Motor power supply system diagrams are shown in Fig. 1, 2, 3.
The reliability and durability of the engine, as well as the dynamic performance and efficiency of the vehicle as a whole largely depend on the state of the power system.
The power supply system consists of two fuel tanks, fuel lines, a switch tap, a fuel pump, a sediment filter, a fine fuel filter, a carburetor with a drive of the throttle and air dampers, and an air filter.
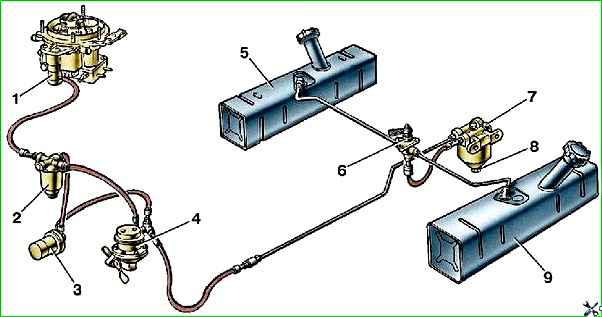
In versions with a pre-heater, an electric fuel pump is included in the power system in parallel with the mechanically driven fuel pump.
Fuel, under the influence of vacuum created by the fuel pump, passes through the fuel intake screen, then through the fuel line and switch valve enters the filter-sump housing.
Water and large mechanical particles remain in the housing, and the fuel passes through a filter element consisting of a set of thin steel plates and is supplied through a fuel line to the fuel pump.
After the pump, the fuel passes through the fine filter element and enters the carburetor.
The air required to form the working mixture is supplied to the carburetor through the air filter.

Fuel tanks are rectangular steel, located on both sides of the car frame.
Tanks are attached to the frame side members from the outside using brackets and clamps.
Cardboard spacers are placed between the clamps and the tank. The tanks are connected by fuel lines to a switch valve installed under the driver's seat. With its help, you can switch the fuel intake from one tank to another.
The capacity of one tank is 39 liters.
At the top of each tank there is a fuel intake, consisting of a tube and a filter in the form of a brass mesh, as well as an electric fuel level indicator sensor.
In some modifications, there is a drain hole with a threaded plug at the bottom of the tank.
The plastic threaded neck plug has inlet and outlet valves to prevent the formation of vacuum and increased pressure inside the tank.
On some vehicles, the fuel tank filler neck is equipped with a retractable pipe for easy refueling.
The fuel tank filler flap is closed with a lid on the outside.
Fuel lines are made of rubber hoses and copper pipes.
The hoses are connected to the fuel pump, fuel tank switch valve, and sediment filter through fittings with union nuts.
On the pipes of the fuel intakes, carburetor and fine fuel filter, the hoses are secured with clamps.
The copper tube is connected to the settling filter at one end through a fitting, and at the other end it is inserted into a rubber hose and tightened with a clamp.

The fuel filter-settler is installed on the left frame side member in front of the fuel tank and is designed to separate water and mechanical impurities larger than 0.05 mm from the fuel.
To clean fuel from mechanical impurities, the filter is equipped with a filter element consisting of a set of thin metal plates.
To remove sediment from the bottom of the filter housing there is a drain hole with a threaded plug.
The fuel pump is a diaphragm pump, driven by an eccentric to a distributor engine dividing shaft.
It is possible to install a pump of one of three models: B9V (451-1106010-40), 900-1106010 and 2105-1106010-50.
The fuel pump consists of a housing, a valve block cover and a drive lever. The valve block is installed in the pump cover.
Above the suction valves there is a filter made of fine brass mesh.
To fill the carburetor with fuel when the engine is not running, the pump has a manual drive lever.
To control the tightness of the diaphragm and prevent fuel from entering the engine crankcase, the pump housing has a drainage hole.
The fine fuel filter can be used in two types: collapsible, with a replaceable filter element, and non-removable.
The dismountable fuel filter is mounted on the cylinder head bracket.
It consists of a housing, a rubber gasket, a rubber sealing bushing, a ceramic or paper filter element, a spring, a plastic settling cup and mounting parts for the settling cup.
A filter with a plastic non-separable housing and a paper filter element is installed on the hose supplying fuel to the carburetor.
The air filter is a dry type, with a replaceable filter element made of non-woven synthetic material, mounted on the cylinder head bracket.
The filter is equipped with an air intake corrugated hose connected to a metal pipe located on the radiator casing bracket on the right.
When the ambient air temperature is below 5 °C, to supply heated air to the carburetor, disconnect the corrugated hose from the filter pipe, and move the flap on the exhaust manifold to the “winter” position.

Why use a 10mm wrench to loosen the nut securing the damper (Fig. 4).
The air filter cover has two pipes for connecting the hoses of the engine crankcase ventilation system.

If the cylinder head cover, due to a malfunction, has two pipes for removing crankcase gases, then to prevent unfiltered air from entering the intake manifold, it is necessary to plug the unused small pipe of the air filter cover in any available way (for example, compress it with pliers).
The throttle valve control drive consists of a pedal, a system of rods and levers, adjusting nut tips, couplings and a spring.
In addition, the cars have a manual throttle valve drive.
It consists of a handle on the instrument panel, a rod in the shell, a bracket and a lever.
The carburetor air damper is controlled by a knob also located on the instrument panel.
It is connected to the damper lever by a rod in the shell.
When the handle is in its original position (recessed), the air damper is fully open.






