The vehicle steering can be equipped with three types of options
The steering mechanism without a booster is shown in Figure 1
The steering mechanism is equipped with a hydraulic booster (Fig. 2), on some vehicles an electric booster can be installed
The steering is trauma-safe with a steering mechanism 11 (Fig. 1), which is a worm gear.
The steering drive includes three rods - the middle 3 (see Fig. 1) and two side rods 1, as well as a pitman arm 2, a pendulum lever 4 with a bracket 10, fixed on the right side member, and steering arms 9 of steering knuckles 7.
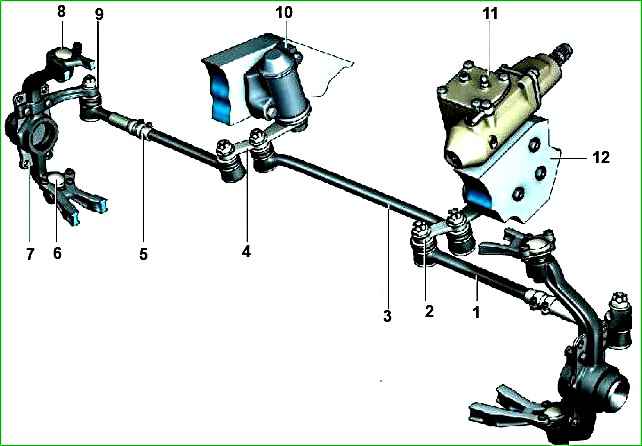
VAZ-2123 steering with mechanical linkage and hydraulic booster.
Steering mechanism of the "screw ball nut sector" type with a distribution valve.
The steering trapezoid is formed by three steering rods (one middle and two side), a steering knuckle, a pendulum lever and steering knuckle levers.
The side rods consist of two tips connected by a threaded split coupling.
The inner (short) tip has a right-hand thread, the outer one has a left-hand thread.
The connecting coupling also has threads of different directions, so when it is turned, the length of the side rod increases or decreases, which is necessary to adjust the wheel alignment.
The coupling is fixed on the tips with tightening clamps. At the ends of the steering rods there are ball joints.
Their pins have a conical fit in the steering arms and are secured with nuts and cotter pins.
The pendulum arm bracket is attached to the right side member with two bolts with self-locking nuts.
Two bearings are installed in the bracket housing, in which the pendulum arm axis rotates.
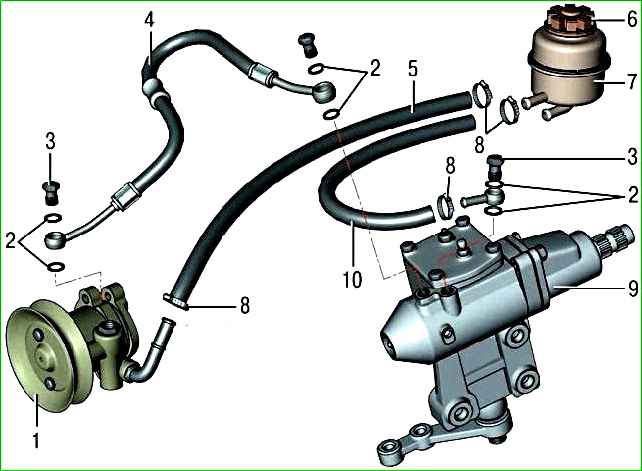
The hydraulic booster system includes: a vane pump, a tank for the working fluid, a radiator for cooling the working fluid, fluid supply and discharge hoses and a steering gear.
The steering gear is attached with three bolts with self-locking nuts to the left side member.
The pump is attached to the bracket on the left side of the engine. The pump shaft is driven by a belt from the auxiliary drive pulley.
The hydraulic fluid from the reservoir is supplied by the pump under high pressure to the distributor located in the steering gear and mechanically connected to the steering column shaft.
When the steering wheel is turned, the distribution valve connects one of the cavities of the power cylinder to the pump discharge line, and the other cavity to the drain.
The power cylinder converts the pressure difference into additional force acting through the piston nut on the sector of the steering linkage and then on the front wheels.
From the drain cavity, the fluid flows through a hose to the power steering radiator, where it is cooled.
Then the hydraulic fluid flows into the reservoir.
If the power steering fails, the ability to control the car is preserved, but the force on the steering increases wheel.
The steering shaft is two-link, consisting of an upper steering shaft and an intermediate shaft.
The upper shaft rotates on two bearings installed in the shaft bracket tube. The steering wheel is secured to the upper splined end of the shaft with a self-locking nut.
The intermediate shaft has cardan joints at the ends with split splined tips, tightened with bolts; the lower one is connected to the steering gear screw shaft, the upper one to the upper steering shaft.
The steering control is injury-safe by folding the steering shaft due to the cardan joints and special fastening of the steering shaft bracket.

The steering column shaft is composed of two parts - an intermediate shaft 1 with a hinge (Fig. 3) and a steering column shaft 7.
At the upper end of the shaft 7, the steering wheel 6 is fixed on conical splines, and at the lower end, a cardan joint 2 is installed.
Possible malfunctions of the steering without a hydraulic booster and how to eliminate them
- Cause of malfunction
Remedy
Increased free play of the steering wheel
- Incorrect adjustment of the lateral clearance of the steering mechanism
Adjust the lateral clearance of the steering mechanism
- Wear of the ball joints of the steering trapezoid
Replace the ball joints
- Wear pendulum arm bearings
Replace the pendulum arm, article - "Pendulum replacement and repair"
- Loosening of the pitman arm mounting nut
Tighten the nut
- Loosening of the steering wheel mounting nut
Tighten the nut
Jamming in the steering mechanism
- Incorrect adjustment of the side clearance of the steering mechanism
Adjust the side clearance of the steering mechanism
- Wear of the roller or worm
Replace worn parts
Oil leakage from the steering mechanism housing
- Wear or damage to the working edge of the oil seals
Replace defective seals
- Increased oil level
Restore the required oil level
- Damaged gaskets or loosened bolts of the crankcase covers
Replace gaskets or tighten the bolts of the covers
Noise (knocking) in the steering
- No oil in the steering crankcase
Eliminate the cause of oil leakage and fill the crankcase with new oil
- Destruction of the working surfaces of the worm and roller
Replace damaged parts
- Increased clearance in the pendulum arm bearings
Replace the bearings or the pendulum arm assembly with the bracket
- Increased clearance in the ball joints of the steering traction
Replace the ends or tie rods
- Loosening of the tie rod ball joint nuts
Check and tighten the nuts
- Loosening of the steering gear mounting bolts or the swing arm bracket
Check and tighten the nuts of the bolts
- Loosening of the pivot arm mounting nuts
Tighten the nuts
- Loosening of the steering shaft mounting bolts
Tighten the nuts of the bolts
- Increased clearance in the front wheel hub bearings
Adjust the clearance
Vibration and jolts noticeable on the steering wheel (with serviceable and balanced wheels and normal tire pressure) tires)
- Steering mechanism not adjusted
Adjust steering mechanism
- Loose nuts of universal joint tie bolts
Tighten fastening nuts
- Play in ball joints of steering trapezoid
Replace ball joints
- Loose tightening of fastenings of steering components
Check and tighten loose fastenings of steering components
Car pulls away from straight-line movement to one side
- Uneven tire pressure
Check and set normal pressure
- Front wheel alignment angles are incorrect
Check and adjust wheel alignment angles
- Different settlement of front springs suspension
Replace defective springs
- Deformed steering knuckles or suspension arms
Check knuckles and arms, replace defective parts
- Incomplete release of one or more wheels
Check the condition of the brake system
Worn front tires in the form of spots
- Low pressure in front tires
Set normal tire pressure
- Steering mechanism not adjusted
Adjust the steering mechanism
Possible power steering malfunctions, their causes and troubleshooting methods
- Cause of malfunction
Remedy
Pump noise in all operating modes
- Worn shaft bearings pump
Replace the pump
Increased noise from the power steering when turning the steering wheel
- The power steering pump drive belt is slipping
Tighten or replace the belt
- Insufficient fluid level in the reservoir, as a result of which air has entered the system
Eliminate fluid leaks from the system, add fluid and bleed the system, article - "Replacing hydraulic system fluid"
- The steering gear is faulty
Replace the steering gear
The booster does not work (increased effort on the steering wheel)
- The filter element in the reservoir is clogged
Replace te tank assembly
- Power steering drive belt slips
Tighten or replace belt
- Pump valves are clogged
Flush valves
- Low viscosity fluid is poured
Replace fluid with recommended one
Uneven force when turning steering wheel right and left
- Hydraulic system is clogged
Flush hydraulic system and steering gear. Replace fluid
- Steering gear is faulty (valves are leaky or parts are damaged)
Replace steering gear
Fluid leaks from the system
- Sealing cuffs are worn
Replace cuffs
- Hoses are damaged, clamps are loose
Tighten clamps, replace hoses
- Gaskets and rubber seals of pump and steering gear covers are damaged
Replace gaskets and seals
- Pump access hole plugs are leaky or lost
Chink plugs to restore tightness, press in new ones to replace lost ones or replace the pump
- Increased pressure in the system caused by the pump flow valve jamming in the closed position
Remove the jammed valve
(it is recommended to perform the work at a service station or replace the pump)
- Increased fluid level in the tank
Pump out excess fluid from the tank





