The diaphragm clutch model 182 (Fig. 1) consists of leading and driven parts, as well as clutch release mechanism parts installed in the clutch housing
The leading part of the clutch — the pressure plate 2 with the casing is installed on the engine flywheel and secured with M10 bolts (12 pcs.) at a diameter of 450 mm.
Centering is carried out along a cylindrical groove with a diameter of 475 mm on the flywheel and clutch casing.
The pressure plate is connected to the casing using 4 plate packs that provide centering, axial movement and transmission of torque from the casing to the pressure plate.
To prevent the diaphragm spring from turning relative to the casing and the pressure plate, 6 pairs of bushings with special brackets are installed.
The use of these brackets allows maintaining constant contact pressure plate with a spring and ensure the withdrawal of the first when the clutch is disengaged.
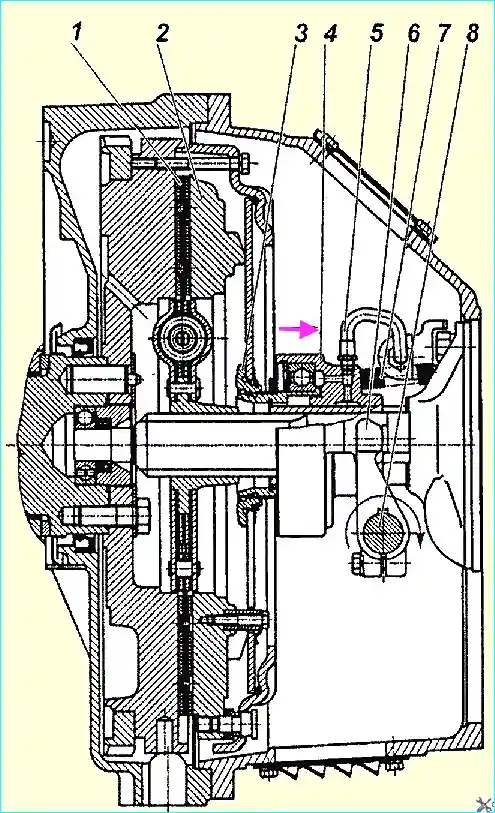
Fig. 1. Clutch model YaMZ-182: 1 - driven disk; 2 - pressure disk: 3 thrust ring; 4 - clutch release sleeve; 5 lubrication hose; 6 clutch release fork 7 release spring; 8 – clutch release fork shaft.
The driven disk 1 is installed between the flywheel and the pressure plate and is centered along the splines of the primary shaft of the gearbox.
Clutches of this type use a driven disk with a spring-friction damper with an elastic mount of one of the friction linings.
Thanks to this, the clutch reduces dynamic loads on the transmission during abrupt engagements (starting off, gear shifting), and also eliminates resonance phenomena and reduces the maximum “peak” torque values during steady-state vehicle movement.
The fastening of the friction linings is shown in Fig. 2.
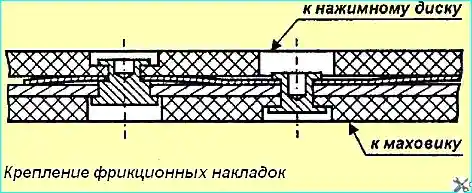
Fig. 2. Fastening of friction linings
The clutch release mechanism consists of a coupling 4 (Fig. 1) with a bearing, a fork 6 and a shaft 8. The coupling is connected through a thrust ring 3 to a diaphragm spring using a locking device.
The release spring 7 (Fig. 1) prevents rotation and axial movements of the sleeve 7 (Fig. 3) relative to the thrust ring 1 (Fig. 3).
As the friction linings wear out, the clutch release coupling 4 (Fig. 1) moves together with the spring towards the flywheel, while the design of the clutch release drive of a car or other vehicle ensures that the fork 6 (Fig. 1) rotates clockwise after selecting the gap between the fork legs and the coupling due to periodic adjustment of the drive or a gradual rotation due to the design hydraulic drive.
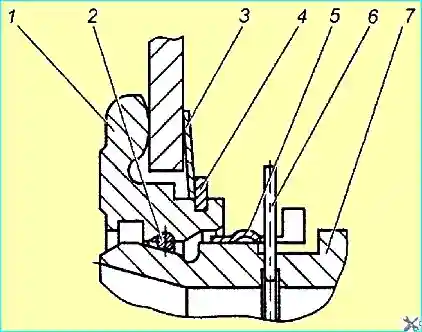
Fig. 3. Locking device: 1 thrust ring: 2 - spring ring; 3 - spring washer; 4 - retaining ring 5 lock ring 6 - safety ring; 7 bearing sleeve
The design of the locking device is shown in Fig. 3.
It includes a thrust ring 1, a clutch bearing sleeve 7 with a shaped groove, a spring ring 2 of circular cross-section, and a lock ring 5.
The thrust ring 1 is installed on the diaphragm spring when assembling the pressure plate with the casing and is held by a spring washer 3 and a lock ring 4. In the figure, the clutch is locked (connected) to the thrust ring.
A safety ring 6 is installed inside the clutch bearing sleeve 7, having a protruding whisker on the outside, preventing the disengagement of the clutch release sleeve and thrust ring 1.
The clutch is disengaged by turning the shaft clockwise.
The permissible direction of movement of the clutch and rotation The shaft for disengaging the clutch is shown in Fig. 1 by arrows. Moving the clutch and turning the shaft in the opposite direction is not allowed.
Clutch Maintenance
The types and frequency of clutch maintenance correspond to the types and frequency of engine maintenance.
Clutch maintenance includes a daily check of the clutch operation on the vehicle, as well as, after one TO-1 (after 500 hours) and at each TO-2, lubrication of the clutch release sleeve with the bearing and the clutch release fork shaft.
A daily check of the clutch operation on the vehicle includes checking for slippage, "driving" and extraneous noises and knocks.
Clutch slippage is detected during gear shifting, when after releasing the clutch pedal and a sharp increase in the crankshaft speed, the speed of the vehicle does not increase.
"clutch disengagement" (incomplete disengagement) has several characteristic features:
- • engaging synchronized gears is difficult;
- • engaging unsynchronized gears occurs with a characteristic grinding noise in the gearbox;
- • the vehicle is moving with a low gear engaged and the clutch pedal depressed.
Lubricant is supplied to the clutch through the hose oiler until grease appears in the gap between the bearing sleeve and the reflector washer.
The clutch release fork shaft is lubricated through two grease nipples, making two strokes with a syringe.
to ensure normal operation of the clutch, periodically check the correct adjustment of the clutch drive.
The frequency and procedure for checking and adjusting the clutch drive are determined by the vehicle operating manual.
Removing the clutch from engine
Removing the clutch from the engine with the gearbox installed is performed in the following order:
- 1. Unscrew the nut securing the lubrication hose.
- 2. Push the lubrication hose into the cavity of the clutch housing.
- 3. Remove the gearbox, while the clutch release sleeve remains on the thrust ring of the diaphragm spring.
- 4. Align the semicircular groove on the clutch release sleeve in its front part with the protruding whisker of the safety ring 6 (Fig. 3) and, having sunk it with some object, hold it in the sunken position through the central hole of the clutch release sleeve.
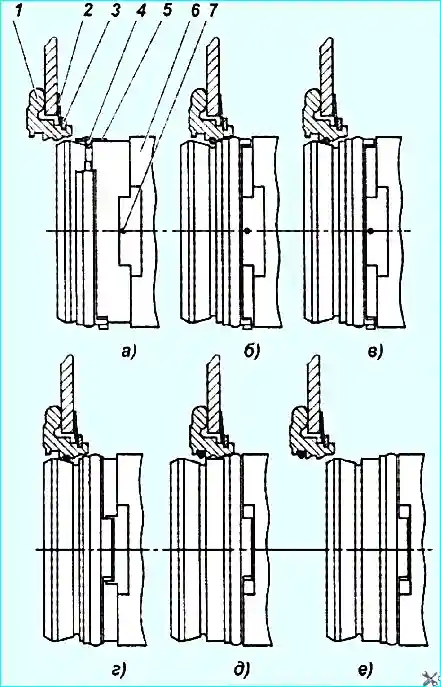
Fig. 4. Main positions of the locking device: 1 - thrust ring 2 - spring washer; 3 - retaining ring 4 - spring ring; 5 - lock ring 6 - bearing sleeve; 7 - safety ring
- 5. Turn the lock ring 5 (Fig. 4) relative to the sleeve 6 so that the ring projections coincide with the sleeve grooves (position “g”).
- 6. Push the coupling towards the flywheel until it stops, while the spring ring 4 will come out of the shaped groove of the thrust ring and will stand in the rectangular one (position “D”)
- 7. Disconnect the coupling, for which move it in the opposite direction (away from the flywheel), while the spring ring will remain in the rectangular groove of the thrust ring (position “e”), and then remove it from it.
- 8. Remove the pressure plate with the casing, for which unscrew the clutch mounting bolts, gradually in several stages, avoiding significant distortions of the pressure spring.
Installing the clutch on the engine
The clutch is installed on the engine in the following order:
- 1. Using a special mandrel, install the driven disk on the flywheel, while the friction lining riveted to the spring plate should be located towards the pressure plate, and the extended part of the hub should be outward (away from the engine).
- 2. Install the pressure plate with the casing assembly, ensuring the alignment of the mounting holes of the clutch casing and the flywheel.
- 3. Manually tighten the clutch mounting bolts to a depth of at least 4 mm.
- 4. Tighten the clutch mounting bolts to 60...70 Nm in several steps, uniformly pulling the pressure plate with the casing toward the flywheel, avoiding significant distortions of the pressure (diaphragm) spring.
- 5. Using a special mandrel, center ring 3 (Fig. 1) relative to the engine crankshaft axis.
The design of the locking device of the clutch release mechanism requires special rules for installing the gearbox on the engine.
The main positions of the locking device are shown in Fig. 4.
Installing the gearbox and engaging the clutch release sleeve with the thrust ring of the diaphragm spring is performed in the following order (the lever is located on the left side of the engine):
- 1. Turn the lock ring 5 on the sleeve so that its projections do not coincide with the grooves of the sleeve of the clutch bearing (position “a”).
- 2. Make sure that the clutch release sleeve is retracted to the stop in the gearbox primary shaft bearing cover by spring 7, Fig. 1.
- 3. Install the gearbox and secure with two bolts.
Do not allow the clutch release sleeve to move towards the flywheel after it is connected to the pressure spring.
- 4. Move the clutch release sleeve to the thrust ring to the stop, for which, using the process lever, turn the clutch release fork shaft counterclockwise.
The spring ring then enters the shaped groove of the thrust ring (position b, Fig. 4).
- 5. Turning the clutch release fork shaft clockwise, move the sleeve away from the engine (position “in”).
- 6. Make sure that the clutch release sleeve is engaged with the thrust ring by applying additional force to the sleeve additional force in the direction away from the engine.
- 7. Finally secure the gearbox.
Check the quality of the clutch installation (lack of “leading”, control of the torque value on the fork shaft) is carried out with the engine off.
To do this, it is necessary to turn the fork shaft by an angle of 9°30’ - 11° clockwise, which corresponds to moving the clutch 11-13 mm from the engine.
In this case, the output shaft of the gearbox, with the gear engaged, should rotate with a torque of no more than 5 Nm (0.5 kgfm).
The clockwise rotation of the clutch release fork shaft is shown in Fig. 1.
Possible malfunctions and troubleshooting methods
Slippage:
- Worn friction linings of the driven disk - Replace the linings or the driven disk.
- Oil getting on the friction surfaces of the clutch through the engine or gearbox seals - Remove oil, eliminate oil leaks.
- Breakage of the pressure spring - Replace the pressure spring or pressure plate with the casing and spring assembly.
- The clutch is partially disengaged due to a faulty release drive - Repair the clutch release drive.
Clutch drag:
- The clutch release drive does not provide the required travel of the release sleeve - Check the operation of the clutch release drive and repair
- Warping of the pressure plate - Replace the pressure plate with the housing assembly
- Driven disk runout due to deformation - Replace the driven disk
- Destruction of the driven disk lining - Replace the driven disk or linings





