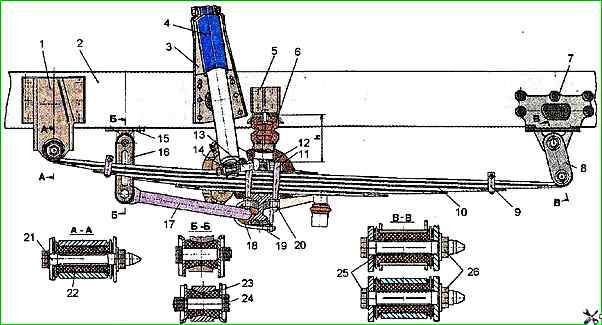
Front suspension - dependent, leaf spring, attached to the frame with elastic hinges.
Guide apparatus and elastic elements - longitudinally located asymmetrical leaf springs
Additional elastic elements - compression buffers with progressive characteristics, anti-roll bar.
Damping elements - shock absorbers
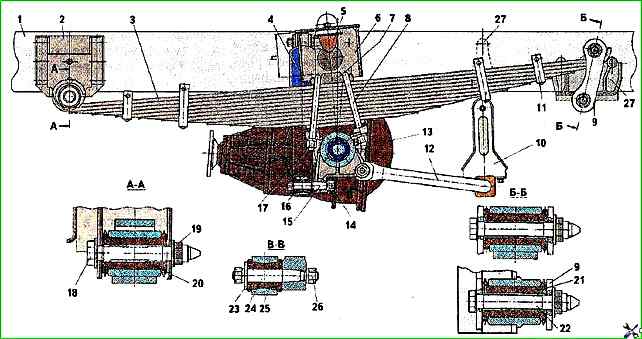
Rear suspension - dependent, spring, attached to the frame with elastic hinges.
Guide apparatus and elastic elements - longitudinally located symmetrical springs with progressive characteristics.
Additional elastic elements - compression buffers with progressive characteristics, anti-roll bar.
Damping elements - shock absorbers
Shock absorbers - hydraulic telescopic, double-acting; are designed to dampen vibrations that occur when a car or bus moves over uneven roads.
Each shock absorber is mounted using pins with rubber bushings.
Wheels - steel, welded. Stamped disk. Rims 6.5Jx16H2 and 6.75x17.5 rolled.
Wheels are centered by the central hole.
The wheels are attached to the hubs with six bolts with M18x1.5 threads, pressed into the hubs at a diameter of 205 mm and nuts with conical pressure washers.
Tires - pneumatic, radial, tubeless, with a universal tread pattern.
Tire sizes: VS-14, V-274, Agilis-101 by Michelin; 225/R16C mod. K-152; 235/75R16C mod. M-254; 215/75R16C mod. M-240, K-163, K-166.
It is allowed to use a tire with a tube.
Determining the condition of the suspension
To determine the condition of the springs of a car or bus, it must be washed and placed on an inspection pit or overpass.
All suspension parts must not have noticeable deformations, cracks or breakages.
Rubber-metal suspension joints must not have a rubber mass tearing off from the reinforcement or cracks on the ends.
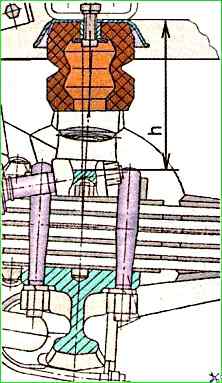
The degree of loss of serviceability of the springs can be determined by measuring the distance "h" between the spring pad and the compression buffer bracket, as shown in Fig. 3.
Measurements must be taken on a vehicle with a full load and its distribution along the axles in the following ratio: on the front axle - 23,500 N; on the rear axle - 49,000 N.
The dimension "h" for springs of one axle should not differ by more than 10 mm.
The criterion for the ultimate state of the spring is a three-time replacement of the leaves in the spring, as well as its subsidence.
Springs with this dimension less than 115 mm for the front suspension and 98 mm for the rear suspension are subject to replacement.
If the riveted joints of the brackets of the front and rear springs are loose, the loosened rivets should be cut off and new ones riveted.
Fastening loose rivets is not allowed.
If the holes for the rivets are worn out, these holes must be drilled out to fit the increased diameter of the rivets.
The rivets must fit tightly into their holes.
A necessary condition for reliable and long-term operation you springs - their lubrication.
Corrosion of the sheets can significantly reduce their durability.
During repair work, the spring sheets should be disassembled and lubricated.
In this case, it is necessary to remove old lubricant and dirt, as well as corrosion products, and then lubricate the rubbing surfaces of the spring sheets with graphite lubricant.
During maintenance of a car and a bus, it is necessary to inspect the condition of the rubber-metal hinges, sheets and brackets; check the tightening force of the U-bolts.
The tightening torque should be 100÷110 Nm for the front springs, and 200÷220 Nm for the rear springs.
Check the tightening of the U-bolts on a fully loaded vehicle.
Particular attention should be paid to tightening the rear nut 12 (see Fig. 1) of the lower pin of the front suspension shock absorber, which should be done after every 4,000 km of travel.





