Depending on the configuration, Lada Granta, Lada Priora, Lada Kalina and other models can be equipped with a VAZ 11183 engine
Eight-valve engines with a displacement of 1.6 liters are based on the VAZ-2111 engine.
They have a cylinder block increased in height by 2.3 mm and an original crankshaft. The cylinder diameter remains the same - 82 mm, the piston stroke is increased to 75.6 mm in contrast to 71 mm for the base engine.
Oil nozzles are installed in the main bearing supports.
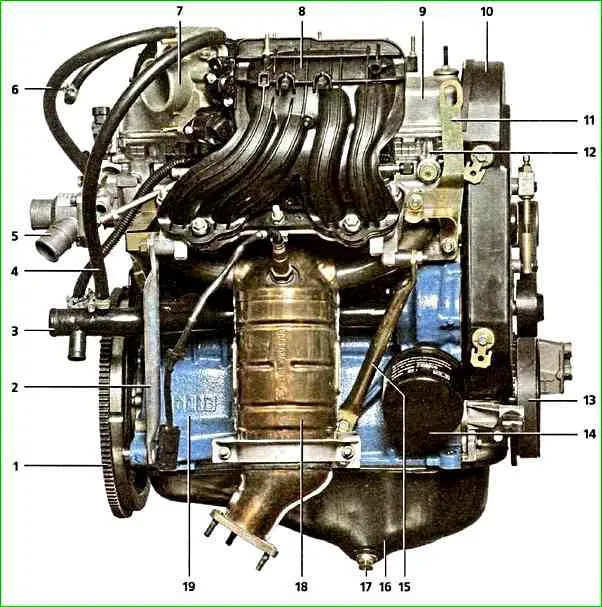
The cylinder head contains one camshaft, eight valves and eight valve tappets with shims.
The camshaft supports are made in the head.
Two camshaft bearing housings are bolted to the upper plane of the head.
The gas distribution mechanism is closed on top with a cap with an oil filler neck.
The camshaft and coolant pump are driven by a timing belt from a toothed pulley mounted on the engine crankshaft.
The tension of the belt and the direction of its movement along the pulleys is carried out by a tension roller.
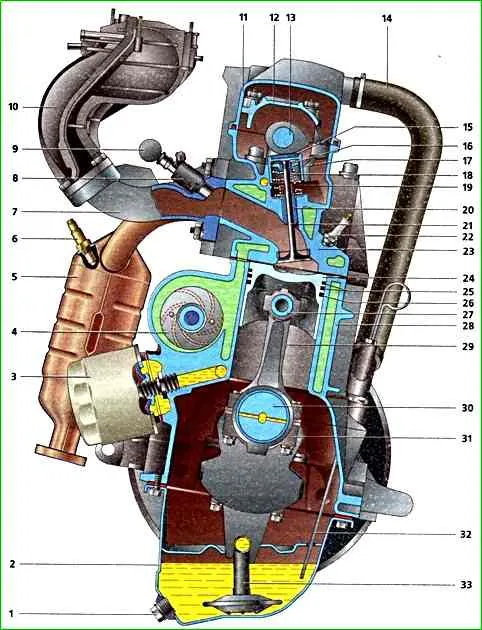
The cylinder block is cast iron, with cylinders machined into it.
The internal cavities of the coolant block are formed by casting, and the oil supply channels are made by drilling.
There are five crankshaft main bearing supports located at the bottom of the cylinder block.
The main bearing caps are not interchangeable and are marked with the serial number of the bearing, starting from the crankshaft pulley.
In the cover of the second main bearing there are two threaded holes for the oil intake bolts.
Steel-aluminum main bearing shells are installed in the supports and covers.
On both sides of the third main bearing support there are sockets for installing thrust half-rings that prevent axial movement of the crankshaft.
The front half-ring is steel-aluminium, the rear half-ring is metal-ceramic, yellow on both sides.
The pistons are cast from aluminum alloy. Each piston has two compression rings and one oil scraper ring.
The lower compression ring is of the scraper type with a groove and a sharp edge on the lower plane.
A spring expander is installed inside the oil scraper ring.
The pins are of the floating type (fixed in the pistons by two spring retaining rings) or fixed in the upper head of the connecting rod using the “shrink fit” method.
A steel-bronze bushing is pressed into the upper head of the connecting rod.
The connecting rod caps are not interchangeable and are installed on the connecting rod in only one position.
The oil pan is attached to the bottom of the cylinder block.
Combined engine lubrication system - under pressure and splashing.
The oil pump is a gear type with internal gearing and driven from the front end of the crankshaft.
Through the oil intake, the pump takes oil from the oil pan and pumps it under pressure into the channels of the engine lubrication system.
To monitor the amount of oil in the pan, a dipstick is installed - a level indicator.
The oil filter is full-flow, with a paper filter element and a check valve that prevents oil from flowing out of the lubrication system channels into the oil pan after the engine is stopped.
Oil nozzles are installed in the main bearing supports.
Oil from the injectors is supplied to the internal surfaces of the pistons to cool them.
Part of the oil falls on the upper heads of the connecting rods and flows through the conical holes made in them onto the piston pins, lubricating them.
Channels are drilled in the crankshaft body. Through them, oil flows to the connecting rod journals, lubricating them.
Oil enters the crankshaft channels from the cylinder block through holes in the main bearing shells and main journals.
Technological openings of the channels are closed with stamped steel plugs.
On the left side of the block there is a cavity for installing a coolant pump and a boss for installing an oil filter.
Generate or is driven by a poly V-belt from the engine crankshaft pulley.
The intake manifold is made of plastic.
Exhaust manifold - steel, combined with catalytic converter
Its connection with the head is sealed with a two-layer metal gasket.
Articles on engine repair are combined into one section.
Replacing the timing belt of the engine 11183
How to adjust the valve clearances of the 11183 engine





