The main brake cylinders (MBC) are connected by two bolts into one unit with pneumatic chambers, which are pneumatic boosters, and are installed on brackets on the front panel of the cabin under the hood of the car for braking the front axle wheels and behind the rear axle for the rear axle wheels
The main causes of the MBC malfunction are wear or loss of elasticity of the rubber cuff, wear of the working surfaces of the cylinder and piston, clogging of the compensation hole.
Disassembling the main brake cylinder
To disassemble the MBC, perform the following operations:
Disconnect the terminal connection of the wires from the brake fluid level sensor on the cover of the brake fluid reservoir;
Disconnect the hose from the brake fluid reservoir and the tube from the pneumatic chamber;
Remove the brake fluid reservoir together with the pneumatic chamber from the bracket by unscrewing the two nuts securing them;
Disconnect the brake fluid reservoir from the pneumatic chamber;
Clean and wash the brake fluid reservoir surface from dirt, mineral oils and other contaminants;
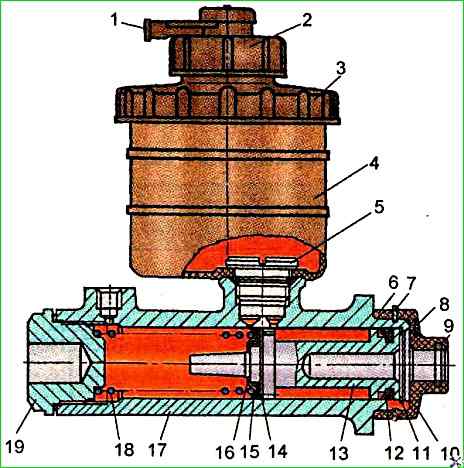
Unscrew the cover 3 of the reservoir together with the sensor and drain the brake fluid;
Place the brake fluid reservoir down and, pressing several times on piston 13 (Fig. 1), remove the remaining brake fluid from the cylinder;
Secure the brake fluid reservoir in a vice with soft sponges;
Remove the reservoir from the cylinder by unscrewing the nipple 5 of its fastening;
Dismantle the coupling 10 and remove the thrust ring 11 using special pliers, holding the piston 13 from falling out;
Use your hand to remove the piston from the housing 17 of the master cylinder.
After disassembling, rinse all parts with clean brake fluid and inspect them carefully.
It is strictly forbidden to allow mineral oils, gasoline, kerosene or diesel fuel to come into contact with the parts, since even traces of these liquids on the parts can lead to the destruction of the rubber seals in the assembled cylinder
The working surface of the master brake cylinder and piston must not have any rust, scratches or other irregularities
To eliminate defects on the mirror of the master cylinder, it is allowed to hone it, but in within the size limits.
If there are defects that cause a significant increase in the diameter of the "mirror", the brake master cylinder body must be replaced.
Every time the brake master cylinder is disassembled, the elasticity of spring 18 must be checked and all rubber seals must be replaced, even if they still appear to be in good condition.
To assemble the brake master cylinder, perform the following operations:
Assemble piston 13, installing new rubber seals 12 and 15;
Secure the crankcase of the master brake cylinder in a vice with soft jaws;
Generously lubricate the "mirror" of the master brake cylinder and the piston with seals with fresh, clean brake fluid.
Install spring 18 in crankcase 17;
Direct piston 13 assembly into the crankcase, pressing spring 18 until it stops.
When the working edges of the seals pass through the groove for the thrust ring, the working edges of the seals must be pressed down with a blunt wooden object;
Having sunk the piston into the cylinder, install the thrust ring using special pliers 11;
Lubricate the working surface of the cylinder to a depth of approximately 15 mm with a thin layer of anti-corrosion grease DT-1 according to TU 38 UkrSSR 2-01-116-76;
Install the coupling sleeve 10 on the GTZ housing;
Test the GTZ for leaks using the following method.
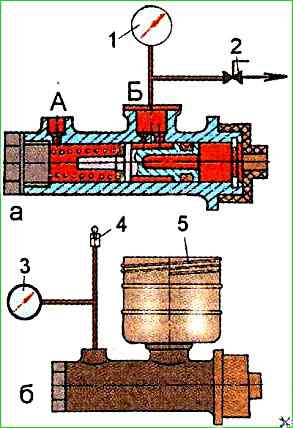
With terminal A open (Fig. 2), move the piston approximately 20 mm, then plug terminal "A" and apply a vacuum of 0.0635±0.0035 MPa to terminal "B"; turn off the vacuum source with valve 2.
The vacuum value should not change for at least 5 s or move the piston by about 20 mm and fix it.
Supply compressed air to terminal "A" under a pressure of 0.15+0.02 MPa, and connect a pressure gauge to hole "B".
No pressure drop is allowed within 5±1 s;
Install reservoir 4 (see Fig. 2) on the crankcase of the hydraulic cylinder and secure it with nipple 5;
Fill the reservoir with brake fluid and bleed it.
Create a pressure of 0.3±0.03 MPa and fix the rod, the pressure should not drop by more than 0.02 MPa for at least 5 s.
Release the piston, while the pressure should drop to zero.
Press the piston, creating a pressure of 14±1.4 MPa.
Fix the rod.
The pressure should not change for at least 10 seconds; there should be no traces of brake fluid on the surface of the brake master cylinder;
Install the brake master cylinder together with the air chamber on the bracket on the bus and secure them with nuts;
Connect a hose to the brake master cylinder, and a tube to the air chamber;
Pour fresh brake fluid into the brake drive hydraulic system;
Tighten the tank caps together with the brake fluid level sensors;
Connect the terminal connections of the wires to the brake fluid level sensors on the covers of the brake master cylinder banks;
Bleed the brake hydraulic drive and check the operation of the brake master cylinder as described above.






