Independent front suspension, on two wishbones on each side, with coil springs, telescopic shock absorbers and anti-roll bar
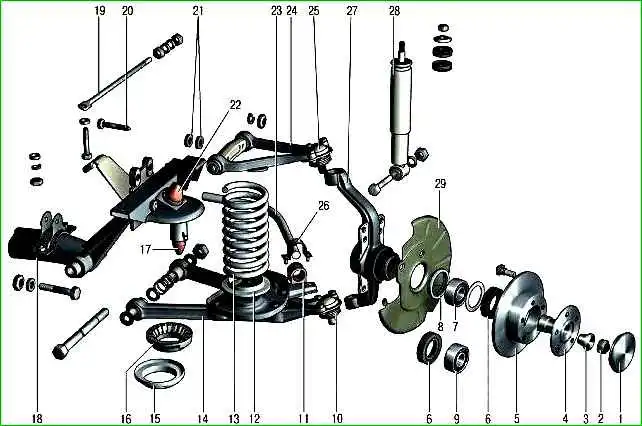
The upper 24 and lower 14 (Fig. 1) transverse levers provide independent movement of each of the front wheels in the vertical plane (when overcoming road obstacles).
The ball joint 10 has the same design as the ball joint 25, and is connected to the steering knuckle and the suspension arm in the same way as the joint.
The upper suspension arm 24 is connected to the crossmember bracket by an axle attached to the bracket with two bolts 20, and the lower arm 14 is attached to the suspension crossmember by an axle bolt.
Adjusting washers are installed between the axle of the upper arm and the bracket; by changing the number of these washers, the camber of the wheels and the longitudinal angle of inclination of the wheel pivot axis are adjusted.
Both suspension arms are connected to axles through rubber-metal hinges (silent blocks), ensuring a gap-free connection of these parts. Such a hinge includes a rubber bushing, outer and inner metal bushings.
The front suspension spring cups are bolted to the lower arms.
Two bearings are installed in the steering knuckle - inner 9 and outer 7, in the inner rings of which the wheel hub is installed with tension.
A brake disc 5 is installed on the hub.
On the brake shield side, the hub is sealed with an oil seal 6, and on the outside - with a cap 1. The tightening of the hub bearings is adjusted with a disposable nut 2.
The springs 13 of the front suspension are cylindrical.
The shock absorbers 28 of the front suspension are telescopic, double-acting.
The upper ends of the shock absorbers are secured in the brackets of the front suspension crossmember through rubber cushions, and the lower attached to the lower arm brackets.
Lateral body roll when cornering is compensated by the anti-roll bar 23, secured via rubber bushings 11 at the ends on the lower arms, and in the middle part - on the front axle gearbox cover and on the body side members.
During each maintenance, as well as during repairs, it is necessary to check the condition of the protective covers of the suspension ball joints, paying particular attention to the absence of mechanical damage to the covers.
It is necessary to carefully inspect the suspension parts, checking for traces of contact with road obstacles or the body, for cracks in the suspension parts, deformations of the lower arm axles, crossmembers or suspension arms and elements of the front of the body, and also check the condition of the ball and rubber-metal joints.
Possible malfunctions of the front suspension and troubleshooting faults
Reason for fault
Remedy
Noise and knocking in suspension when vehicle is moving
- Shock absorbers are faulty
Replace shock absorbers
- Wear of rubber-metal hinges of levers
Replace hinges
- Wear of rubber cushions of fastening of anti-roll bar to lower levers and to front axle gearbox
Replace cushions
- Shock absorber fastening has become loose or rubber cushions and bushings of shock absorber fastening have become worn
Tighten bolts and nuts of fastening, replace cushions and bushings
- Wear of ball joints of suspension arms
Replace ball joints joints
- Increased clearance in the front wheel hub bearings
Adjust the clearance or replace the bearings
- Large wheel imbalance
Balance the wheels
- Deformation of the rim or wheel disk
Replace the wheel
- Settling or breakage of the suspension spring
Replace the springs as a set
- Knocking from suspension breakdown due to destruction of compression buffers
Replace damaged buffers
- Loose tightening of the bolts and nuts securing the upper and lower arms
Tighten the bolts
Front wheel alignment angles cannot be adjusted
- Deformation of the lower arm axis
Replace axle
- Wear of rubber-metal hinges
Replace hinges
- Deformation of steering knuckles, suspension arms or body side members
Replace deformed parts, restore geometric dimensions of side members
Car drifts away from straight-line movement
- Different air pressure in tires
Set normal air pressure in tires
- Violation of front wheel alignment angles
Adjust wheel alignment angles
- Incorrect clearance in front wheel hub bearings
Adjust clearance
- Deformed steering knuckle or suspension arms
Replace deformed parts
- Uneven elasticity of suspension springs
Replace the springs as a set
- Incomplete release of the wheel brake mechanism
Repair the brake mechanism malfunction
- Significant difference in tire wear
Replace worn tires
- Increased imbalance of the front wheels
Balance the wheels
Self-excited angular oscillation of the front wheels ("shimmy")
- Air pressure in the tires does not correspond to the norm
Set the normal pressure in the tires
- Increased clearance in the front wheel hub bearings
Adjust the clearance
- Shock absorbers do not work
Replace shock absorbers
- Loose ball joint pin nuts
Tighten the nuts
- Front wheel alignment angles are out of alignment
Adjust the alignment angles
- Worn rubber-to-metal joints of the levers
Replace the joints
- Large wheel imbalance
Check and balance the wheels
- Worn ball joints
Replace the joints
- - Increased clearance in the ball joints
- - Wear of the rubbing surfaces of the ball joint parts as a result of contamination caused by a leaky protective cover or damage to it
Replace the ball joint and protective cover
Frequent suspension breakdowns
- Suspension springs settling
Replace the springs as a set
- Shock absorbers not working
Replace the shock absorbers
- Deformation of the front suspension arms
Replace the deformed arms
Uneven wear of the tire tread pattern
- Violation of the front wheel alignment angles
Adjust the front wheel alignment angles
- Increased play in the front wheel hub bearings
Adjust the bearing tightening
- Reduced shock absorber performance
Replace the shock absorbers
- Wheels not balanced
Balance wheels
- Worn rubber-metal hinges of the front suspension arms
Replace the hinges
Squeaking in the suspension on road irregularities
- Worn rubber-metal hinges of the front suspension arms
Replace the hinges
Decreased efficiency of the front shock absorber
- Fluid leaking from the front shock absorber
Replace the front shock absorber





