The ECU is the central device of the engine management system. The unit is fixed to the rear wall of the battery platform.
The ECU is a special-purpose mini-computer, which includes a random access memory (RAM) and a programmable read-only memory (EPROM).
The RAM is used to temporarily store current information about engine operation (measured parameters) and calculated data. The RAM also records codes for any faults that occur.
This memory is volatile, i.e. when the electrical power is interrupted (the battery is disconnected or the wiring harness is disconnected from the ECU), its contents are erased.
The EPROM stores the engine control program, which contains a sequence of operating commands (algorithms) and calibration data (settings).
The EPROM determines the most important engine operating parameters: the nature of the change in torque and power, fuel consumption, ignition timing, composition exhaust gases, etc.
The EPROM is nonvolatile, i.e. its contents do not change when the power supply is disconnected.
The ECU receives information from the control system sensors, the switch and the air conditioner refrigerant pressure sensor, the power steering pressure sensor, and also controls actuators such as the fuel pump, injectors, ignition coils (coil - K7M engine), idle speed controller, electromagnetic purge valve of the adsorber, electric fan of the cooling system, engine overheating alarm, electromagnetic clutch of the air conditioner compressor, and various system relays.
When the ignition is turned on, the ECU sends a control signal to the main relay, and when the ignition is turned off, it delays the switching off of the main relay for the time required to prepare for the next switching on (to complete calculations, set the idle speed controller, control the electric fan of the cooling system). The ECU also performs diagnostic functions of the engine management system (on-board diagnostics system).
The ECU determines the presence of faults in the control system elements and stores fault codes in its memory.
When a fault is detected, in order to avoid negative consequences (burnout of pistons due to detonation, damage to the catalytic converter in the event of misfires of the air-fuel mixture, exceeding the maximum values for the toxicity of exhaust gases, etc.), the ECU turns on the fault indicator in the instrument cluster and switches the system to emergency operating modes.
Their essence is that if any sensor or its circuit fails, the ECU uses replacement data stored in the EPROM to control the engine.
When the ignition is turned on, the ECU activates the control system:
- turns on the fuel pump to create the required pressure in the fuel rail and processes signals from the coolant temperature and throttle position sensors flaps for calculating the composition of the fuel-air mixture when starting the engine. If the crankshaft has not been turned by the starter during this time, the ECU switches off the fuel pump after 2 seconds and switches it on again after the cranking has started.
When the engine is running, the ECU processes information from the sensors:
crankshaft position, throttle position, coolant temperature, absolute air pressure, intake air temperature, vehicle speed (on a vehicle without ABS), wheel speed (on a vehicle with ABS), oxygen concentration.
Depending on the engine operating mode, the ECU controls the operation of the injectors, ignition coils, idle speed control, canister purge valve, and engine cooling fan.
When the air conditioner is turned on, the ECU increases the engine crankshaft speed at idle and sends a signal to engage the air conditioner compressor clutch.
The ECU calculates the ignition timing angle depending on the crankshaft speed engine shaft, engine load and coolant temperature.
The mixture composition is regulated by the duration of the control pulse supplied to the injectors - the longer the pulse, the greater the fuel supply, and vice versa.
Under normal engine operating conditions, fuel is injected alternately into each cylinder at the start of the intake stroke.
To do this, the ECU uses information from the crankshaft position sensor, which determines the TDC of pistons 1st and 4th, as well as 2nd and 3rd cylinders.
The system does not have a camshaft position sensor (phase sensor). Therefore, to determine which of the two cylinders to inject fuel into, the ECU uses the following algorithm.
Each time the engine is stopped, the ECU stores the last injector that was used, and when the engine is restarted, the command is first sent to this injector.
If fuel is injected into cylinder not at the start of the intake stroke, the ECU includes a test program and determines the required order of fuel injection into the cylinders.
If there is no signal from the crankshaft position sensor (the shaft does not rotate or the sensor and its circuits are faulty), the ECU shuts off the fuel supply to the cylinders.
The fuel supply is also shut off when the ignition is turned off, which prevents spontaneous combustion of the mixture in the engine cylinders.
During engine braking (with the gear and clutch engaged), when the throttle valve is completely closed and the engine crankshaft speed is high, fuel injection is not performed to reduce the toxicity of exhaust gases.
When the voltage in the vehicle's on-board network drops, the ECU increases the energy accumulation time in the ignition coils (for reliable ignition of the combustible mixture) and the duration of the injection pulse (to compensate for the increase in the injector opening time).
When the voltage in the on-board network increases, the accumulation time energy in the ignition coils and the duration of the pulse supplied to the injectors are reduced.
The ECU controls the activation of the electric fan of the cooling system (via a relay) depending on the engine temperature, crankshaft speed and operation of the air conditioner (if installed).
The electric fan of the cooling system is activated if the coolant temperature exceeds the permissible value.
Removing the ECM
We install the car to perform the work.
We remove the ECM unit for replacement or when performing car repair operations associated with the possibility of damaging the electronic components of the unit (for example, when drying the car in a drying chamber after painting, etc.). Disconnect the wire terminal from the negative terminal of the battery.
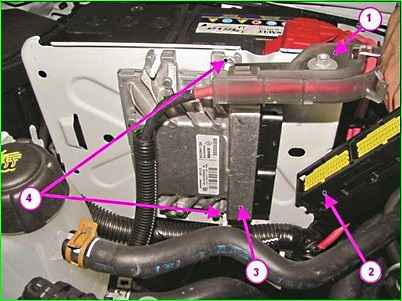
Using a 10 mm head, unscrew the mounting bolt, disconnect bracket 1 and move it to the side.
Disconnect connector 2 of the wiring harness from controller 3 of the ECM.
Using a 10 mm head, unscrew nuts 4 and remove the ECM.
Installation
Install controller 3, ECM on the vehicle, install and tighten nuts 4. Tightening torque of nuts 8 Nm (0.8 kgf.m) (replaceable head 10, extension, ratchet, torque wrench).
Connect connector 2 of the wiring harness to the ECM.
Install bracket 1, install and tighten the bracket mounting bolt (replaceable head 10, extension, ratchet).
Connect the ground wire terminal to the battery.
Assignment of ECU ECM contacts
Contact. Purpose
- Control of ignition coil of cylinders 2-3
- Not used
- «Ground»
- Control of electromagnetic valve of purge of adsorber
- Not used
- Not used
- Not used
- Control signal «-» to relay of low speed of fan of engine cooling system
- Warning lamp of emergency temperature of coolant
- Control signal «-» to relay of air conditioner compressor
- Signal of fuel consumption
- Control signal 1 to regulator of idle speed
- Signal of sensor of coolant temperature
- Not used
- «Ground» of sensor of absolute pressure
- Signal of sensor of absolute pressure
- Not used
- Coolant pressure sensor signal
- Knock sensor shield
- Knock sensor + signal
- Not used
- Not used
- Not used
- Engine speed signal
- Not used
- Diagnostic connector line L
- Not used
- «Ground»
- «+» after ignition switch
- «+» storage battery
- Not used
- Ignition coil control for cylinders 1-4
- «Ground»
- Emission control system malfunction indicator lamp control
- Not used used
- Not used
- Not used
- Control signal "-" to the high speed relay of the engine cooling fan
- Control signal "-" to the coil of the relay of actuators
- Not used
- Control signal 2 to the idle air control valve
- Control signal 3 to the idle air control valve
- Signal "+" of the throttle position sensor
- Signal of the downstream oxygen sensor
- Signal of the upstream oxygen sensor
- Air conditioning request signal
- Not used
- Not used
- Signal "+" of the air temperature sensor
- Not used
- Not used
- Not used
- Vehicle speed signal
- Engine crankshaft speed signal
- Not used
- Diagnostic connector line K
- Not used
- Electronic immobilizer system signal
- Control signal "-" to injector of cylinder #1
- Control signal "-" to injector of cylinder #3
- Not used
- Not used
- Control signal "-" to heating element of upper oxygen sensor
- Not used
- Control signal "-" to heating element of lower oxygen sensor
- "+" after relay of executive devices
- Not used
- Control signal "-" to the fuel pump relay coil
- Not used
- Signal to the tachometer
- Not used
- Control signal 4 to the idle speed control valve
- "-" coolant temperature sensor
- "+" throttle position sensor
- "-" throttle position sensor
- "Ground" lower oxygen sensor
- "-" air temperature sensor
- "+" absolute pressure sensor
- "-" knock sensor
- "Ground" upper oxygen sensor
- Not used
- "-" coolant pressure sensor
- "+" coolant pressure sensor
- Not used
- Power steering pressure sensor signal
- Not used
- Not used
- Not used
- Not used
- Control signal "-" to injector of cylinder #4
- Control signal "-" to injector of cylinder #2
Replacing, programming or reprogramming the ECU
When replacing the ECU, it is necessary to program the new ECU.
The ECU is programmed using the PB programmer, according to the operating instructions supplied with the programmer.
After performing the ECU programming / reprogramming procedure, it is necessary to start and then stop the engine (to initialize the ECU) and wait 30 seconds, then turn it on again "ignition" and perform the following operations using the diagnostic device:
- - write the VIN code of the car into the ECU memory - to do this, select the "Additional" mode on the diagnostic device. tests" – "Identification number (VIN)";
- - after programming or reprogramming the ECM, stored faults may appear in the memory of other ECMs, so it is necessary to delete fault information from the memory of these ECMs;
- - perform the necessary programming (programming the engine crankshaft torque and adaptive air-fuel ratio correction parameters).
Configuring the ECM
The ECM automatically configures itself depending on the presence of sensors and/or optional equipment available on the vehicle.
- LC001 Vehicle speed communication type
- → Multiplex network
- LC003 Upstream oxygen sensor
- → 1 wire
- LC004 Downstream oxygen sensor
- → C
- LC005 Gearbox type
- → Automatic
- → Manual
- LC008 Camshaft phase shifter
- → WITHOUT
- LC032 Configuration reading: air conditioning
- → C
- → WITHOUT
- LC075 ABS control unit communication with injection control unit
- → WITHOUT
- LC077 Electronic immobilizer system of engine start
- →TYPE #3
- LC078 Control of electric cooling fans with engine running
- → C
- LC079 On-board diagnostic system warning light OBD
- → WITH
- LC080 Gear shift panel
- → WITHOUT
- LC090 Low-capacity fuel pump
- → WITHOUT
- LC095 Receipt of information on the operation of the air conditioning refrigeration circuit to the ECU
- of the injection system
- → WITH
- LC105 Heated windshield
- → WITHOUT
- LC138 Constant-capacity compressor
- → WITHOUT
- LC140 Finger-type ignition coil
- → WITH
- → WITHOUT
- LC152 Normally closed contact brake light switch
- → WITHOUT
- LC168 Interior heating element
- → WITHOUT
- LC176 DF terminal
- → WITHOUT
Fault code table
Code - Description
- DF001 Coolant temperature sensor circuit
- DF002 Air temperature sensor circuit
- DF022 OBD warning light circuit
- DF023 Coolant temperature warning light circuit
- DF038 ECU
- DF040 Cylinder # injector circuit 1
- DF041 Cylinder 2 Injector Circuit
- DF042 Cylinder 3 Injector Circuit
- DF043 Cylinder 4 Injector Circuit
- DF081 Evaporative Canister Purge Solenoid Valve Circuit
- DF082 Evaporative Canister Purge Solenoid Valve Circuit Upstream HO2S Heater Circuit
- DF083 Downstream HO2S Heater Circuit
- DF084 Actuator Relay Control Circuit
- DF091 Vehicle Speed Information
- DF092 Upstream HO2S Circuit
- DF093 Downstream HO2S Circuit
- DF123 Emissions Misfire
- DF124 Catalytic Converter Misfire
- DF232 Coolant Pressure Sensor Circuit
- DF328 Throttle Position Sensor Circuit
- DF330 Knock Sensor Circuit
- DF336 Sensor Circuit engine crankshaft position and speed
- DF352 Electronic immobilizer circuit
- DF353 Absolute pressure sensor circuit
- DF360 Idle speed control circuit
- DF361 Ignition coil circuit for cylinders #1 and #4
- DF362 Ignition coil circuit for cylinders #2 and #3
- DF378 ABS ECU to injection ECU communication
- DF390 Oxygen sensor malfunction
- DF394 Catalytic converter malfunction
- DF514 Fuel pump relay circuit
- DF524 Actuator relay output voltage
- DF587 Supply voltage +5V sensors





