The fuel system of the diesel engine, in accordance with the diesel engine configuration, consists of:
- - Common RAIL fuel injection system, including a fuel pump,
injection pump drive step-up gearbox, injectors, high-pressure fuel accumulator, speed sensors (crankshaft and primary shaft of the injection pump drive gearbox), working environment condition sensors (fuel and air pressure and temperature), electromagnetic actuators (fuel pressure regulator, injector electromagnetic valves), electronic control unit;
- low-pressure fuel lines;
- high-pressure fuel lines; intake manifold; exhaust manifold;
- turbocharger;
fine fuel filter; fuel pre-filter (rough), air cleaner, fuel tank, intercooler, muffler.
The diagram of the diesel fuel system indicates a means of facilitating diesel starting in conditions of low ambient temperatures - a glow plug.
The diagram of the diesel fuel system is shown in Figure 1.
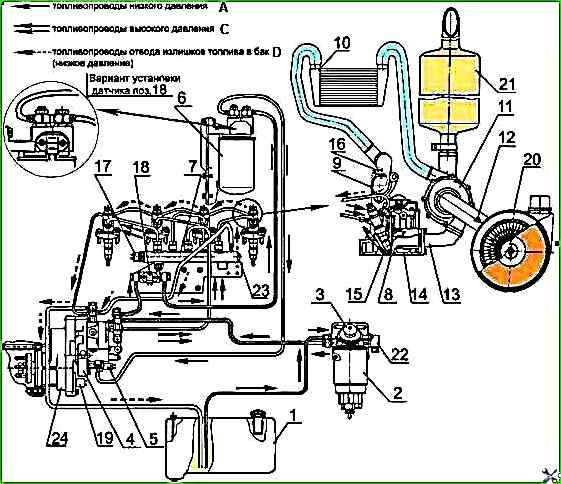
1 - fuel tank; 2 - fuel pre-filter; 3 - manual fuel priming pump; 4 - high-pressure fuel pump; 5 - electromagnetic pressure regulator; 6 - fine fuel filter; 7 - high-pressure fuel accumulator; 8 - injector; 9 - intake manifold; 10 - charge air cooler; 11 - turbocharger; 12 - air filter clogging sensor; 13 - exhaust manifold; 14 - cylinder head; 15 - glow plug; 16 - charge air temperature and pressure sensor; 17 - high-pressure fuel sensor; 18 - fuel temperature and pressure sensor; 19 - camshaft speed sensor; 20 - air cleaner; 21 - muffler: 22 - fuel heater; 23 - pressure limiting valve; 24 - fuel injection pump drive reducer; A - low-pressure fuel lines; C - high-pressure fuel lines; D - fuel drain lines to the tank
The diagram of the control and monitoring circuits of the COMMON RAIL fuel system is shown in Figure 2.
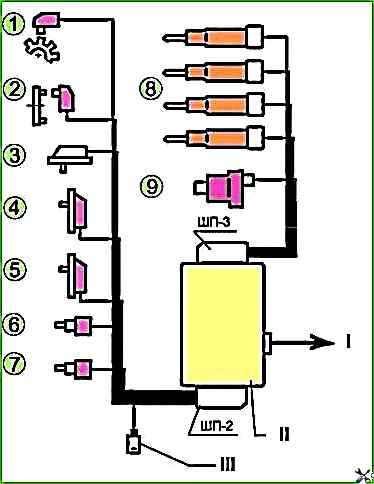
The location of the sensors and actuators in Figure 2 and in the table.
Power to the electronic unit of the control, management and communication circuits must be supplied directly from the battery terminals.
The crankshaft speed sensor is installed on the valve timing cover
The speed sensor of the primary shaft of the fuel injection pump drive gearbox is installed on the housing of the high-pressure fuel pump gearbox
The fuel temperature and pressure sensor is installed on the fuel line from the booster pump to the fine fuel filter or in the housing of the fine fuel filter
The oil temperature and pressure sensor is installed in the cylinder block
The boost air temperature and pressure sensor is installed in the intake manifold
The high-pressure fuel sensor is installed in the fuel ramp
The coolant temperature sensor is installed in the thermostat housing
The pressure regulator is installed in the high-pressure fuel pump





