The car has a rigid rear axle in the form of a beam, consisting of a main gear housing and axle housings pressed into it
The main gear with the differential forms a gearbox, which is installed in the crankcase hole and secured with bolts
This bridge design is called a “banjo” bridge.
Some cars are equipped with a non-removable gearbox, the parts of which are directly installed in the axle housing.
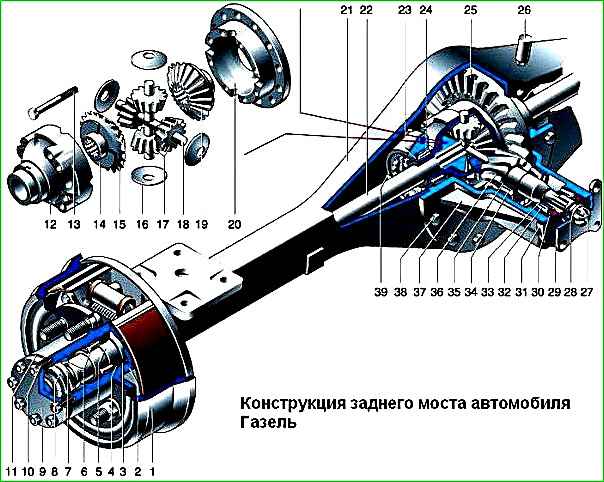
The main gear is hypoid, the axis of the drive gear is shifted downwards relative to the driven axis by 42 mm.
The final drive gear ratio is 5.125 (on vehicles with ZMZ-406 and ZMZ-402 engines), or 4.556 (with UMZ-4215 engines).
The drive gear is integral with the shaft and mounted on two tapered roller bearings.
The preload of the bearings is determined by a spacer ring installed on the shaft between them.
The position of the drive gear relative to the driven gear is set by an adjusting ring placed between the gear and its internal bearing.
The driven gear is bolted to the differential box and together with it is mounted on two tapered roller bearings.
The bearings are adjusted by ring nuts and they can also be used to change the position of the driven gear relative to the drive gear.
The differential gear box consists of two parts connected by bolts.
It contains two satellite axes, four satellites and two bevel semi-axial gears with support washers.
The splined ends of the axle shafts fit into the splined holes of the semi-axial gears.
There are flanges at the opposite ends of the axle shafts, which are connected to the hubs of the rear wheels using eight studs with nuts.
Each hub is mounted on the rear axle axle housing on two tapered roller bearings.
They are adjusted by nuts screwed onto the threaded ends of the casings.
Six bolts are pressed into the hub, to which the dual rear wheels with a brake drum are secured with nuts.
The rear axle is lubricated with transmission oil poured into the crankcase in a volume of 3.0 liters (2.2 liters for an axle with a fixed gearbox).
The wheel bearings are lubricated with the same oil supplied to the hubs from the crankcase through the axle housings.
The oil is kept from leaking out by rubber cuffs installed on the drive gear shaft and in the hubs.
To prevent pressure build-up inside the bridge during operation, a breather is installed on the left side of the crankcase.
Removing the rear axle
It is more convenient to work on an inspection ditch, better with an assistant.
Draining the oil, article - How to change the oil in the rear axle gearbox of a gazelle
We disconnect the driveshaft from the rear axle, article - How to remove the driveshaft of a Gazelle car
Disconnect the hand brake cables from the equalizer, article - How to repair and adjust the parking brake of a Gazelle car
Disconnect the pressure regulator rod and shock absorbers from the rear axle.
Disconnect the rear brake hose
We hang the rear part of the car with a jack with a load capacity of at least 2 tons, installing it under the main gear housing, placing two factory-made racks with a height of about 700 mm and a load capacity also of at least 2 tons under the ends of the frame side members.
We leave the jack under the middle of the rear axle.
Remove the rear wheels on both sides, article - How to remove the rear wheels and axle shafts of a Gazelle car

Using a 24mm socket, unscrew the four nuts on the rear springs on both sides of the car

When removing spring and regular washers, pay attention to the order in which they are installed.

Remove the spring ladders

Remove the spring pads. Using a jack, we lower the bridge onto the trolley and roll it out from under the car

This operation can be performed using a rolling jack.
Install the bridge in reverse order.
After installing the bridge, we adjust the pressure regulator, article - How to replace and adjust the brake force regulator of a Gazelle car






