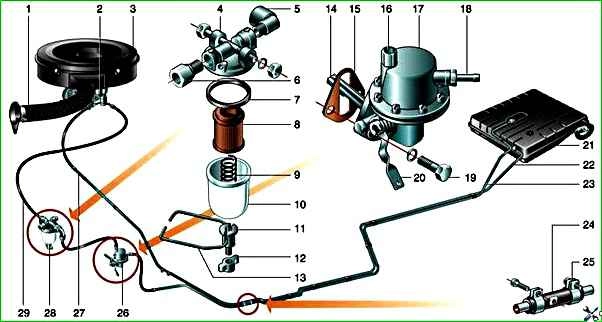
The power supply system consists of a fuel tank, fuel lines, a fuel pump, a sump filter, a fine fuel filter, a carburetor with throttle and air damper drives, and an air filter.
Fuel from the tank flows through the fuel line to the diaphragm pump. It is driven by the camshaft eccentric, which acts on the pump drive lever.
A fine brass mesh filter is installed on the pump inlet.
When the engine is not running, fuel is pumped into the carburetor using the manual pump lever.
There is a hole at the bottom of the pump housing. Fuel leaking from it indicates a leak in the diaphragm.
The fuel then passes through a fuel filter, consisting of a housing, a plastic settling cup and a filter element.
Then the fuel enters the K-151 carburetor.
The air filter is a dry type, with a replaceable filter element made of porous cardboard, installed on the carburetor through a rubber gasket.
To reduce air intake noise, the filter is equipped with an air intake corrugated hose connected to a metal pipe located on the right side of the mudguard.
When the ambient air temperature is below 5° C, to supply heated air to the carburetor, the air intake hose must be disconnected from the branch pipe located on the mudguard and connected to the screen branch pipe installed on the engine exhaust pipe.
It is necessary to use filter elements with the following designations:
3102-1109013-02 (-03-04-05,-Ob) or 31029-1109013 (-01-02,-03)
The B-9V fuel pump is a diaphragm type, driven by an eccentric located on the engine camshaft.
The fuel pump consists of a housing assembly with a diaphragm 8 and a drive lever 9, a head with valves 4 and 7, and a cover. a diaphragm of four blades made of varnished fabric is clamped between the housing and the pump head.
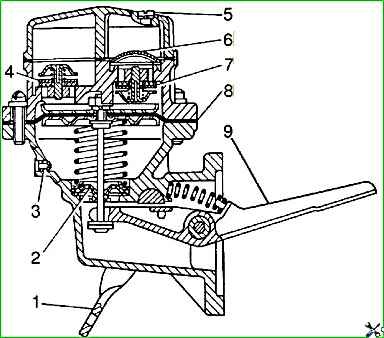
The diaphragm rod is sealed with a rubber seal 2. The valve consists of a holder made of zinc alloy, a rubber valve and a brass washer, pressed by a spring (made of bronze wire).
A filter 6 made of fine brass mesh is installed above the suction valves of the pump. To fill the carburetor with fuel when the engine is not running, the pump has a device for manual drive.
To control the tightness of the diaphragm, there is a hole in the pump housing with a mesh filter 3.
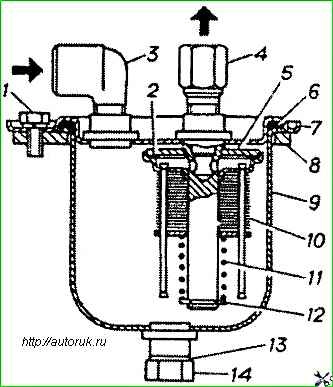
The K-151 carburetor consists of three main detachable parts connected through sealing gaskets with screws.
The upper part - the carburetor cover includes an air pipe, divided into two channels, with an air damper in the channel of the first chamber.
The middle part consists of a float and two mixing chambers and is the carburetor body.
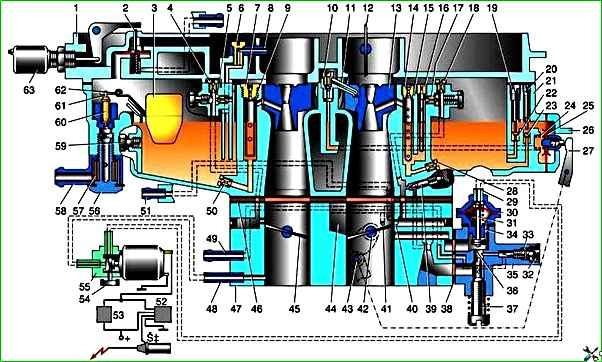
Lower part - the throttle body includes mixing pipes with throttle valves of the first and second carburetor chambers.
The gasket between the middle and lower parts of the carburetor is sealing and heat-insulating.
Structurally, the carburetor consists of two mixing chambers - the first and second. Each of the carburetor chambers has its own main metering system.
Idle system - with quantitative regulation of constant mixture composition (autonomous idle system).
In the second chamber of the carburetor there is a transition system with fuel supplied directly from the float chamber, which comes into operation when the throttle valve of the second chamber is opened.
The accelerator pump is of the diaphragm type. to enrich the combustible mixture at full load, an econostat is provided in the second chamber.
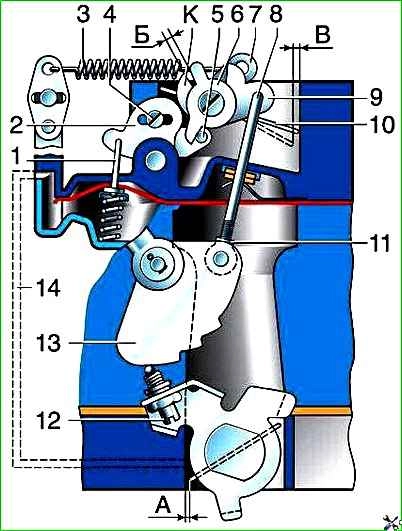
Starting device diagram 1 - diaphragm mechanism rod; 2 - the left part of the double-arm trigger lever; 3 - air damper closing spring; 4 - coupling screw of the double-arm lever; 5 - antenna on the right side of the double-arm lever; 6 - lever at the front end of the air damper axis; 7 - closing lever at the rear end of the air damper axis; 8 - starting device thrust; 9 - intermediate lever; 10 - air damper; 11 - threaded head at the end of the rod (for early models of carburetors); 12 - adjusting screw-stop for slightly opening the throttle valve; 13 - cam; 14 - channel for supplying vacuum to the diaphragm of the starting device; A, B, C - gaps; K - lever protrusion 9
When the accelerator pedal is released, the contacts of microswitch 35 must be open.
The fuel shut-off system works as follows.
When the accelerator pedal is released and the engine crankshaft speed is more than 1400, the control unit does not supply voltage to the solenoid valve, as a result of which, through the channels of the solenoid valve, atmospheric air enters the forced idle economizer, the valve of which closes the idle channel.
If the normal operation of the fuel supply shut-off system is disrupted (the engine does not start or “stalls” when the throttle pedal is released), you must first make sure that the electrical contacts of the system elements are reliable, after which you should sequentially check the functionality of the solenoid valve, microswitch and control unit .
To check the solenoid valve and microswitch, you need to disconnect the electrical connector of the control unit, turn on the ignition (do not start the engine!) and in the engine compartment, smoothly open and close the carburetor throttle valves several times with one hand, and hold the solenoid valve with the other.
If the solenoid valve and fuse are working properly and if the microswitch is working properly and correctly adjusted, you should feel the activation of the solenoid valve (vibration, clicks).
To check the control unit, you need to insert the connector into the unit, turn on the ignition, start the engine and warm it up.
Then, from the engine compartment side, open the throttle valves approximately 1/3 of the way with one hand, and hold the solenoid valve with the other.
Release the throttle valves sharply. In this case, if the control unit is corrected, the solenoid valve should turn off, and when the crankshaft speed decreases to approximately 1050, the solenoid valve should turn on.
All carburetor systems are connected to a float chamber, the fuel level in which is maintained by float 2 and fuel valve 1





