The engine fuel system includes units, parts and assemblies designed for thorough cleaning and uniform distribution of strictly metered portions of fuel to the cylinders
The fuel system operates as follows.
Fuel from the fuel tank 4 is sucked by the fuel pump 5 through the coarse fuel filter 3.
From the pump, the fuel enters the fine filter 1, where it is finally cleaned of the smallest contaminants and then enters the high-pressure pump 6.
From the pump, metered portions of fuel are fed through high-pressure fuel lines to the injectors for injection into the cylinders.
The fuel pump supplies more fuel to the high-pressure pump than is necessary for engine operation.
Excess fuel is diverted through the bypass valve of the fuel pump back to the fuel tank.
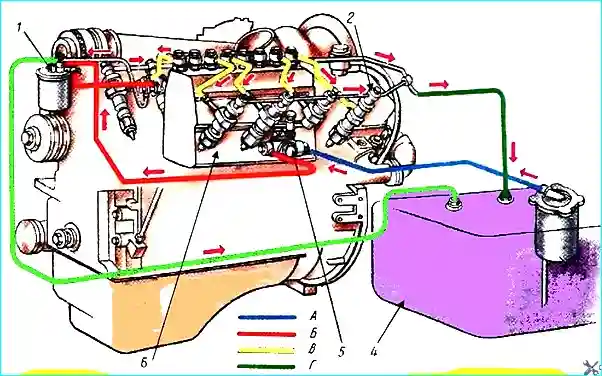
The bypass valve, adjusted to a fuel pressure of 0.5-1.0 kgf/cm², creates constant fuel pressure in the pump channels, which ensures good conditions for filling the above-plunger space with fuel regardless of the engine crankshaft speed.
In addition, circulation through the bypass valve helps remove air bubbles from the fuel, which, when they enter the sub-plunger space of the pump, can adversely affect the amount of fuel supplied.
The removal of air bubbles from the fuel is also facilitated by the continuous circulation of fuel through the filter jet cleaning race and along the fuel line into the tank.
Fuel leaking into the cavity of the injector spring through the gap between the needle and the sprayer is diverted to the fuel tank.
Possible system malfunctions power supply and how to eliminate them
The main faults in the fuel system include:
- - leaky fuel lines and their connections;
- - insufficient fuel supply to the high-pressure fuel pump;
- - malfunction of the high-pressure fuel pump and injectors.
Lack of tightness of fuel lines and their connections
A common cause of difficult engine starting, its unstable operation, and loss of power is air entering the fuel system.
Leaks in the intake part of the fuel system: fuel tank - fuel pump, have a particularly strong effect on engine operation.
The slightest leak in the connections in this area leads to air entering the fuel system, which reduces the fuel supply to the combustion chamber and leads to disruption of the normal operation of the engine.
If starting the engine is difficult, then to remove air from the fuel system, unscrew the handle of the manual priming pump and, moving it up and down, bleed the system for 2-3 minutes.
After bleeding, tighten the pump handle until it stops.
If, after bleeding the system, starting the engine remains difficult and the engine does not develop power, then wipe the fuel lines, connections, priming pump, coarse filter cover, fine filter with a rag and determine the place of air suction.
The tightness of the low-pressure fuel lines from the fuel priming pump to the high-pressure pump can be checked with a hand pump. To do this, disconnect the drain fuel line from the tank and plug it with a plug, then pump the hand pump several times.
Emulsion or fuel will leak out in places where the system is leaky.
Leaks in the connections are eliminated by tightening the threaded connections, replacing the corresponding sealing gaskets or fuel lines.
If the air leak cannot be found, it is recommended to remove the coarse fuel filter housing from the fuel tank and check it for leaks.
After eliminating the leak, it is necessary to remove the air from the fuel system. To do this, loosen the air release plugs from the high-pressure fuel pump housing and pump the system with a hand pump until fuel flows out without air bubbles. Then the plugs are tightened.
Insufficient fuel supply to the high-pressure fuel pump.
Disruption of normal fuel circulation in the system is expressed in a drop in engine power, uneven and unstable operation, difficult starting, and engine stops during operation at low crankshaft speed.
Insufficient fuel supply to the high-pressure fuel pump can be caused by:
- - air suction into the fuel system;
- - malfunction of the fuel pump;
- - fuel leakage at the joints of high-pressure fuel lines;
- - clogging of the filter element of coarse or fine fuel filters, as well as fuel lines;
- - freezing of water in the fuel lines or fine filter in winter;
- - thickening of the fuel if the fuel grade does not match the season and the car is stored in an open area.
Before looking for a malfunction, you should make sure that there is fuel in the fuel tanks and there is no leakage at the joints of high-pressure fuel lines.
Then you need to check the system for air leaks and, if necessary, fix the malfunction.
If the fuel supply is not stopped when pumping with a hand pump, then most likely the booster pump is faulty.
The most common reasons abnormal operation of the booster pump are: dirt getting between the seats and valves, breakage of springs or piston hanging.
If after washing and blowing out the valve parts the normal operation of the pump is not restored, then it is necessary to remove the booster pump from the engine and send it to the workshop for repair.
The intensity of fuel circulation in the system can be checked using a control pressure gauge connected to the hole under the plug on the fuel injection pump body for releasing air, the air pressure in the line should be within 0.5 - 1 kgf / cm², at a crankshaft speed of 2100 min.
Pressure below 0.5 kgf / cm² can be caused by clogging of the filter elements of the coarse or fine fuel filters or clogging of the fuel lines.
In this case, the filter elements are replaced with new ones, and the fuel lines are blown out compressed air.
If the pressure in the system remains below normal even after replacing the fine and coarse filter elements and checking the fuel pump, then check the condition of the bypass valve of the high-pressure fuel pump.
Faulty operation of the bypass valve can be caused by dirt getting between the seat and the valve, as well as breakage or weakening of the valve spring.
The pressure can be adjusted by turning the seat of the bypass valve of the high-pressure pump, and after adjustment, calk the valve seat.
If the bypass valve is in good condition, then you need to remove the fuel injection pump from the engine and send it to the workshop for inspection and repair.
Violation of the normal operation of the fuel injection pump and injectors
If the engine does not develop power, smokes, runs unevenly at low speeds, then this most often indicates poor operation of the injectors (in the absence of air suction).
The main reason for the incorrect operation of the injectors is the deterioration of the quality of fuel atomization.
This phenomenon occurs due to a violation of the adjustment of the pressure of the beginning of the needle lift, the ingress of various mechanical impurities into the atomizer, coking, clogging or wear of the holes in the atomizer body, as well as improper assembly or installation of the injectors on the engine.
A faulty injector can be detected directly on a running engine, for this, loosen the tightening of the union nut at the nipple of the injector being tested so that fuel does not enter it.
When turning off the injector, observe the quality of the exhaust gases and the speed of the engine crankshaft.
If after turning off the injector the speed of the engine crankshaft does not change, and the smoke of the exhaust gases decreases, then the injector being tested is faulty - it must be removed and sent to repair.
When a serviceable injector is switched off, the engine crankshaft speed will decrease, and the smoke content of the exhaust gases will not change.
If necessary, it is recommended to start checking the high-pressure fuel pump only after checking the injectors, making sure that they are in good working order.
During operation, the normal operation of the pump may be disrupted due to mechanical wear of the plunger pairs and discharge valves, breakage of the pusher springs, wear of the bypass valve or its seat, due to stripping of the threads of the fittings at the junction of the high-pressure fuel lines and violation of the pump adjustments.
As a result of wear of the plunger pairs, the fuel supply by the pump sections per cycle decreases, which leads to a decrease in the power and efficiency of the engine.
Wear of the discharge valves along the shut-off cone and unloading belt changes the start and nature of the injection, and also worsens cut-off of fuel supply by the injector needle.
This leads to fuel leakage through the atomizer and coking of the injector spray holes.
Wear of the bypass valve causes a decrease in fuel pressure in the pump cavity and leads to deterioration in filling the above-plunger space.
In the conditions of repair and mechanical workshops, repair of fuel equipment in most cases comes down to replacing defective parts, monitoring and adjusting the fuel equipment.
Repair must be carried out in fuel equipment departments or workshops equipped with the necessary devices, tools, control and adjustment stands and devices.
It is recommended to disassemble the high-pressure fuel pump, fuel pump and injection advance clutch only after examining the technical condition and to the extent necessary to eliminate the identified deficiencies, since unjustified disassembly disrupts the mutual running-in of parts to each other, leading to a decrease in the service life of the unit as a whole.
In all cases, when removing the fuel equipment from the engine after disconnecting the fuel lines, the fittings of the fuel and booster pump, injectors, filters and pipeline openings must be protected from dirt with plugs, caps, plugs or clean insulating tape.
Before disassembling, the units and components of the fuel equipment are thoroughly cleaned and washed in clean kerosene.
In this case, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of contaminated fuel getting into the internal cavities of the fuel equipment.
During assembly and disassembly, the parts and units of the fuel equipment must be thoroughly washed and placed in a clean container, ensuring their safety from damage and corrosion.
When assembling all units of the fuel equipment, it is necessary to remember that plunger and valve pairs, injector sprayers, as well as the bushing with the rod of the booster pump are precision pairs and are not subject to disassembly. They can only be replaced as a set.





