Starter type 5722.3708 (Fig. 1) is a DC electric motor with excitation from permanent magnets, combined with a planetary gearbox and an electromagnetic two-winding traction relay
Covers 2, 6 and stator housing 3 are pulled together by two studs.
Armature shaft 23 rotates in two metal-ceramic liners installed in cover 2 and support 21.
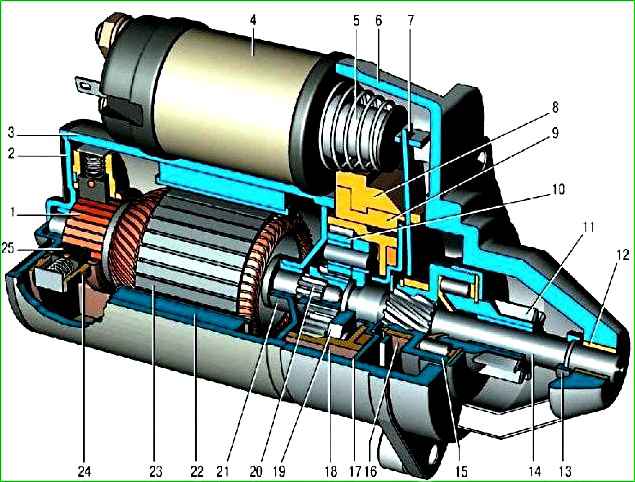
Four permanent magnets 22 are fixed in the stator housing.
Rotation from the armature shaft 23 is transmitted to the drive shaft 14 through a planetary gearbox, which consists of a central gear 20, three planetary gears 10, a carrier 19 and a gear 18 with internal engagement.
The planetary gears rotate on needle bearings.
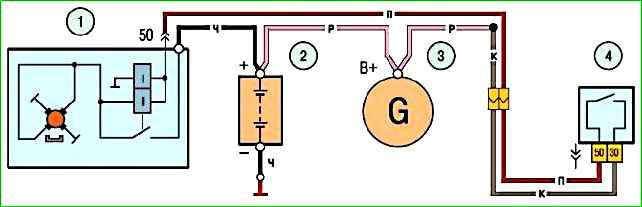
The starter connection diagram is shown in Fig. 2.
When the starter is turned on, the voltage from the battery 2 is supplied to both windings of the starter traction relay (pull-in II and holding I) via the ignition switch 4.
After the contacts of the traction relay are closed, the pull-in winding is disconnected.
Technical characteristics of the starter
Rated power, kW - 1.55
Current consumption at maximum power, A, no more than - 375
Current consumption in the braked state, A, no more than - 700
Current consumption at idle, A, no more than - 80
To avoid many starter malfunctions, follow a number of simple rules when operating it.
When starting the engine, turn on the starter for no more than 10–15 sec and again after 20–30 sec.
Continuous long-term operation of the starter can lead to overheating of the anchor and stator windings.
If the engine does not start after three attempts, then the faults in the engine power supply system or in the ignition system should be checked and eliminated.
After starting the engine, immediately turn off the starter, since prolonged rotation of the flywheel drive gear can lead to jamming of the starter overrunning clutch.
Do not move the car using the starter. This causes its significant overload and damage.





