ZIL vehicles and their modifications are equipped with a mechanical five-speed gearbox with synchronizers (Fig. 1).
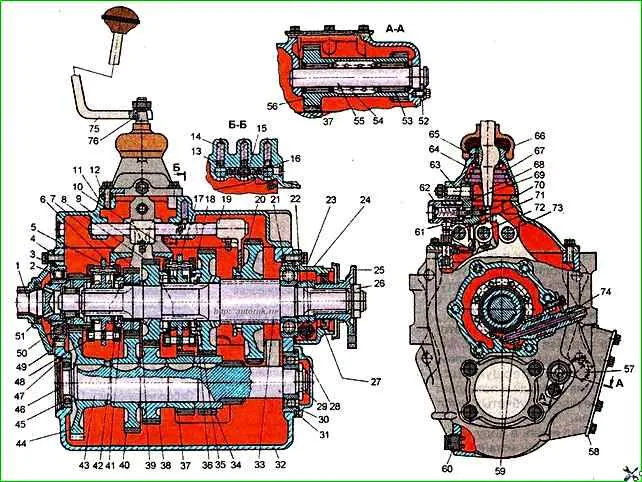
The use of synchronizers in the gearbox makes it easier to control the car, ensures silent gear shifting and increases the durability of the gear clutches.
It should be borne in mind that the gearboxes are equipped with a worm 22 and a gear 59 of the speedometer drive, designed for a certain gear ratio in the rear axle.
Type of gearbox mechanical with five gears for moving forward and one backward
Gear ratios:
- - first gear 6.45
- - second gear 3.56
- - third gear 1.98
- - fourth gear 1.275.
- - fifth gear 1.00 (direct)
- - rear stroke 6.15
Maximum torque transmitted to the gearbox, Nm 410
Gear shifting is mechanical, with a rocker arm mounted on the gearbox cover
Power take-off. From the reverse gear block
Maximum power of the power take-off, kW (hp) 22.08 (30)
Possible gearbox malfunctions
Cause of malfunction - Method of elimination
Difficult to engage all gears, reverse gear and first gear engage with a grinding noise
Incomplete disengagement of the clutch (the clutch "leads") - Adjust the free play of the clutch release bearing sleeve
Engagement of gears with impact and grinding
Worn conical rings of synchronizers or locking chamfers of fingers and carriage - Replace synchronizers
Self-disengagement of gears on the move
Incomplete engagement of gears due to a malfunction of the shift mechanism, wear of the fork grooves or loosening of the fork fastening and levers - Fix faults, replace worn parts
Gears do not engage
Destruction of bearings of driven shaft gears, broken pins or synchronizer locks - Replace faulty parts - Replace synchronizers
Increased noise level during gearbox operation
Worn or broken gear teeth. Destruction of bearings - Replace faulty parts.
Oil leak from gearbox
Worn seals or loss of elasticity
Increased pressure in gearbox crankcase, leakage along sealing surfaces - Replace seals
Flush breather. Tighten fasteners, replace gaskets





