The rear suspension of the car is dependent on two longitudinal semi-elliptic leaf springs with hydraulic telescopic shock absorbers
The five-leaf spring is assembled using plastic anti-creaking gaskets and rubber gaskets under the clamps.
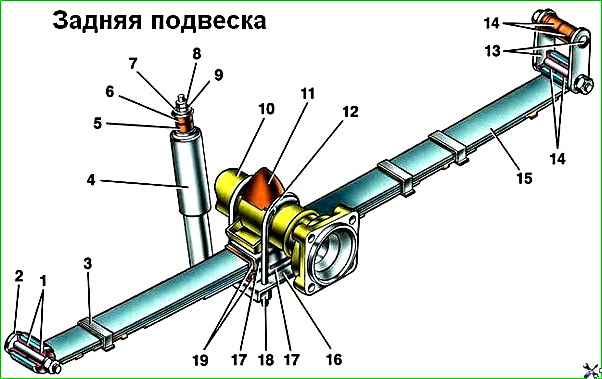
Rear suspension: 1 – bushing; 2 – pin with front bracket washer; 3 – clamp; 4 – engine support bracket; 5 – shock absorber; 6 – upper shock absorber mounting pad; 7 – cup of the upper pillow; 8 – lock nut; 9 – nut; 10 – rear axle beam; 11 – rear suspension buffer; 12 – stepladder; 13 – crankcase ventilation hose; 14 – spring shackle with pin; 15 – spring; 16 – spring lining; 17 – cushion clip; 18 – stepladder fastening nut; 19 – spring cushion
The front end of the spring is attached through rubber bushings 1 to the body bracket, and the rear end is attached to the shackle 13.
The spring is attached to the rear axle using stepladders 12 through rubber cushions 19.
Shock absorbers 4 are designed to dampen vibrations of the rear suspension.
Protruding from the shock absorbers through rubber cushions 5 and 6 are fixed to the floor of the body, and the lower ones are attached to the pins of the spring pads.
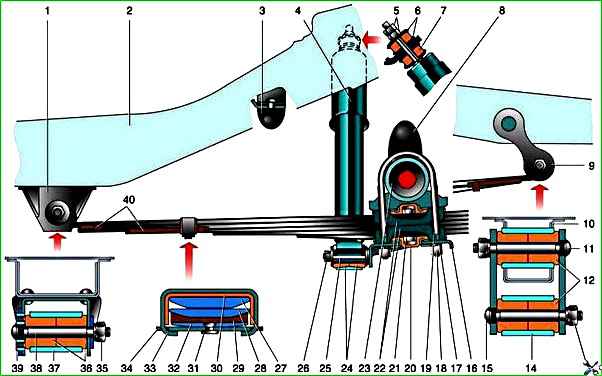
Elements of the rear suspension of the GAZ-3110 car: 1 – bracket; 2, 10 – body floor spars; 3 – additional buffer; 4 – shock absorber; 5 – nut and locknut of the upper shock absorber mounting; 6 – steel washers; 7 – rubber cushions; 8 – main buffer; 9 – spring earring; 11 – finger; 12 – rubber bushings; 13 – nut; 14 – rear spring eye; 15 – finger; 16 – spring lining; 17 – spring washer; 18 – stepladder nut; 19 – stepladder; 20 – rubber cushion; 21 – center bolt; 22 – clips; 23 – rear axle beam; 24 – rubber bushings of the shock absorber; 25 – bolt; 26 – nut; 27 – main leaf of the spring; 28 – second leaf of the spring; 29, 40 – polyethylene anti-squeak gaskets; 30 – clamp gasket; 31 – rivet; 32 – third leaf of the spring; 33 – clamp; 34 – clamp plate; 35 – nut; 36 – rubber bushings; 37 – front spring eye; 38 – finger; 39 – washer with threaded holes
The spring is attached to the body through the top sheet (main), the ends of which are bent into rings (ears).
A pin with rubber bushings is inserted into the front eye of the main sheet and into the bracket of the rear spar.
The rear eye is attached to the side member through an earring that compensates for changes in the distance between the ends of the spring during operation of the rear suspension.
The spring sheets are collected in packages of 5 pieces (flat side up, convex side down) and tightened with a central bolt (GAZ-310221 spring is made up of 6 sheets).
All movable suspension joints are made on rubber bushings (front and rear spring mounts, lower shock absorber mounts) or cushions (upper shock absorber mounts).
The rear axle is mounted on springs with stepladders, through clips with rubber cushions, to reduce the transmission of vibrations to the body when the car is moving.
The upward travel of the rear axle is limited by two rubber buffers installed on it at the points of attachment to the springs.
Another buffer is attached to the bottom of the car above the neck of the rear axle housing, limiting the upward movement of the rear axle and preventing it from hitting the body.
Shock absorbers – telescopic, twin-tube, collapsible.
They are attached with the lower end (reservoir) to the spring lining, and with the upper end (rod) to the power elements of the underbody.





