The Russian SUV Niva has gained popularity not only in Russia, but also abroad
An inexpensive and easy-to-maintain car that can be successfully used in any weather conditions both in the far north and in the south
Niva VAZ-2121 and its modifications with increased cross-country ability.
All wheels are permanently driven (non-disconnectable all-wheel drive), there is a mode for locking the center differential.
The body is load-bearing, all-metal, welded.

Engine — four-cylinder, in-line, petrol, four-stroke; location — front, longitudinal.
The VAZ-21213 is equipped with a carburetor engine mod. 21213 with a working volume of 1.7 liters, the VAZ-21214 — engine 21214 of the same volume with distributed fuel injection. (Previously, the VAZ-21214 cars were equipped with the 21214 engine with central fuel injection and a microprocessor ignition system).
The VAZ-21215 (supplied for export) is equipped with a 1.9-liter XUD-9SD diesel engine from the Peugeot-Citroen concern.
Gasoline engines with central injection and diesel engines are almost never found in Russia.
The vehicle identification number (VIN) is stamped on the mudguard of the right front wing.
The duplicate vehicle identification number (VIN) is stamped on the floor of the luggage compartment on the right.
The vehicle data is provided on a plate attached to the horizontal shelf of the front shield.
The engine number is stamped on the cylinder block on the left above the oil filter.
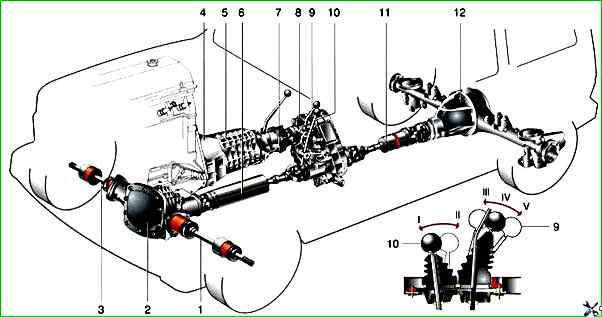
VAZ-2121 transmission units: 1, 3 - front wheel drives; 2 - front axle; 4 - clutch; 5 - gearbox; 6 - front propeller shaft; 7 - intermediate shaft; 8 - transfer case; 9 - transfer case gear shift lever; 10 - differential lock lever; 11 - rear propeller shaft; 12 - rear axle; I - differential unlocked; II - differential locked; III - low gear engaged; IV - neutral position; V - the highest gear is engaged
The Niva is a four-wheel drive vehicle, i.e. all wheels are driven.
All-wheel drive is permanent: the torque from the engine is always transmitted to both axles at once (the axles are not disconnected).
This design increases the vehicle's cross-country ability, while reducing the load on the transmission units, but slightly increases fuel consumption.
The front and rear axles are connected via an interaxle differential, which allows the front and rear wheels to rotate at different angular speeds depending on the trajectory and driving conditions.
The interaxle differential is located in the transfer case and is similar to the interwheel differentials located in the front and rear axles.
Unlike them, the interaxle differential can be forcibly locked (the locking lever is on the floor tunnel).
In this case, the front and rear cardan shafts become rigidly connected to each other and rotate at the same frequency.
This significantly increases the vehicle's cross-country ability (on slippery slopes, in mud, snow, etc.), but it worsens controllability and increases wear of transmission parts and tires on surfaces with good traction.
Therefore, the differential lock can only be used to overcome difficult sections and at low speeds.
A control lamp on the instrument panel warns the driver that the lock mode is on.
The differential lock can be turned on while the car is moving, if the wheels are not slipping.
Locking the center differential does not save the car from the danger of "diagonal hanging", when one of the wheels on each axle loses traction with the ground - in this case, soil is poured under the suspended wheels or dug under the rest.
The low gear in the transfer case serves to increase the torque supplied to the wheels, its gear ratio is 2.135.
High gear, designed for normal driving conditions, has a gear ratio of 1.20.
Thus, the driver can use one of two rows of gear ratios - with a higher or lower gear in the transfer case.
The total gear ratios of the "upper" row (from 1st to 5th gear) are 4.40; 2.52; 1.63; 1.20; 0.98, "lower" - 7.82; 4.47; 2.90; 2.13; 1.75.
The lower gear in the transfer case is engaged before overcoming snowy, sandy areas, steep climbs, when towing loads, etc., when there is a lack of engine traction or for driving with very low speed.
It is necessary to engage the lower gear in the transfer case in advance, with the car parked, since the gear shift clutch does not have synchronizers.
With some skill, it is possible to engage the higher gear even when driving at a speed of no more than 30–35 km/h; if possible, it is better to reduce the speed or stop.
A car with permanent all-wheel drive places special demands on tires. They should be the same not only in size, but also in the degree of wear.
Different rolling radii of tires will cause increased wear of differentials under normal driving conditions, and with the lock engaged - increased wear of other transmission parts and wheel slippage.
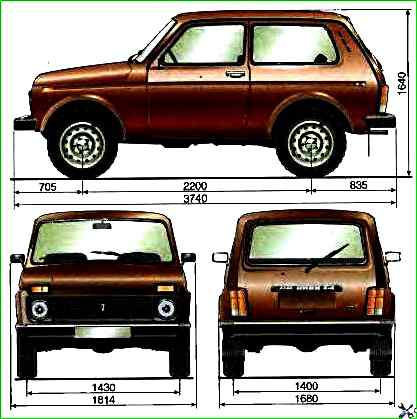
Technical characteristics of the VAZ-2121 car
Body - All-metal, load-bearing, two-volume
Number of doors 3
Number of seats (with folded rear seats) 4-5 (2)
Curb weight, kg 1210
Load capacity, kg 400
Gross weight, kg 1610
Ground clearance of the car with a full load with a static radius of tires 315 mm (175/80R16)/322 mm (696-16), not less than, mm:
- - to the front suspension crossmember 221/228
- - to the rear axle beam 213/220
Gross weight of the towed trailer, kg:
- - not equipped with brakes 400
- - equipped with brakes 1490
Smallest turning radius along the track of the outer front wheel, m 5.5
Maximum speed, km/h:
- - with driver and passenger 137
- - with full load 135
Time acceleration from standstill to 100 km/h:
- - with driver and passenger 19
- - with full load 21
Maximum climb that a fully loaded vehicle can overcome without acceleration in first gear, % 58
Brake distance of a vehicle during emergency braking with the permitted maximum weight from a speed of 80 km/h on a horizontal section of a smooth asphalt highway, no more than, m:
- - when using the working system 40
- - when using one of the circuits of the working system - 90
Fuel consumption* per 100 km of travel, no more than, l:
- - on the highway at a speed of 90 km/h in fifth gear 8.3
- - on the highway at speed of 120 km/h in fifth gear VAZ-21213 - 11.5
- - on the highway at a speed of 120 km/h in fifth gear VAZ-21214 - 11.2
- - in the urban cycle VAZ-21213 - 10.3
- - in the urban cycle VAZ-21214 - 10.2
Engine VAZ-21213, VAZ-21214
Type - Four-stroke gasoline
Number and arrangement of cylinders 4, in line
Firing order of cylinders 1-3-4-2
cylinder diameter and piston stroke 82x80 mm
Displacement, l 1.69
Compression ratio 9.3
VAZ-21213 engine
Rated power according to GOST 14846-81 (net), kW (hp) - 58.0 (78.9)
Crankshaft speed at rated power, min -1 - 5200
Maximum torque, Nm (kgcm) according to GOST 14846-81 - 127 (12.9)
Crankshaft speed at maximum torque, min -1 - 3000
Minimum crankshaft speed in idle mode, min -1 - 750—800
Fuel system - With carburetor
Fuel - Gasoline with an octane rating of 92—95
Ignition system - Contactless
Initial ignition advance angle, degrees 1±1
VAZ-21214 engine
Rated power according to GOST 14846—81 (net), kW (hp) - 59.5 (80.9)
Crankshaft speed at rated power, min -1 - 5200
Maximum torque, Nm (kgcm) according to GOST 14846—81127 - 127.5 (13.0)
Crankshaft speed at maximum torque, min -1 - 4000
Minimum crankshaft speed at idle, min -1 - 820—880
Fuel system - Distributed injection
Fuel - Unleaded gasoline with an octane rating of 92—95
Ignition system - Microprocessor
Initial ignition advance angle - Not subject to adjustment
Transmission
Clutch - Single-plate, dry, with diaphragm spring
Clutch engagement drive - Hydraulic
Gearbox - Mechanical.
Five forward gears, one reverse.
All forward gears are synchronized
Gearbox ratios:
- 1st gear 3.67
- 2nd gear 2.10
- 3rd gear 1.36
- 4th gear 1.00
- 5th gear 0.82
- reverse 3.53
Two-stage transfer case; with interaxle differential with forced locking
Transfer case gear ratios:
- - high gear 1.2
- - low gear 2.135
Intermediate shaft (from gearbox to transfer case) - With elastic coupling and equal-angle joint speeds
Front and rear propeller shafts (from the transfer case to the front and rear axles) - Tubular cross-section, with two cardan joints on needle bearings with grease nipples
Main gear (front and rear axles) - Bevel, hypoid
Main gear ratio 3.9
Front wheel drive - Open shafts with constant velocity joints
Rear wheel drive - Half-shafts passing in the rear axle beam
Suspension, chassis
Front suspension - Independent, on wishbones, with coil springs, with telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers and anti-roll bar
Rear suspension - Dependent (rigid beam), on four longitudinal and one transverse levers, with cylindrical springs and telescopic hydraulic shock absorbers
Steering
Steering gear - Globoidal worm with double-ridge roller
Steering gear ratio 16.4
Steering drive - Three-link: with one middle and two lateral split rods; with pendulum lever





