Lada Largus cars are equipped with a steering system with a rack and pinion type steering mechanism and a hydraulic booster
The steering drive consists of two steering rods connected by ball joints to the levers of the steering knuckles of the front suspension
The steering mechanism is installed on the front suspension subframe and secured to it with two bolts.
In the steering gear housing, the rack is pressed against the pinion shaft by a spring through the stop.
The lateral clearance between the pinion and the rack is adjusted by turning the adjusting plug, which presses the spring.
Adjustment is performed during assembly of the steering gear at the factory.
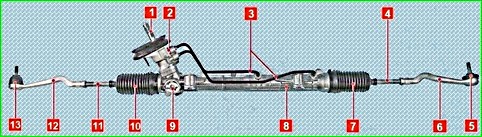
The steering gear consists of two steering rods connected to the steering rack and the steering knuckle arms.
Each rod is attached with its inner end to the steering rack through a non-separable ball joint - the threaded end of the joint is screwed into the rack hole.
The tip of the steering rod has a non-separable ball joint that does not require replenishment of the grease supply placed inside it for the entire service life.
The right and left steering rods are the same, but the tips are different.
The connection of the steering rack and the ball joint of the steering rod is protected from dirt and moisture by a corrugated rubber boot.
The boot is secured with a disposable steel clamp on the steering gear housing, and on the steering rod the cover is held in place by a spring clamp — the narrow belt of the cover must match the groove made on the steering rod.
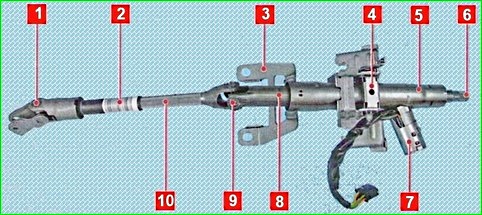
The steering column shaft is attached to the steering gear pinion shaft via an intermediate shaft with two cardan joints.
The steering wheel is mounted on the splines in the upper part of the steering column shaft, secured with a screw.
The steering column is injury-safe, adjustable in tilt angle
The steering column is attached to the crossbar bracket located under the instrument panel.
The power steering system includes: a steering gear, a pump, a reservoir for working fluid and connecting tubes of the lines.
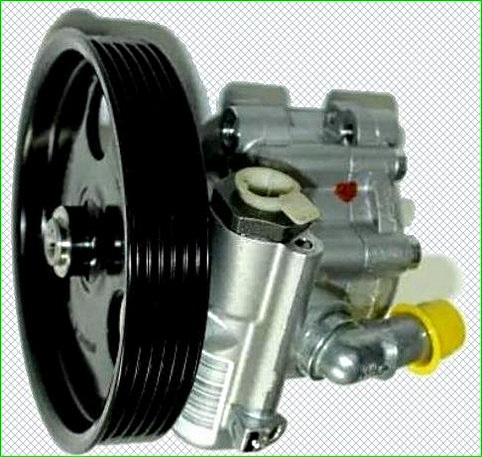

The pump is driven by a belt from the accessory drive pulley.
Hydraulic fluid from the reservoir enters the pump, and from it is supplied under high pressure to the distributor device located in the steering gear housing and mechanically connected to the steering column shaft.
The piston of the hydraulic cylinder is fixed to the toothed rack of the steering gear.
When the steering wheel is turned, the distributor device connects one of the chambers of the hydraulic cylinder to the pump discharge line, and the other chamber to the drain.
In this case, the piston of the hydraulic cylinder due to the difference in pressure of the working fluid moves the rack to the left or right and through the steering rods and the knuckle arms turns the steered wheels of the car.
The radiator is located behind the front bumper - attached to the front suspension subframe in front of the air conditioner condenser and the radiator of the cooling system.
If the hydraulic booster fails, the ability to control the car is retained, but the force on the steering wheel increases.

The power steering reservoir is installed in the engine compartment on the upperth cross member of the radiator frame
To control the fluid level, the translucent body of the tank has MIN and MAX marks.
Possible steering malfunctions and troubleshooting methods
Cause of malfunction - Troubleshooting method
Increased free play of the steering wheel and knocks in the steering
Loose tightening of the steering gear mounting bolts - Tighten the bolts
Worn ball joints of the steering rods - Replace the joints
Worn universal joint of the steering shaft - Replace the steering shaft
Difficulty turning the steering wheel
Slipping of the power steering pump drive belt - Replace the belt
Damaged pump drive belt - Replace the belt
Insufficient level of working fluid - Restore the level to normal
Air entering the hydraulic system - Remove air
Kinked or damaged hoses - Eliminate kinking or replace hoses
Insufficient power steering pump pressure - Replace the pump
Increased internal leaks in the pump - Replace the pump
Fluid leaks from the steering gear - Replace defective parts
Unclear return of the steering wheel to the center position
Difficult to turn the inner joints or joints of the tie rod ends - Replace the tie rod ends
Distortion of the steering rack - Replace the steering gear
Damaged pinion bearing - Replace the steering gear
Kinked or damaged power steering hoses - Eliminate kinking or replace hoses
Damaged pressure regulating valve - Replace pressure regulating valve
Damaged pump rotor shaft bearing - Replace pump
Noise (knocking) in steering
Loose tightening of steering gear mounting bolts - Tighten bolts
Loose fastening of steering rods or ball joints of rod ends - Tighten nuts
Worn ball joints - Replace worn parts
Increased noise from power steering pump
Insufficient level of working fluid - Restore fluid level to normal
Air entering hydraulic system - Remove air
Loose tightening of pump mounting bolts - Tighten bolts





