Before starting the adjustment, flush the oil chamber of the pump and regulator with clean diesel fuel and fill with fresh engine oil up to the level of the drain hole
For the duration of the test, plug the oil drain plug.
Inspection and adjustment of the fuel pump must be carried out by qualified personnel in a workshop environment.
List of equipment for monitoring fuel pumps: stands of Motorpal, Hansman or KI-15711 with a drive power of at least 11 kW:
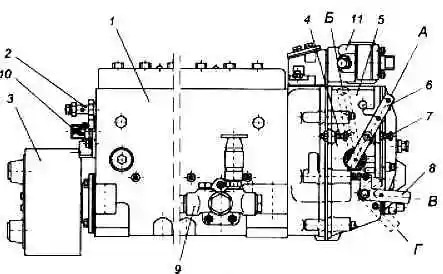
Model 173 high pressure fuel pump: 1 - high pressure fuel pump; 2 - bypass valve; 3 - damper clutch; 4 - bolt limiting the maximum speed; 5 - speed controller; 6 - regulator control lever; 7 - bolt limiting the minimum speed; 8 - stop bracket; 9 - fuel priming pump; 10 - starting feed adjustment bolt; 11 - boost fuel supply corrector; A - the position of the lever at the minimum idle speed; B - lever position at maximum idle speed; B - the position of the bracket during operation; G - the position of the bracket when the feed is off
- – stand equipment and devices must meet the requirements of GOST 10758;
- – scales of medium accuracy class according to GOST 29329;
- - a device for controlling the lift of the pusher Т9590-27;
- - a device for controlling the beginning of the action of the regulator Т9597-111.
The stand must be equipped with an additional system for supplying filtered oil to the fuel pump with regulated pressure up to 0.4 MPa (4 kgf / cm 2) and a compressed air supply system with a device for smooth pressure control from 0 up to 0.15 MPa (from 0 to 1.5 kgf/cm 2).
Pump tests should be carried out on filtered diesel fuel grade L in accordance with GOST 305-82 or a calibrated (process) fluid consisting of its mixture with industrial oil in accordance with GOST 20799-88, aviation oil in accordance with GOST 21743-76 or lighting kerosene in accordance with TU 38.401-58-10-90 having a viscosity of 5-6 mm 2/s (cSt) at a temperature of (20±5)°С.
It is allowed to use a mixture of working fluids consisting of 40% RZh-3 TU 38.101.964 and 60% RZH-8 TU 38.101.883, having a viscosity of 5-6 mm 2/s (cSt) at a temperature of (20±5)°С.
The temperature of the fuel, measured at the outlet connection of the stand with the fuel line to the tested pump, when controlling the magnitude and unevenness of the cyclic feeds, should be (32 ± 2) ° С.
Before installing the pump on the stand, check the absence of axial play of the camshaft. If there is backlash, ensure an interference fit of 0.01-0.07 mm, after adjusting the play of the camshaft 0.03-0.09 mm by installing shims, controlled by a force of 90-100 N (9-10 kgf), and then remove two shims with a thickness 0.05 mm.
When the cover bolts are tightened, the camshaft must turn freely in the bearings.
Checking and adjusting the fuel pump should be carried out with a bench set of injectors model 26-03С, having an effective flow area μf = 0.244 mm 2.
It is allowed to check and adjust the fuel pump with a working set of injectors. Each nozzle must be assigned to the corresponding section of the fuel pump and subsequently installed in the engine cylinder that is connected to this section.
For the bench set of high pressure fuel lines, tubes 415±3 mm long should be used, the difference in the throughput of the fuel lines that make up the bench set should not exceed 0.5 mm 3/cycle.
Determine the throughput of the fuel line on one high-pressure section, with one nozzle and on one bench defoamer.
Before checking and adjusting, you need to make sure that the low pressure system and the oil cavity of the high pressure fuel pump are tight, for which:
Plug off the opening of the bypass valve, the outlet opening of the fuel priming pump, the fittings of the high-pressure fuel pump, the oil supply screw of the boost corrector, the fuel extraction opening for the electric torch device, install the rack cover.
To the oil drain plug in the injection pump housing, tightly connect a tube with an internal volume of not more than 25 cm 3 (internal diameter not more than 8 mm).
Dip the free end of the tube into a vessel with fuel to a depth of no more than 20 mm.
Supply compressed air to the injection pump fuel inlet and to the fuel inlet of the fuel priming pump.
The injection pump is considered suitable if, with a uniform (within 10-20 s) increase in pressure in the system from 0 to 0.5 MPa (from 0 to 5 kgf / cm 2), bubbles are not observed air in fuel tank.
Connect compressed air to the oil drain plug and immerse the injection pump in a container of diesel fuel.
The injection pump is considered sealed if at a pressure of 0.01-0.015 MPa (0.1-0.15 kgf / cm 2) no air bubbles are observed through the connections of the injection pump for 20 s, except the following connections: the locking screw of the rail - the injection pump housing, the axis of the boost corrector lever - the membrane housing.
When checking the fuel pump, the following is monitored:
- – start of fuel supply by pump sections;
- - the amount and unevenness of the fuel supply.
The beginning of the fuel supply by the pump sections is determined by the lift of the pusher, the angle of rotation of the pump camshaft when it is rotated clockwise, as viewed from the drive side, with the rack position corresponding to the nominal feed, i.e. position in which the rail protrudes from the end of the pump by (11 ± 1) mm.
The start of fuel supply by the first section of the pump must correspond to the lift of the pusher 5.2 ± 0.05 mm.
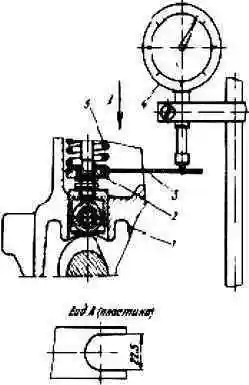
A device for checking the pusher lift: 1 - high pressure fuel pump housing; 2 - lower plate of the pusher spring; 3 - plate; 4 - indicator; 5 - pusher spring
Measure the lift of the pusher with an indicator (Fig. 2).
At the moment the first section starts feeding fuel, the marks on the fuel injection start indicator and on the torsional vibration damper must match. The mismatch of the marks should not exceed 0.5°.
Pump sections should begin delivery in the following order (in degrees of camshaft rotation):
- Section #1 - 0° Section #4 - 180°
- Section #3 - 45° Section #5 - 225°
- Section #6 - 90° Section #7 - 270°
- Section #2 - 135° Section #8 - 315°
The deviation of the angles of the camshaft corresponding to the start of pumping fuel by the pump sections relative to the geometric start of fuel injection by the first section of the pump should be ± 30 minutes, no more.
Adjustment of the beginning of the fuel supply is carried out by gaskets installed under the flanges of the section body, and their number and thickness must be the same on both sides, and the thickest gasket should be on top.
When the thickness of the gaskets is increased, the fuel supply starts later, when the thickness is reduced, it starts earlier.
In order to avoid damage to the pump, the minimum thickness of the gaskets should not be less than 0.6 mm.
Check and adjust the amount and uniformity of fuel supply in the following order:
1. Check the pressure at the beginning of the opening of the discharge valves, which should be 0.06±0.04 MPa (0.6±0.4 kgf/cm 2).
The pressure of the start of opening of the discharge valves should be monitored at the moment when the fuel starts to flow out of the fuel line with an inner diameter of (2 ± 0.05) mm with a gradual increase in pressure at the inlet to the fuel pump and the rack position corresponding to the off fuel supply.
2. Check the fuel pressure in the line at the inlet to the fuel pump. The pressure should be 0.175±0.025 MPa (1.75±0.25 kgf/cm 2) at the rated speed of the camshaft and the control lever against the maximum speed limit bolt.
If necessary, unscrew the bypass valve plug and adjust the opening pressure with washers.
3. Check the rack travel reserve. Under the power reserve of the rack to understand the free travel of the rack (backlash) in the direction of turning off the feed at 450-600 min-1 and when the regulator control lever rests against the minimum speed limiting bolt.
If there is no rack travel reserve, it is necessary to unscrew the power adjustment screw to the stop and then adjust the rack travel reserve within 1-1.3 mm with the backstage screw and lock it.
Protrusion of the yoke screw beyond the outer end of the regulator cover is not allowed
4. Check the start of turning off the starting fuel supply at 230-250 min -1 when the control lever rests on the minimum speed limit bolt at the start of the rack movement.
If you need to increase the speed, remove the spring hook from the rack lever and screw it into the spring. To reduce the speed, the hook turns out. After that, put the hook on the rail lever.
5. Check the value of the average starting fuel supply, which should be within 210-240 mm 3/cycle at a pump camshaft speed of 80±10 min -1.
Adjusted by the starting feed adjustment bolt 10 (Fig. 1). When turning the bolt out of the rail, the starting feed decreases, when screwing it in, it increases.
6. With the control lever resting against the maximum speed limit bolt, check the speed of the pump camshaft, corresponding the beginning of the ejection of the rack, determined by the moment the rack starts moving towards the feed off.
The start of the ejection of the rack should occur at a speed of 1080-1100 min -1.
Adjustment should be done with the maximum speed limit bolt.
7. Check the speed corresponding to the end of the rack ejection, determined by the moment when the fuel supply by the injectors stops.
The end of shutdown should occur at a speed of 60-120 min-1 more than the speed of the start of the rack ejection.
Adjust with the screw of the two-arm lever.
When screwing in, the speed of the end of the ejection of the rack decreases, when screwing out, it increases. At the same time, the start of switching off also changes, so its subsequent check and adjustment is necessary.
8. Check and, if necessary, adjust with the bench set of injectors model 26-03 C with the regulator control lever resting on the maximum speed limit bolt, the average cyclic fuel supply, the increment in the average cyclic supply and the unevenness of the fuel supply in sections, which should be:
Frequency of rotation of the cam shaft, min -1 - Average cyclic fuel supply by pump sections, mm 3 / cycle - Uneven fuel supply by pump sections,% no more
- 1030±10 - 152–158 - 5;
- 900±10 - q - (2–8) - -;
- 650±10 - q - (5–11) - 8;
- 500±10 - 152 - 162 - -
q - average cyclic fuel supply by the pump in nominal mode.
When checking the pump on the control stand, an additional deviation of the average cyclic flow of ± 1% is allowed.
The value of the average cyclic feed is calculated as the sum of the feed of all sections divided by the number of sections.
The uneven fuel supply by sections is calculated by the formula:
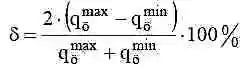
- - qcmax – maximum cyclic fuel supply by sections, mm 3/cycle;
- - qcmin – minimum cyclic fuel supply by sections, mm 3/cycle.
8.1. Adjust the value of the average cyclic feed in the nominal mode with the nominal feed screw: when the screw is turned clockwise, the feed decreases, counterclockwise it increases.
Regulate the uniformity of the cyclic fuel supply by each pump section by turning the section housing relative to the pump housing, after loosening the flange fastening nuts.
Turning the section clockwise increases the cycle feed, counterclockwise decreases it. After adjustment, tighten the flange nuts securely.
- 8.2. The increment of the average cyclic feed at a speed of 800 min -1 adjust the body of the negative corrector. Lock the housing securely after adjustment.
- 8.3. The increment of the average cyclic feed at a speed of 650 min -1 corresponding to the maximum torque and 500 min -1 adjust the negative corrector nut.
When tightening the nut, the increment in feed is reduced, when it is turned out, it is increased. Lock the nut securely after adjustment.
Check the fuel pumps according to points 1-8 in the absence of air and oil pressure in the boost corrector.
9. Check the operation of the fuel boost corrector, for this:
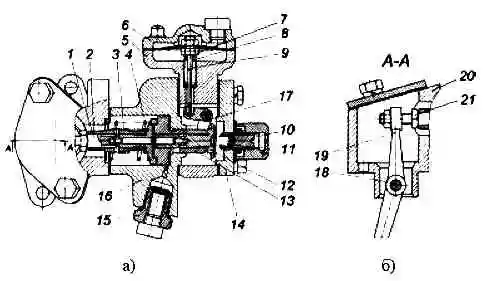
Supercharge fuel supply corrector: a) horizontal section: b) vertical section; 1 - stop sleeve; 2 - emphasis; 3 - sleeve spring; 4 - piston spring; 5 - membrane body; 6 - membrane cover; 7 - locknut of the membrane rod; 8 - spring; 9 - rod with a membrane; 10 - corrector spring housing; 11 - corrector spring; 12 - spool; 13 - piston; 14 - corrector cover; 15 - oil supply fitting; 16 - corrector housing; 17 - lever; 18 - lever axis; 19 - lever; 20 - spacer; 21 - lever adjusting bolt
- 9.1. Rinse the mesh filter of the fitting 15 (Fig. 3) in clean gasoline and blow it thoroughly with compressed air.
- 9.2. Clean the calibration hole in the corrector body with a soft wire with a diameter of (0.5-0.7) mm.
- 9.3. Check the tightness of the membrane cavity. To do this, supply air at a pressure of 0.06 ± 0.01 MPa (0.6 ± 0.1 kgf / cm 2) to the hole on the cover of the membrane housing.
When the supply air duct is completely closed, the pressure drop in the membrane cavity over a period of 2 minutes should not exceed 0.01 MPa (0.1 kgf / cm 2).
- 9.4. At the emphasis of the growlha of control in the bolt limiting the maximum speed, set the speed to 650 min -1 and bring oil to the corrector under pressure of 0.275 ± 0.025 MPa (2.75 ± 0.25 kgf / cm 2 ).
To put the boost corrector into operation, turn off the fuel supply once using the backstage bracket, then move the bracket to the “off supply” position.
- 9.5. Check the value of cyclic fuel supply at various air pressures in the membrane cavity, which should be:
Average cyclic fuel supply by pump sections, mm 3/cycle at air pressure in the cavity of the corrector diaphragm, MPa (kgf/cm 2)
- 0.05-0.1 (0.5-1.0); 0.035±0.001 (0.35±0.01); 0 - 0.02 (0 - 0.2)
- q - (5 - 11)*; (140 - 146)*; (132 – 138)*
q is the average cyclic fuel supply by the pump in nominal mode.
The cyclic feeds marked with an (*) must be provided at an oil pressure at the corrector inlet of 0.275±0.025 MPa (2.75±0.25 kgf/cm 2).
When the oil pressure drops to 0.15 MPa (1.5 kgf/cm 2), it is allowed to change the actual cyclic feed by 3 mm 3/cycle / from given values.
When the air pressure at the corrector inlet changes from 0.06 MPa (0.6 kgf/cm 2) to 0.14 MPa (1.4 kgf/cm 2) sup>), the cyclic fuel supply must be constant and correspond to the value marked with (*) and the change in its value must not exceed ± 2 mm 3/cycle.
If the measured values of cyclic feeds differ from those indicated, it is necessary to re-adjust the corrector.
Adjustment of the amount of cyclic fuel supply at an excess air pressure on the membrane equal to 0 MPa (kgf / cm 2) is performed by adjusting bolt 21 (Fig. 3).
When screwing in a bolt, the feed rate increases, when screwing out, it decreases. After adjustment, lock the bolt with a nut.
The amount of cyclic fuel supply at intermediate air pressures on the membrane is regulated by the spring housing 10 (Fig. 3).
When the spring housing is screwed in, the amount of fuel supply decreases, when it is turned out, it increases. After adjustment, lock the spring housing with a nut.
Before replacing a worn diaphragm (if necessary), measure the protrusion of the stem from the lower end of the nut on the diaphragm with the stem assembly.
After that, replace the membrane and assemble it with a rod with the same protrusion of the rod with an accuracy of 0.1 mm, while the sinking of the end of the spool 12 relative to the end of the piston 13 should be 0.2-0.9 mm in the absence of a gap between the end piston and corrector body.
When installing the boost corrector after dismantling (if necessary) on the regulator, move the pump rail to the extreme off position with the backstage bracket and install the boost corrector into the regulator housing, then release the bracket.
Check the adjustment of the boost corrector for the presence of a shutdown of the fuel supply by the regulator.
10. With the power adjustment screw, when the control lever rests against the maximum speed limitation bolt, limit the nominal cyclic feeds, which should be:
Pump camshaft speed, min -1
Average cyclic fuel supply by pump sections, mm 3/cycle 1030±10 136 – 142
Securely lock the power adjusting screw.
Check the travel reserve of the rack when the governor control lever rests against the minimum speed limit bolt and at a camshaft speed of 500 min -1.
The travel margin of the rail should be at least 0.5 mm.
11. Check the switching off of the cyclic feed by the link bracket when turning 40-45 ° from the initial position.
The fuel supply from the injectors of all sections of the fuel pump at any speed and any position of the regulator control lever should be completely turned off.
Install the caps on the fuel pump and regulator and seal them.
Place a seal on the maximum speed adjustment bolt.
On the engine block, install the fuel pump in a vertical position, tighten the mounting bolts evenly, avoiding blockage of the pump.
The final tightening torque of the pump mounting bolts is 30-40 Nm (3-4 kgcm). Connect the fuel lines after fixing the fuel pump.





