engines
There are many internal combustion engines powered by gasoline, diesel, propane, or natural gas; hybrid vehicles, plug-in hybrids, hydrogen-powered fuel cell vehicles, and all-electric vehicles. Fuel-powered vehicles have an advantage due to their limited range and high battery costs. Some options require a network of refueling or charging stations.
- Features of the exhaust system of the VAZ-21114 engine
- Features of the fan drive with a KEM 32-23 solenoid valve
- Features of the power supply system of the ZMZ-406 engine
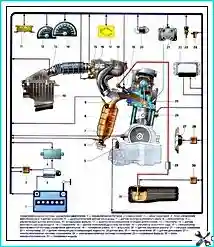
- Features of the VAZ engine - 11183
- Flywheel ZMZ-406
- Fuel injection nozzle of the YaMZ-238 engine
- Fuel rail VAZ-21126 removal and installation
- Fuel system of the VAZ-21114 engine
- G4KE Engine Compression Check
- G6EA engine valve clearance adjustment