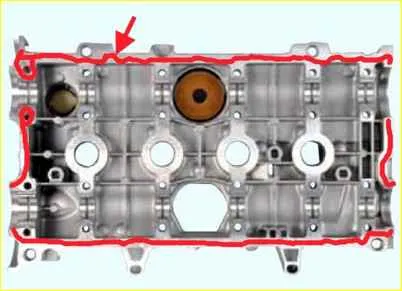
Applying sealant to the mating surface of the cover
Install the cylinder head cover and tighten the bolts to the prescribed torque in the sequence shown in the table.
Tightening sequence of the cylinder head cover bolts:
- Tighten bolts - 22, 23, 20, 13 - tightening torque 8 Nm (0.8 kgf.m);
- Tighten bolts 1 through 12, 14 through 19, 21 and 24 - tightening torque 15 Nm (1.5 kgf.m);
- Loosen bolts 22, 23, 20, 13;
- Tighten bolts 22, 23, 20, 13 - tightening torque 15 Nm (1.5 kgf.m)
After installing the cylinder head cover, use a tool head or a piece of pipe of a suitable size to press new camshaft oil seals into the cylinder head sockets, having previously applied a thin layer of engine oil to the working edges of the oil seals.
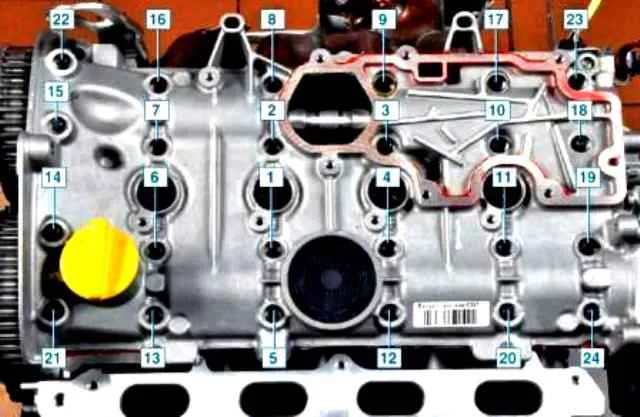
Numbering of the cylinder head cover bolts
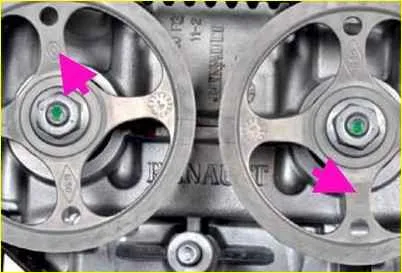
After checking the valve timing and securing the shafts, install the toothed pulleys on the camshaft noses so that the "Renault" emblems on the pulley spokes are positioned vertically upwards (exhaust valve shaft) and downwards (intake valve shaft).
After tightening the pulley mounting nuts, tighten them slightly.
Install them on the pulleys and tighten the timing belt.
Tighten the camshaft pulley mounting nuts to a torque of 30 Nm and turn them an additional 84˚.
Turn the crankshaft clockwise two turns and check that the valve timing is set correctly.
If necessary, repeat the valve timing installation.
Checking and flushing hydraulic valve lifters
Hydraulic valve lifters serve to compensate for thermal expansion of the drive elements.
The operation of the hydraulic lifter is based on the principle of incompressibility of engine oil, which constantly fills the internal cavity of the hydraulic lifter during engine operation and moves its plunger when a gap appears in the valve drive, ensuring constant contact of the roller of the valve drive pressure lever with the camshaft cam without a gap.
Thanks to this, there is no need to adjust the valves during maintenance.
Hydraulic lifters are non-separable compact devices inserted into the cylinder head sockets.
Knocking of the valves of a running engine can be caused by:
- - air entering the above-plunger cavities of the hydraulic lifters when the oil level in the crankcase, as well as when the car is parked on a slope for a long time;
- - contamination of the precision surfaces of the hydraulic compensators of the clearances in the valve drive mechanism with sludge from low-quality engine oil (or when it is not replaced in a timely manner, as well as when the oil filter is damaged);
- - wear of the hydraulic compensators.
If pumping or flushing fails to restore to improve the performance of the hydraulic compensators, replace them, since their design is non-separable.
First, make sure that the extraneous noise during engine operation is caused by a malfunction of the hydraulic compensators:
- start the engine. If the hydraulic compensators are faulty, extraneous noise in the cylinder head cover area appears immediately after starting the engine and changes in accordance with the change in the engine crankshaft speed.
If the noise does not appear immediately after starting the engine or does not change with a change in the crankshaft speed, the malfunction is not caused by a malfunction of the hydraulic compensators.
Moreover, if the noise does not change with a change in the crankshaft speed, the cause of the extraneous noise is probably not in the engine;
- when the engine is idling, make sure that the noise level does not change with a change in load (for example, when switching the automatic transmission selector from position "N" to position "D" when disengaging the clutch of a car with a manual transmission or when turning on electrical consumers and air conditioning).
If the noise level changes, the cause may be a collision of parts due to wear of the connecting rod and main bearing shells of the crankshaft, and not a malfunction hydraulic compensators;
- - warm up the engine to operating temperature. If the noise has decreased or disappeared, it is possible that the knocking of the hydraulic compensators is caused by oil contamination. In this case, it is necessary to flush the hydraulic compensators:
- - if the noise does not disappear, it is likely that air has entered the hydraulic compensators and should be removed.
If the oil level in the crankcase is too low, the oil pump will suck in air along with the oil; if the oil level in the crankcase is too high, the oil is shaken and foamed by the crankshaft counterweights.
When the car is parked on a slope for a long time, oil flows out of the cavities of the hydraulic compensators and oil channels, and the supply of oil to the hydraulic compensators after starting the engine requires some time, during which air has time to enter the cavity of the hydraulic compensator.
In all these cases, when oil with air gets into the above-plunger cavity of the hydraulic compensator, the air inside the cavity will be compressed when the valve opens and the hydraulic compensator will not be compressed enough, which will lead to the appearance of a characteristic knock of the valve mechanism with increased clearances.
To remove air from the hydraulic compensators, do the following:
check the oil level in the engine crankcase and, if necessary, bring it up to normal;
- - start the engine and warm it up at idle for 1-3 min;
- - increase the crankshaft speed to 3000 min -1, then sharply reduce to idle speed and let the engine idle;
- - repeat the cycle and check if the noise of the valve drive mechanism has disappeared.
If the hydraulic lifters are in good condition, the noise will disappear after 10-30 cycles;
- - after the noise has disappeared, repeat to bleed air five more times;
- - let the engine idle for 1-3 minutes and make sure that the noise of the valve drive mechanism has disappeared.
If the noise of the valve drive mechanism has not disappeared after bleeding air and warming up the engine to operating temperature, identify faulty hydraulic lifters as follows.
- 1. Turn off the engine and immediately after stopping, set the piston of the 1st cylinder to the TDC position of the compression stroke, remove the cylinder head cover.
- 2. Remove the camshafts.
- 3. To check the operability of the engine hydraulic compensators, press on the shoulder of the rocker arm resting on the hydraulic compensator. If the rocker arm can be moved with virtually no effort, the hydraulic compensator is faulty.
- 4. Similarly, check the condition of the hydraulic compensators of the remaining cylinders (firing order of cylinders 1-3-4-2).
After identifying the faulty hydraulic compensators, first try to flush them as follows.
- 1. Remove the valve rocker arms.
- 2. Remove the faulty hydraulic compensator from the cylinder head socket.
- 3. Prepare three identical containers with a capacity of approximately 2 liters for flushing the hydraulic compensators. The dimensions of each container should be sufficient for the hydraulic compensator, lowered to the bottom of the container in a vertical position, to be completely immersed in liquid. Fill the containers with clean diesel fuel.
- 4. Place the hydraulic compensator in the first container and clean its outer surface.
- 5. Having immersed the hydraulic compensator in the first container halfway, with the plunger down, lightly press the wire through the hole to press the valve ball and, holding the ball pressed, move the plunger of the hydraulic compensator 5-10 times until the plunger movement becomes completely free. If it is not possible to achieve easy plunger movement, replace the hydraulic compensator.
- 6. Remove the hydraulic compensator from the container and, having pressed the ball valve, move the plunger until all diesel fuel flows out of the hydraulic compensator.
- 7. Place the hydraulic compensator in the second container and repeat step 5.
- 8. Remove the hydraulic compensator from the container and drain the diesel fuel from it as described in step 6.
- 9. Place the hydraulic compensator on the bottom of the third container vertically, with the plunger facing up, and press the ball of its valve with a wire.
- 10. Keeping the valve ball pressed down, move the plunger down and then slowly move it up so that the above-plunger cavity of the hydraulic compensator is filled with diesel fuel.
- 11. Remove the hydraulic compensator from the container; holding it with the plunger upwards, press the plunger with a little force and make sure that it remains stationary.
At the same time, check the overall height of the hydraulic compensator, comparing it with a new hydraulic compensator.
If during the check it was possible to move the plunger of the hydraulic compensator, repeat operations 9 and 10 until the cavity of the hydraulic compensator is completely filled with diesel fuel. If after this the hydraulic compensator does not reach the working condition or its overall height is less than the height of the new hydraulic compensator, replace it.
Before assembling the valve drive mechanism, store filled hydraulic compensators only in the vertical position with the plungers upwards. Avoid getting dirt into the hydraulic compensators.
Install the hydraulic compensators on the engine as soon as possible after refueling to prevent possible loss of diesel fuel.
- 12. Install the hydraulic compensators and all removed parts in the reverse order of removal.
- 13. Start the engine and let it idle for 1-3 minutes. If necessary, bleed the hydraulic compensators as described above.






