The scope of maintenance includes control and diagnostic, fastening, lubrication, adjustment, electrical and assembly-disassembly work related to the testing and adjustment of individual units and assemblies on special stands and equipment
If during maintenance there is any doubt about the complete serviceability of an individual assembly unit, then check it with a special device or on a stand.
Maintenance of KamAZ vehicles (road trains) is divided into maintenance during the initial and main periods of operation.

Maintenance during the initial period of operation:
- - daily maintenance;
- - maintenance after the first 1000 km (service A);
- - maintenance after the first 4000 km (service B);
- - service 1 after the first 8000 km;
- - service 2 after the first 12000 km.
Maintenance during the main period of operation:
Frequency of vehicle maintenance
- - daily, maintenance;
- - service 1;
- - service 2;
- - seasonal maintenance (service C).
The main purpose of daily maintenance is general monitoring of the condition of units and systems that ensure traffic safety, and maintaining proper appearance.
During the initial period of operation, the running-in of parts in the vehicle units occurs, therefore, when performing maintenance during this period, perform preventive fastening and lubrication and cleaning work with special care.
Maintenance during the initial period is carried out regardless of the operating conditions.
During the main period of operation, maintenance work is carried out at a frequency corresponding to the category of operating conditions
Frequency of vehicle maintenance depending on the characteristics of the operating conditions:
Roads with asphalt concrete, cement concrete and equivalent pavement outside the suburban area
Roads with asphalt concrete, cement concrete and equivalent pavement in the suburban area, streets of small towns (with population up to 100 thousand residents):
- - service 1: 4000 km;
- - service 2: 12000 km;
- - service C: 24000 km.
Motor roads with asphalt concrete and equivalent surfaces in mountainous areas. Streets of large cities
Motorways with crushed stone or gravel surfaces
Dirt profiled and logging roads
- - service 1: 3200 km;
- - service 2: 9600 km;
- - service C: 19200 km.
Motorways with crushed stone or gravel surfaces in mountainous areas
Non-profiled roads and stubble. Quarries, pits and temporary access roads
- - service 1: 2400 km;
- - service 2: 7200 km;
- - service C: 14400 km.
Seasonal maintenance includes additional autumn work, which is performed once a year.
All types of maintenance are carried out within the timeframes specified in the service book.
Lubrication
The name of the oils, quantity and frequency of lubrication are indicated in the vehicle lubrication chemotological chart, and the location of the assembly units and units requiring periodic replenishment or replacement of oil is shown in Figure 2.
Remember that the use of substitutes significantly reduces the service life of the vehicle assembly units (for example, the power steering - by three to four times) and is allowed only as a temporary measure.
When switching from one recommended grade of oil to another, flush the gearbox with a mixture of 50% diesel fuel and 50% fresh oil intended for subsequent filling, cranking the engine for 5-10 min in neutral in the gearbox.
Chemical map of Kamaz vehicles
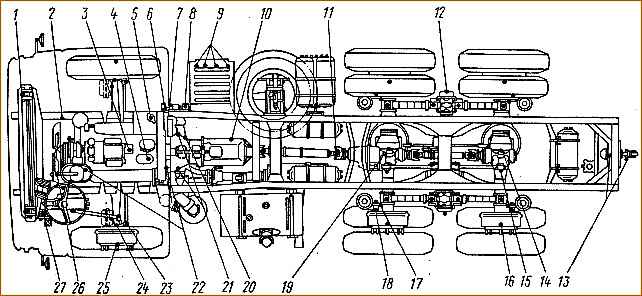
Lubrication points diagram: 1 - front cab support axle; 2 - front spring pins; 3 - fuel injection advance clutch; 4 - tank power steering pump; 5 - cooling system; 6 - engine housing; 7 - freeze protection; 8 - battery switch; 9 - battery terminals; 10 - gearbox housing; 11 - cardan shaft joints; 12 - balancer shoes; 13 - towing hitch hook stem; 14 - rear axle housing; 15 - torque rod joints, 16 - hub bearings; 17 - brake adjusting levers; 18 - expander knuckle shaft bushings; 19 - intermediate axle housing; 20 - clutch release bearing; 21 - clutch release fork shaft bearing; 22 - supports of the front and intermediate remote control drive rods; 23 - steering rod joints; 24 - steering knuckle kingpins; 25 - front axle wheel hub bearings; 26 - splitter control valve cable; 27 - clutch release hydraulic drive
- Vehicle engine fuel system
Main:
In summer: Diesel fuel L-02-40 GOST 305 (at air temperature 0 °C and above)
In winter: Diesel fuel 3-02 minus 35 GOST 305 (at air temperature minus 20 °C and above); Diesel fuel 3-02 minus 45 GOST 305 (at air temperature minus 30 °C and above); Diesel fuel A-02 GOST 305 (at air temperature minus 50 °C and above)
Duplicate:
In summer: Diesel fuel L-0540 GOST 305 (at air temperature 0 °C and above)
In winter: Diesel fuel 3-05 minus 35 GOST 305 (at air temperature minus 20 °C and above); Diesel fuel 3-05 minus 45 GOST 305 (at air temperature minus 30 °C and above); Diesel fuel A-05 GOST 305 (at an air temperature of minus 50 °C and above)
- Oil sump (engines: 7403.10, 740.11-240, 740.13-260, 740.0-260, 740.30-260) - vehicles with a wheel arrangement 6x6, capacity 36 liters; - vehicles with a wheel arrangement 6x4, 8x4, - capacity - 30 liters
All-season: Motor oil Ufalub HD Extra 15W-40 TU 0253-00211493112; LUKOIL-Super SAE 15W-40 CE/SG; LUKOIL-Super SAE 15W-40 CF- 4/SG LUKOIL-Super SAE 5W-40, CF- 4/SG, TU 0253-07500148636
Summer: Motor oil M-10-D (m) GOST 8581
Winter: Motor oil M-8-D (m) GOST 8581
Foreign oils - API CE, CF-4 SAE 15W-40 SAE 5W-40
During daily maintenance - check the oil level in the crankcase and top up if necessary
- At TO-5500 - change the oil;
- At TO-2 - change the oil
- The fuel injection advance clutch (if present) is lubricated with engine oil. Capacity 0.140 liters
At TO-1000 – bring the oil level to the norm
During repair – change the oil when checking and adjusting the high-pressure fuel pump on the stand
- Gearbox housing:
- KP-142(14) – 8.5 liters;
- KP-152(15) – 12 liters;
- KP-161 – 11 liters;
- ZF-9S109 – 8 liters
All-season: Oil TSP-15K GOST 23652 Oil TM3-18 KAMA TU 38 301-19-63 (at an ambient air temperature not lower than minus 30 "C)
All-season: Oil "Omskoyl K" TU 38 301-19-93 (at an ambient temperature of not lower than minus 30 "C); A mixture of oil TSP-15K with 1518% diesel fuel grade "3" or "A" (at a temperature below minus 30 "C)
Foreign oils: API GL-3, APIGL-4 SAE 80W-90 SAE 85W-90
- At TO-1000 - bring the oil level to normal;
- At TO-5500 - change the oil;
- At TO-2 - bring the oil level to normal;
At 100,000 km. – Change oil
- Crankcase:
- - front axle – 5.8 liters;
- - middle axle – 7.0 liters;
- - rear axle – 7.0 liters
All-season: TSP-15K oil GOST 23652 TM3-18 KAMA oil TU 38 301-19-63 (at ambient temperature not lower than minus 30 "C)
All-season: Omskoyl K oil TU 38 301-19-93 (at ambient temperature not lower than minus 30 "C); A mixture of TSP-15K oil with 15-18% diesel fuel grade “3” or “A” (at temperatures below minus 30 “C)
Foreign oils: API GL-3, APIGL-4 SAE 80W-90 SAE 85W-90
- At TO-1000 – bring the oil level up to the norm;
- At TO-5500 – change the oil;
- At TO-2 – bring the oil level up to the norm;
- At 50,000 km mileage – change the oil at least once a year
- Transfer case:
- - with power take-off box – 5.4 liters;
- - without power take-off box – 4.5 liters;
All-season: TSP-15K oil GOST 23652 TM3-18 KAMA oil TU 38 301-19-63 (at an ambient temperature of not lower than minus 30 "C)
All-season: Omskoyl K oil TU 38 301-19-93 (at an ambient temperature of not lower than minus 30 "C); A mixture of TSP-15K oil with 15-18% diesel fuel grade “3” or “A” (at temperatures below minus 30 “C)
Foreign oils: API GL-3, APIGL-4 SAE 80W-90 SAE 85W-90
- At TO-1000 – bring the oil level up to normal;
- At TO-5500 – change the oil lo;
- During TO-2 – bring the oil level up to the norm;
- At 50,000 km – change the oil at least once a year
- Balance suspension shoes, two lubrication points, 2.0 liter capacity
The same oil is used as when servicing the gearbox
- During TO-1000 – bring the level up to the norm;
- During TO-2, service station – change the oil when adjusting the axial clearance
- Interaxle differential housing:
The same oil is used as when servicing the gearbox, 1.2 liter capacity. At the service station, change the oil when disassembling and repairing the unit
- The cavity of the ball joints of the front axle - two lubrication points, capacity 6.0 liters.
A mixture of 50% TSP-15K oil GOST 23652 with 50% Litol-24 grease GOST 21150
Disassemble the joint and replace the grease
- Upper kingpin bearings - two lubrication points with a capacity of 0.2 liters
A mixture of 50% TSP-15K oil GOST 23652 with 50% Litol-24 grease GOST 21150
During TO-10000 and TO-2, lubricate through grease nipples
- Gear splitter control valve cable – gearbox oil, 0.002 liter capacity
During service maintenance, lubricate with a grease nipple
- Steering knuckle pins – four lubrication points
Lita grease TU 381011308, Litol-24 grease, Shell foreign grease: Aeroshell, Grease 6, 22, 0.072 kg capacity
During TO-1000, TO-5500, TO-1 – lubricate through a grease nipple, making no more than three strokes
- Clutch release bearing – one lubrication point, 0.015 kg. At TO-1000, TO-5500, TO-2 – lubricate through a grease nipple
- PGU - one lubrication point, 0.06 kg – lubricate during repair and assembly of the unit
- Clutch release fork shaft sleeve – two lubrication points, the same grease, 0.015 kg. At TO-1000, TO-5500, TO-2 – lubricate through a grease nipple
- Front cover guide (clutch model 17) – one lubrication point
Lita grease TU 381011308, Litol-24 grease, foreign Shell grease: Aeroshell, Grease 6, 22, capacity 0.015 kg
At TO-1000, TO-5500, TO-2 – lubricate through a grease nipple, making no more than two strokes with a syringe
- Front bearing of the primary shaft – one lubrication point, 0.015 kg. The same grease – lubricate when removing the gearbox
- Gearbox shift lever ball bearing* The same grease – 0.01 kg – lubricate when assembling and repairing the unit
- Gearbox control rod axle* - 0.008 kg – the same grease – lubricate when assembling and repairing the unit
- Gearbox control rod ball joint* - 0.01 kg – the same grease – lubricate when assembling and repairing the unit
- Torque rod ball joints* - 0.02 kg – the same grease – lubricate when assembling and repairing the unit
- Gearbox remote control drive ball joints* - 0.02 kg – the same grease – lubricate when assembling and repairing the unit
- Engagement valve demultiplier* - 0.02 kg - the same grease - lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Gear lock lock* - 0.005 kg - the same grease - lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Remote control rod bearings for gearbox* 0.05 kg - the same grease - lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Gear shift lever tip* - 0.03 kg - the same grease - lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
(* For gearbox 161 as part of a power unit with engine 740.20-260, 740.30-260)
- Gear divider control valve - one lubrication point - 0.01 kg - grease Tsiatim-221 or grease Lita TU 381011308, foreign grease Shell: Aeroshell, Grease 6, 22 – lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Gear divider engagement valve - 0.02 kg - the same grease – lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Gear divider shift mechanism – two lubrication points - 0.02 kg - the same grease – lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Mechanism control pressure-reducing valve - 0.01 kg - the same grease – lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Gear divider control mechanism air distributor, one lubrication point. Tsiatim-221 grease or Lita grease TU 381011308, foreign Shell grease: Aeroshell, Grease 6.22, Alvania Ep 2 – lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Cavity of replaceable gears of the speedometer sensor - 0.015 kg - the same grease – lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Radiator shutter control rod – one lubrication point. Litol-24 grease, Solidols Zh, foreign grease Shell, Alvania Ep 2 - 0.03 kg - lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Engine stop manual control rod - one lubrication point, 0.03 kg - the same grease - lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Ball pins of the ends of the fuel injection pump lever drive rods - two lubrication points. Litol-24 grease, foreign grease Shell, Alvania Ep 2 - 0.015 kg - grease the same – lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Telescopic pusher of fuel supply control – one lubrication point. Lubrication is the same – add 0.005 kg of grease
- Cooling system drain valve – Litol-24 grease, Tsiatim-221, foreign Shell grease: Aeroshell, Grease 6.22, Alvania Ep
- Splined joints of cardan shafts of bridges. Lubrication is the same – During assembly and repair, lubricate the splines and add grease to the splined joints
- Cardan shaft joints have two lubrication points. Lubricate at TO-1000, TO-2 during operation through grease nipples until fresh grease is squeezed out from under the seal edges
- Front axle wheel hub bearing two lubrication points, front, second axle (KamAZ-6540) four lubrication points. Litol-24, Tsiatim-221 grease, foreign Shell grease: Aeroshell, Grease 6.22, Alvania Ep. With the hub removed, apply grease between the rollers and separators evenly throughout the entire bearing cavity
- Middle and rear axle wheel hub bearing - two lubrication points. The same grease, 0.8 kg each. With the hub removed, apply grease between the rollers and separators evenly throughout the entire bearing cavity
- Spare wheel carrier (rubbing surfaces). Litol-24 grease, Solidols Zh, foreign grease Shell, Alvania Ep 2 - 0.03 kg - lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Steering rod joints - four lubrication points. The same grease - 0.150 kg. At TO-1000, TO-5500, TO-1 - lubricate through grease nipples until fresh grease is squeezed out
- Steering cardan shaft joints - eight lubrication points. Litol-24 grease, Tsiatim-221, foreign grease Shell: Aeroshell, Grease 6.22, Alvania Ep - lubricate during repair and assembly of the unit
- Steering cardan shaft splines. Lubricate during repair and assembly of the unit. The grease is the same 0.040 kg.
- Front spring pins - two lubrication points.
- Rear and front springs (leaves), for KAMAZ-6540
- Brake mechanism adjusting levers, for KAMAZ-6540
- Expanding knuckle shaft bushings:
- - front bracket;
- - front bracket for KAMAZ-6540
- Expanding knuckle shaft bushings: - rear bracket. Lubricate through grease nipples until fresh grease is squeezed out
- Brake shoe roller and roller axle – lubricate with a thin layer during assembly and repair of the unit
- Brake shoe axle seats – lubricate with a thin layer during assembly and repair of the unit
- Control cable for the right and left heating system dampers, heating system valve – lubricate with a thin layer during assembly and repair of the unit
- Axles of the front cabin supports – during TO-1000, TO-5500, TO-1 – lubricate through a grease nipple until fresh grease is squeezed out
- Battery switch – lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Springs of the rear cabin mount – two lubrication points. Graphite grease USs-A, foreign - Shell: Alvania HDX 2, Rhodina EP 2. Lubricate during disassembly and repair of the unit
- Driver's seat torsion plates - lubricate if necessary
- Torsion screw bearing - lubricate during repair and disassembly of the unit
- Roller axes and guides of the driver's seat levers - lubricate during repair and disassembly of the unit
- Treadmills of balls and rollers of the guide mechanisms of movement of the driver's seat - lubricate if necessary
- Door opening limiter - lubricate if necessary
- Cabin lock - lubricate if necessary
- Cabin door hinge - 0.010 kg - Lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit
- Cabin door window regulator. Grease Lita TU 381011308 or Tsiatim-201 GOST 6267, Grease Litol-24 GOST21150, Shell: Aeroshell Grease 6, 22 0.020 kg. Lubricate during assembly and repair of the unit.
- Cabin door lock - 0.020 kg - Lubricate if necessary.
- Cabin door lock drive. Grease Lita TU 381011308, Grease Litol-24 GOST 21150 Shell: Aeroshell Grease 6, 22 Alvania EP 2 - 0.020 kg. Lubricate if necessary
- Outer cabin door handle - 0.005 kg - Lubricate if necessary
- Cabin heater control valve - 0.002 kg - Lubricate during repair and assembly of the unit
- Heating system drain valve. Litol-24 Grease GOST 21150, Lita Grease TU 38 1011308, Shell: Aeroshell Grease 6, - 22 0.002 kg - Lubricate during repair and assembly of the unit
- Battery terminals - Litol-24 Grease GOST 21150, Shell: Alvania EP 2 0.020 kg TO-2 - Lubricate with a thin layer
- Plug connections of electrical equipment - Litol-24 Grease GOST 21150, VNI-INP-510 Grease TU 38 101910, Shell: Alvania EP 2 Retinax EP 2 - 0.008 kg STO - Lubricate with a thin layer once a year
- Starter - Lita Grease TU 38 1011308, Tsiatim-201 Grease GOST 6267, Shell: Aeroshell Grease 6, 22 - 0.025 kg STO (once every 2 years) STO (once every 2 years) Lubricate the splined drive shaft.
- Water pump bearing. Litol-24 Grease GOST 21150, Lita Grease TU 381011308, Shell: Alvania EP 2 - 0.015 kg TO-2 TO-2 - Lubricate through a grease nipple
- Platform hinge pins 2 Litol-24 Grease GOST 21150, Solidols Zh GOST 1033 or Solidols S GOST 4366 Shell: Alvania EP 2 Retinax EP 2 - 0.036 kg TO-1. Lubricate through a grease nipple until fresh grease is squeezed out
- Ball joints of the hydraulic cylinder - 0.100 kg - Lubricate during repair and assembly of the unit
- Hydraulic cylinder mounting axes 0.100 kg - Lubricate during repair and assembly of the unit
- Platform mounting axes - 2 lubrication points. Litol-24 grease GOST 21150, Solidols Zh GOST 1033, Shell: Alvania EP 2, Rhodina RL2 - 0.010 kg. Lubricate during repair and assembly of the unit
- Platform stabilizer frame mounting axles 2 - 0.010 kg - Lubricate during repair and assembly of the unit
- Traction hitch - 0.200 kg. Lubricate with a pressure oiler once a week
- Coupling device matrix - 0.025 kg STO - Lubricate the nut, filling the matrix cover halfway with grease
- Seat device - 0.170 kg TO-2 TO-1000 TO-1 - Lubricate through grease nipples
- Saddle support surface - 0.400 kg: TO-2 TO-1000 TO-1 - Lubricate the support plate with an even layer
- Towbar hook stem - 0.039 kg. TO-1000, TO-2 - Lubricate through a grease nipple
- Towbar nut - 0.025 kg. TO-1000 TO-2 - Lubricate through the grease nipple
Timber-hauling technological equipment
- Bonus axle. Grease Litol-24 GOST 21150, Solidols Zh GOST 1033, Shell: Alvania EP 2, Rhodina RL2. TO-1000, TO-1 - lubricate through the grease nipple
- Bonus pillar axle - two lubrication points. The same lubrication. Lubricate during assembly and if necessary
- Lower plane of the turntable. The same
- Friction surfaces of the locking device mechanism. The same
- Tow frame pins. Ditto
- External surfaces of process equipment not protected by paint and varnish coating (when stored in open areas). Gun grease (PVK) GOST 19537, Solidols Zh GOST 1033
Winch
- Winch gearbox. Oil used in the gearbox - 3.900 liters. Oil change once a year
- Winch guide rollers
- Winch cable
- Winch drum shaft bearing in the crossmember. Ligol-24 grease GOST 21150
- Winch cardan shaft joints. Litol-24 grease
- Splined joint of the cardan transmission
- Front suspension shock absorbers
- Cabin shock absorbers. Shock absorber fluid AZh-12T GOST 23008
- Power steering - for KAMAZ-6540
- Hydraulic lift of the cabin and spare wheel
- Hydraulic system of the platform lifting mechanism: - KAMAZ-65111 - KAMAZ-65115 - KAMAZ-6540. In summer: Industrial I-20A GOST 20799 In winter: Industrial I-12A GOST 20799
- Hydraulic drive for disengaging the clutch. Brake fluid.
- Engine cooling system 740.20-260, 740.30-260 - with heater 15.8106; - with PZhD-30; - with PZhD-12B
- Engine cooling system 7403.10, 740.11-240, 740.13-260 – 33.5 liters – During daily maintenance - bring the level to normal.
- - with heater 15.8106 – 38 liters - Change the fluid once a year. The change period for coolant “Lena” is once every two years
- - with PZhD-30; - with PZhD-12B - Change the fluid once a year. The coolant change period for “Lena” is once every two years
Fastening works
The list of maintenance operations includes fastening works, the implementation of which is mandatory.
To control the execution of fastening works, the article - "Tightening torques of KamAZ fasteners" provides a table of tightening torques for threaded connections tightened during maintenance.
Features of repair work
Routine repair of a car consists of eliminating faults and damages that arise during operation or maintenance by means of repair operations associated with partial or complete disassembly of units, assemblies or their replacement, as well as with the replacement of individual parts (except for basic ones).
The basic part of the unit is the most complex and expensive part (housing, base, frame, block, etc.), to which all other parts.
Before disassembling the unit (engine) or any assembly located on it, check the general condition of the unit (engine) using diagnostic equipment and collect as much data about it as possible.
This will help determine the cause of the malfunction.
For a faster and more thorough check, clean the unit (engine) from dirt and wash it before inspection.
Remove, transport and install the unit (engine) using lifting and transport vehicles equipped with devices that guarantee complete safety of the work.
When performing repair operations, be guided by the following general principles
Disassemble and assemble parts of any assembly or unit on a special stand or workbench, using special tools and devices
Assemble all assemblies and units in the sequence, reverse disassembly. Therefore, when disassembling, arrange the parts in a certain order.
Parts connected by welding, riveting or fixed fits, disassemble only in cases where this is required by the repair conditions.
Unscrew the studs only when this is necessary due to the conditions of disassembling the unit or assembly, when replacing the stud and part.
Before tightening the cylinder head bolts (if they were removed), remove oil or water from the threaded holes in the block.
Do not depersonalize pairs of parts that are installed on the engine only as a set:
- - main bearing caps with a block, connecting rods with connecting rod caps, plunger pairs of the high-pressure fuel pump, piston with cylinder of the hand fuel priming pump, rod with bushing of the rod of the low-pressure fuel pump;
- - driven and driving gears, main transmission of drive axle gearboxes.
Carefully separate the gaskets from the mating surfaces using a screwdriver; Press out parts only with tools, if none are available, use special punches or light blows with a copper (wooden) hammer.
To check the technical condition of all parts after disassembly, clean them from dust, scale, carbon, varnish deposits, rust, rinse and dry.
Do not rinse parts made of aluminum and zinc alloys in alkaline solutions.
Inspection of parts, start with an external inspection, use magnifying glasses or a magnetic flaw detector to detect defects on critical parts.
Demagnetize parts that have passed the magnetic flaw detector test.
During inspection, reject:
- - parts with significant scoring, chipping or flaking, traces of burning;
- - parts with cracks on the working surfaces and in places that experience heavy loads during operation (for example, cracks are not allowed on crankshafts and connecting rods);
- - fasteners with thread damage of more than two threads;
- - bolts and nuts with worn edges, as well as screws with clogged or torn off head slots;
- - cotter wire and lock washers with bending edges;
- - rubber parts that have lost elasticity;
- - hoses with cracks and delaminations;
- - pipelines with dents that reduce their cross-section, or with cracks on the flared ends;
- - crushed brass couplings;
- - metal panels and plumage parts that have dents, cracks and punctures;
- - fuel tanks with dents, leaks, damage to the coating or paint layer.
Before assembly, prepare all parts as follows:
- - clean nicks and burrs on the mating surfaces of the parts;
- - restore threads damaged within acceptable limits;
- - weld cracks or cavities in unloaded areas of the parts (for example, in the walls of water jackets and exhaust gas pipelines); after welding, clean the seams to give the part a proper appearance;
- - correct the parting planes, where the warping slightly exceeds the permissible limit, by scraping;
- - check the water and oil cavities of the parts and assemblies for leaks, as well as the high-pressure and low-pressure fuel lines;
- - remove the anti-corrosion coating used during storage of the parts;
- - wash the parts and assemblies of the high-pressure fuel pump, hand pump and injectors with clean summer diesel fuel, precision parts (plunger pairs, discharge valves and sprayers) - with gasoline.
After washing, blow the parts with compressed air.
Do not wipe the fuel equipment parts with wiping material.
Before assembly, sealing gaskets, threads in Lubricate the plug holes and threads in through holes with a non-drying sealing paste, and impregnate the felt seals with grease.
Readiness for assembly means that all assembly units subject to restoration have been restored or replaced with new ones and are ready for assembly.
During assembly work, inspect each mechanism and make sure that nothing was missed during restoration.
Carry out assembly in conditions that guarantee the cleanliness of the parts.
When tightening connections sealed with rubber gaskets, do not apply great force, otherwise the gaskets will be destroyed.
During assembly, tighten threaded connections, providing the torques recommended in the article - "Tightening torques for KamAZ fasteners"
When pressing in rolling bearings, the tool must rest against the pressed ring.
When installing seals and cuffs, use mandrels.
After repairing the assembly units and replacing them on the vehicle, run them in to ensure that all mechanisms and systems are in good working order and that they interact correctly.






