Check the angular free play of the steering wheel with the engine idling, shaking the steering wheel until the steering wheels begin to turn
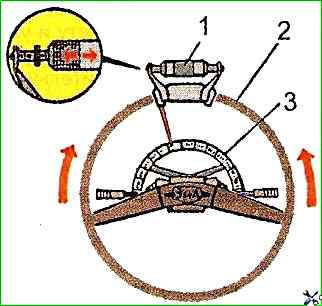
The check can be carried out using the K-402 device (Fig. 1).
The angular free play of the steering wheel with the engine running should not exceed 25°.
The free play should be checked by first setting the front wheels straight.
If the free play of the steering wheel is greater than the permissible value, you need to check the air pressure in the tires, the adjustment of the wheel bearings, steering rods and steering gear, the gaps in the joints and splines of the cardan shaft, since all this affects the operation of the steering.
If the adjustment of the steering mechanism or rods is disturbed, the unit must be repaired.
If there are increased gaps in the cardan joints of more than 2°, the cardan shaft must be replaced.
After making sure that the listed units are in satisfactory condition, you should check the tightening of the nut of the thrust bearings of the steering gear.
Axial movement of the steering wheel is unacceptable.
If there is any, tighten the nut on the lower end of the shaft, having previously straightened the tabs of the lock washer.
After adjustment, bend one of the tabs into the groove nuts.
The torque of the steering shaft disconnected from the cardan shaft should be 0.3-0.8 Nm.
Excessive tightening of the nut followed by its unscrewing to obtain the specified torque of the shaft is unacceptable, as it can cause damage to the bearing.
To check the steering mechanism, place the front wheels of the bus straight so that the steering wheel takes the middle position, disconnect the longitudinal steering rod and measure with a spring pressure gauge 1 (Fig. 1), attached to the steering wheel rim, the force in three positions.
First - the steering wheel is turned more than 2 turns from the middle position, the force on the steering wheel rim should be within 5.5-13.5 N.
Second - the steering wheel is turned 3/4 ÷ 1 turn from the middle position, the force should not exceed 23 N.
Third - the steering wheel passes the middle position, the force on the steering wheel rim should be 8.0 ÷ 12.5 N more than the force measured in the second position, but should not exceed 28 N.
If the forces do not correspond to those specified, then the steering mechanism must be adjusted.
The steering mechanism has two adjustments: external and internal.
Adjustment should begin with setting the force on the steering wheel rim in the third position by turning the adjusting screw the pitman arm shaft, since this does not require disassembling the steering gear.
When the screw is turned clockwise, the force will increase, and when it is turned counterclockwise, it will decrease.
The discrepancy in the forces on the wheel rim in the second position is caused by damage to the parts of the ball nut assembly, and in the first position - by the same reasons, as well as incorrect preload of the thrust ball bearings.
To adjust the force in the first position, you need to partially disassemble the steering gear to tighten the nut of the thrust bearings.
After checking and adjusting the steering, connect the pitman arm to the longitudinal rod and check the free play of the steering wheel.
When checking the steering wheel rotation torque, it is necessary to remember that the quality of the steering control is significantly affected by the rotation torque of the pitman arm shaft.
When checking the rotation torque of the pitman arm shaft on a car, you should:
Disconnect the longitudinal tie rod with the ball pin, start the engine and warm up the power steering system to approximately 50°C, then set the steering wheel to the middle position;
Hook the dynamometer to the hole for the ball pin in the pitman arm and pull in any direction, maintaining the angle between the dynamometer and the pitman arm at approximately 90°C.
In this case, the dynamometer should show no more than 545 N.
Exceeding these values may occur due to the failure of a number of parts.
In this case, the steering mechanism must be disassembled for a detailed inspection and elimination of the defect.
Checking for excessive clearance in the connections of the adjusting screw and the pitman shaft
For To determine the amount of play in the connection of the adjusting screw and the pitman shaft, it is necessary to:
- disconnect the longitudinal steering rod, turn the steering wheel more than one and a half turns in each direction from the middle position, measure the axial movement of the pitman shaft relative to the steering gear housing using an indicator, applying the required axial force to the pitman shaft.
If this movement in any of the two positions exceeds 0.2 mm, it is necessary to partially disassemble the steering gear to determine the causes of the increased clearance.
Checking the pump and power steering on a car
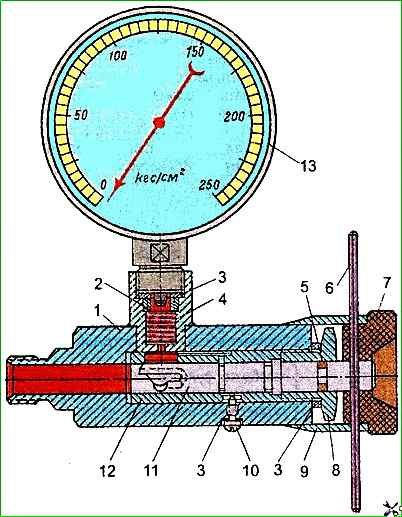
On a car, the pump should be checked using a slot throttle-flow meter KI-1097 (DR-70), which is installed between the pump and the high-pressure hose (Fig. 2).
When turning the throttle handle 7, the gap in the sleeve is gradually covered by the plunger 11, as a result of which the pressure in the discharge line slowly increases.
The flow rate of the working fluid flowing through the flow section of the sleeve gap at a pressure of 10 MPa and a temperature of 50±5°C is determined by the limb, on which a scale with the oil flow rate is applied.
If the volumetric efficiency of the pump is less than 0.6, it must be repaired.
Using this device, you can also determine the response pressure of the safety valve of the power steering mechanism.






