Automatic transmission electrical circuit checks
Below are general methods for checking the integrity of electrical circuits, checking for short circuits using an ohmmeter and voltmeter.
Checking the integrity of an electrical circuit
Loss of electrical circuit integrity can be caused by the following reasons:
- - disconnection of the harness block;
- - poor connection of the harness block;
- - contamination, oxidation, corrosion of contacts;
- - deformation of contacts;
- - damage to the wire.
Check the integrity of the circuit in the following sequence:
- 1. Disconnect the ground wire terminal from the battery.
- 2. Visually check that the harness pads are connected on both sides of the electrical circuit, the locking latches are snapped.
- 3. Disconnect the pads, visually check the contacts for dirt, corrosion, deformation.
- 4. Pull the wires near the pad to make sure that the wire and terminal are tightly crimped, that the terminal is fixed inside the pad.
- 5. Using a probe of the specified diameter and length corresponding to the size of the contact in the mating pad, make sure that the terminals of the harness pads provide a reliable connection (the terminals are not recessed into the pad, the probe fits tightly into the terminal).
- 6. Using an ohmmeter, measure the resistance of the circuit between the pads. The resistance of a healthy circuit should be less than 1 Ohm.
To avoid damaging the terminals, it is permissible to use probes of a specified diameter for measurements, corresponding to the size of the contacts in the mating blocks.
Checking the short circuit of the circuit to ground
Carry out the check in the following sequence:
- 1. Disconnect the blocks on both sides of the electrical circuit.
- 2. Connect the tester, with one end connected to the + of the battery, to the terminal of the circuit being checked. If the probe lights up, the circuit being tested is shorted to ground.
To avoid damaging the terminal, the probe must be connected using a probe of a specified diameter corresponding to the size of the contact in the mating socket.
Checking the circuit for shorting to the on-board network
Perform the check in the following sequence:
- 1. Disconnect the socket on one side of the electrical circuit.
- 2. Connect the probe, with one end connected to ground, to the terminal of the circuit being tested.
- If the probe lights up, the circuit being tested is shorted to the on-board network.
- 3. Connect the disconnected socket.
- 4. Disconnect the socket on the other side of the electrical circuit. Perform test 2.
To avoid damaging the terminal, the tester must be connected using a probe of a specified diameter corresponding to the size of the contact in the mating socket.
Measuring the voltage at the contacts of the wiring harness
Perform the test in the following sequence:
- 1. Disconnect the socket on one side of the electrical circuit.
- 2. Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to the terminal of the circuit being tested, and the negative lead to the vehicle ground.
Record the voltage value.
To avoid damaging the terminal, the positive lead of the voltmeter must have a probe of a specified diameter corresponding to the size of the contact in the mating socket.
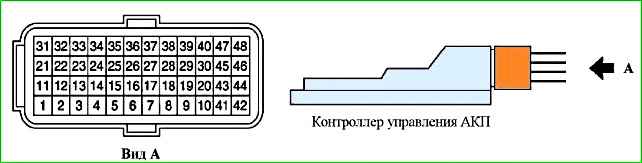
Assignment of the automatic transmission control controller contacts (21126-1412020)
Contact - Circuit
- 1 - Output. On/Off (switching) solenoid valve
- 2 - Input. Mode "1" of the automatic transmission range (mode) switch
- 3 - Input. Mode "2" of the automatic transmission range (mode) switch
- 4 - Input. Mode "D" of the automatic transmission range (mode) switch
- 5 - Input. Mode "N" of the automatic transmission range (mode) switch
- 6 - Input. Mode "R" of the automatic transmission range (mode) switch
- 7 - Input. Mode «P» of the automatic transmission range (mode) switch
- 8 – 10 - Not used
- 11 - Ground of input devices
- 12 - Input. Transmission fluid (oil) temperature sensor
- 13 – 20 - Not used
- 21 - Output. ROM (EEPROM) resolution
- 22 - Input. ROM (EEPROM) data
- 23 - CAN line
- 24 - Input. Secondary (output) shaft speed sensor (DSA)
- 25 - Not used
- 26 - Output. Sensor power supply +5 V
- 27 – 29 - Not used
- 30 - Output. Solenoid valve for downshift clutch
- 31 - Output. ROM synchronization (EEPROM)
- 32 - Not used
- 33 - CAN line
- 34 - Not used
- 35 - Input. Primary (input) shaft speed sensor
- 36 - Not used
- 37 - Output. Solenoid valve for downshift clutch
- 38 - Output. Solenoid valve for downshift clutch
- 39 - Output. Solenoid valve for downshift clutch
- 40 - Output. Solenoid valve for downshift clutch
- 41 - Output. Solenoid valve for downshift clutch
- 42 - Output. Solenoid valve for downshift clutch
- 43 - Output. Solenoid valve for downshift clutch
- 44 - Output. Solenoid valve for downshift clutch
- 45 - Output. Solenoid valve for downshift clutch
- 46 - Output. Solenoid valve for downshift clutch
- 47 - Output. Solenoid valve for downshift clutch
- 48 - Output. Solenoid valve for downshift clutch
- 49 ...pressure regulation in the line
- 38 - Output. Solenoid valve of the torque converter lock-up clutch
- 39 - Output. Solenoid valve of the 2-4 gear brake
- 40 - Output. Solenoid valve of the upshift / downshift brake clutch and reverse gear
- 41 – 42 - Ground of power stages
- 43 – 44 - Not used
- 45 - Input. Terminal "30" + battery
- 46 - Not used
- 47 – 48 - Input. Terminal 15 of the ignition switch
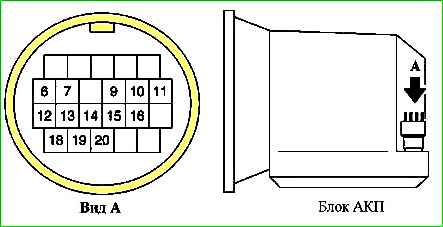
Assignment of contacts of the automatic transmission connector (21902-1700010)
Contact - Circuit
- 1 – 5 - Not used
- 6 - Solenoid valve of the downshift clutch
- 7 - Solenoid valve of the upshift clutch / downshift brake and reverse gear
- 8 - Not used
- 9 - EEPROM resolution
- 10 - primary (input) shaft speed sensor
- 11 - transmission fluid (oil) temperature sensor
- 12 - 2-4 brake solenoid valve
- 13 - line pressure regulating solenoid valve
- 14 - +5 V sensor supply
- 15 - EEPROM synchronization
- 16 - sensor ground
- 17 - Not used
- 18 - torque converter lockup clutch solenoid valve
- 19 - on/off (shift) solenoid valve
- 20 - EEPROM data (EEPROM)
- 21 – 22 - Not used
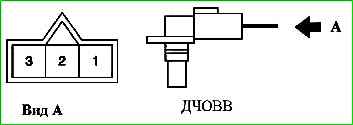
Assignment of contacts of the DCHOVV connector (21902-3843010)
Contact - circuit:
- 1 - sensor ground;
- 2 - sensor signal;
- 3 - sensor power supply
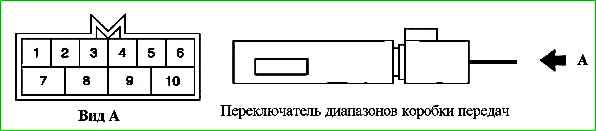
Pin assignment of the gearbox range (mode) switch connector
Contact - Circuit
- 1 - Not used
- 2 - Mode "2" of the automatic transmission range (mode) switch
- 3 - Mode "1" of the automatic transmission range (mode) switch
- 4 - Mode "D" of the automatic transmission range (mode) switch
- 5 - Mode "R" of the automatic transmission range (mode) switch
- 6 - Power supply. Terminal "15" of ignition switch
- 7 - Starter (+)
- 8 - Mode "N" of automatic transmission range (mode) switch
- 9 - Mode "P" of automatic transmission range (mode) switch
- 10 - Starter (-)
List of fault codes for automatic transmission controller 21126-1412020-00
Fault codes for automatic transmission controller
Code - Description
- P062F - Controller, EEPROM read/write error
- P0705 - Automatic transmission range switch position sensor, circuit faulty
- P0706 - Range switch position sensor circuit Automatic Transmission, Signal Out of Range
- P0711 - Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit, Signal Out of Range
- P0712 - Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit, Low Input
- P0713 - Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit, High Input
- P0717 - Input Speed Sensor Circuit, No Signal
- P0720 - Output Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- P0731 - Gear 1 Incorrect Ratio
- P0732 - Gear 2 Incorrect Ratio
- P0733 - Gear 3 Incorrect Ratio
- P0734 - Gear 4 Incorrect Ratio ratio
- P0740 - Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Malfunction
- P0743 - Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Malfunction
- P0744 - Torque Converter Clutch Circuit Intermittent
- P0863 - Transmission Control Module Communication Circuit Malfunction
- P0962 - Pressure Control Solenoid Control Circuit Short to Ground
- P0963 - Pressure Control Solenoid Control Circuit Short to Battery
- P0973 - Shift Solenoid Control Circuit Short to Ground
- P0974 - Shift Solenoid Control Circuit Short to Battery
- P1701 - Power Supply Circuit Malfunction
- P1735 - Gear 1 Locked
- P1736 - P2nd Gear Locked
- P1737 - 3rd Gear Locked
- P1738 - 4th Gear Locked
- P1744 - Torque Converter Lockup Clutch Circuit Erratic
- P17AA - Downshift Clutch Solenoid Control Circuit Short to Ground
- P17AB - Downshift Clutch Solenoid Circuit Malfunction
- P17AD - 2-4 Brake Solenoid Control Circuit Short to Ground
- P17AE - 2-4 Brake Solenoid Circuit Malfunction
- P17BO - Upshift/Downshift and Reverse Brake Clutch Solenoid Control Circuit Short to Ground
- P17B1 - Downshift Clutch Solenoid upshift/brake downshift and reverse gear, circuit faulty
- U0073 - CAN bus disconnected
- U0100 - CAN bus, no data from ECM
- U0140 - CAN bus, no data from brake pedal switch
- U0155 - CAN bus, no data from instrument cluster
- U0300 - CAN bus, incompatibility of message parameters
- U1000 - CAN bus, circuit faulty
If several fault codes are detected simultaneously, check the codes in accordance with the list of priorities.
List of fault codes priorities
- Priority - Code malfunctions
-1-
- P0863 Transmission Control Module Communication Circuit Malfunction
- U0073 CAN Bus Disabled
- U0100 CAN Bus No Data from ECM
- U0140 CAN Bus No Data from Brake Pedal Switch
- U0155 CAN Bus No Data from Instrument Cluster
- U0300 CAN Bus Message Parameter Incompatibility
- U1000 CAN Bus Circuit Malfunction
- 2 -
- P0740 Torque Converter Lockup Clutch Circuit Malfunction
- P0743 Torque Converter Lockup Clutch Circuit faulty
- P0962 Pressure control solenoid, control circuit short to ground
- P0963 Pressure control solenoid, control circuit short to battery
- P0973 Shift solenoid, control circuit short to ground
- P0974 Shift solenoid, control circuit short to battery
- P17AA Downshift clutch solenoid, control circuit short to ground
- PI7AB Downshift clutch solenoid, circuit faulty
- P17AD 2-4 brake solenoid, control circuit short to ground
- P17AE 2-4 brake solenoid, circuit faulty
- P17BO Upshift/Downshift and Reverse Brake Clutch Solenoid control circuit short to ground
- P17B1 Overdrive/Downdrive and Reverse Brake Solenoid Circuit Malfunction
- 3 -
- P062F Controller EEPROM Read/Write Error
- P0705 Range Switch Position Sensor Circuit Malfunction
- P0706 Range Switch Position Sensor Circuit Out of Range
- P0711 Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit Out of Range
- P0712 Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit Low
- P0713 Transmission Fluid Temperature Sensor Circuit High
- P0717 Input Speed Sensor Circuit No signal
- P0720 Output shaft speed sensor, circuit malfunction
- P1701 Power supply circuit malfunction





