The gearbox is mechanical, two-shaft, with five forward gears. It is structurally integrated with the differential and final drive.
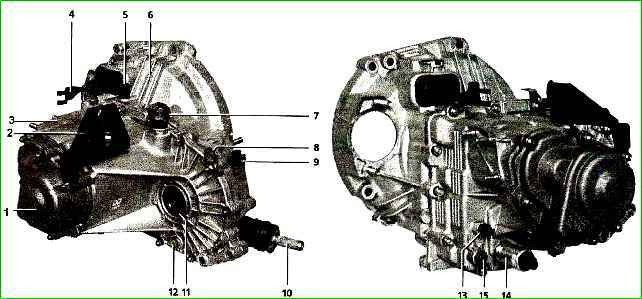
The gearbox housing consists of three parts: clutch housing 25, gearbox housing 7 and gearbox housing rear cover 1.
During assembly, a petrol-oil-resistant sealant is applied between them - a gasket.
A special magnet is located in the clutch housing socket, which holds metal wear products.
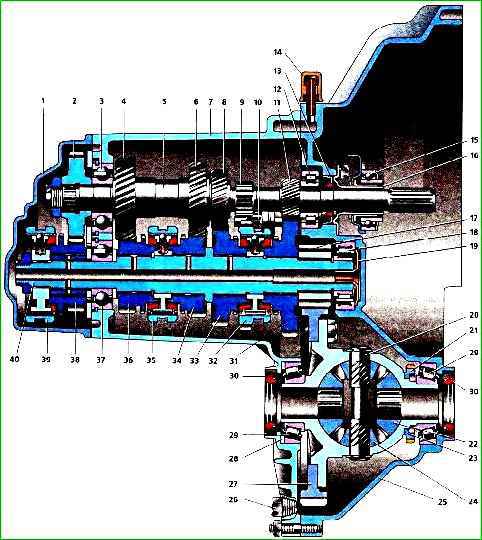
The primary shaft 5 is designed as a block of drive gears that are in constant engagement with the driven gears of all forward gears.
The secondary shaft 40 is hollow (to supply oil under the driven gears), up to the removable drive gear of the main gear 17.
It contains driven gears 31, 33, 34, 36, 38 and synchronizers 32, 35, 39 of the forward gears.
The front bearings of shafts 18 and 12 are roller bearings, the rear 3 and 37 are ball bearings.
The radial clearance in the roller bearings should not exceed 0.04 mm.
An oil sump is located under the front bearing 18 of the secondary shaft 19, directing the oil flow inside the shaft.
Differential - dual-satellite. The preload in bearings 29 (0.25 mm) is adjusted by selecting the thickness of ring 28 installed in the socket of the gearbox housing under the outer ring of the differential bearing.
The driven gear of the main gear 27 is attached to the flange of the differential box. The gearbox communicates with the atmosphere through the breather 14 located in its upper part.
The gearbox control drive consists of a gearshift lever, a ball joint, a control rod, a gearshift rod and a gearshift mechanism.
To prevent the gears from spontaneously disengaging due to axial movement of the power unit when the car is moving, a reaction rod is introduced into the gearbox control drive, one end of which is connected to the power unit, and the other end is attached to the base of the gearshift lever.
A switch (lever) is attached to the inner end of the rod, which acts on the three-arm lever of the gearshift mechanism gears.
This mechanism is made as a separate unit and is attached to the clutch housing. There are three axles in the gear shift mechanism housing.
One has a three-arm gear selection and engagement lever and two locking brackets.
The other axle passes through the holes in the locking brackets, preventing them from turning.
The gear selector, mounted on the rod, acts on the arm of the gear selector lever, which in turn engages forward gear with one arm and reverse gear with the other.
A reverse gear engagement fork is mounted on a separate axle.
A reverse gear lock solenoid is installed in the gearbox to prevent accidental engagement of reverse gear.
The protruding part of the solenoid core prevents the locking brackets from moving along the axles until the reverse gear is engaged.
A solenoid switch is installed on the gear shift lever.
When the ring under the handle is lifted, the switch contacts close and voltage is supplied to the solenoid.
The solenoid core retracts and makes it possible to engage reverse gear.
If the solenoid fails or its electrical circuit is broken, the reverse gear is engaged it becomes impossible to move.
In order to engage reverse gear and drive to a garage or service station where the malfunction can be fixed, you should unscrew the solenoid from the gearbox housing and screw in the gear shift fork rod retainer plug in its place, which we recommend that you carry with you.
In this case, be careful not to accidentally engage reverse gear instead of first.
After fixing the malfunction, you should add oil to the gearbox, since some of it will leak out when you unscrew the solenoid.
The gearbox is filled with transmission oil at the factory, designed for 75,000 km of run.
The oil level should be between the control marks on the oil level indicator.
Basic data for monitoring, adjustment and maintenance
Transmission oil (API group) GL—4 or GL—4/5
Recommended SAE transmission oil viscosity grade:
- —40 ˚C— +35 ˚C - 75W80, 75W85
- —40 ˚C— +45 ˚C - 75W90
- —26 ˚C— +35 ˚C - 80W85
- —26 ˚C— +45 ˚C - 80W90
Filling volume - 3.1 l
Drive oil seal sizes (right *2110-2301034, 2110-2301034-01; left* - 2110-2301035, 2110-2301035-01), mm:
- Outer diameter - 57
- Inner diameter - 35
- Width - 9
Dimensions of the primary shaft oil seal (2110-1701043), mm:
- Outer diameter - 45
- Inner diameter - 25
- Width - 9
Dimensions of the gear selection rod oil seal (2108-1703042-01), mm:
- Outer diameter - 30
- Inner diameter - 16
- Width - 7
* the seals of the left and right drives are not interchangeable, as they have different directions of the oil drain grooves
Tightening torques of threaded connections of the gearbox
Name of units and parts - Thread - Tightening torque, Nm (kgf.m)
- Threaded drain plug М22х1.5 - 28.7—46.3 (2.9—47)
- Reverse light switch М14х1.5 - 28.4—45.3 (259—4.6)
- Nut for fastening the housing of the speed sensor М6 - 4.5—7.2 (11.7—18.6)
- Nuts for fastening the gearbox to clutch housing M8 - 15.7-25.5 (1.6-2.6)
- Bolt with conical part of the joint of the gear shift rod M8 - 16.3-20.1 (1.7-2.1)
- Bolts for fastening the gear shift lever housing M8 - 15.7-25.5 (1.6-2.6)
- Bolts for fastening the gear shift mechanism M6 - 6.4-10.3 (0.7-1.1)
- Nuts for clamps of the gear shift rod M8 - 15.7-25.5 (1.6-2.6)
- Bolt for fastening the gear shift lever limiter M6 - 11.7-18.6 (1.2-1.9)
- Bolts for fastening the torque rod bracket M8 - 14.0—32.0 (1.4—3.2)
- Reverse fork retainer plug М16х1.5 - 28.4—35.0 (2.8—3.6)
* left and right drive oil seals are not interchangeable, as they have different oil drain groove directions
Possible gearbox malfunctions and troubleshooting methods
- Cause of malfunction
Troubleshooting methods
Gearbox noise (Noise decreases or disappears if clutch is depressed):
- Insufficient oil level in gearbox housing
Check level, top up oil if necessary. Check for leaks. Blow out breather
- Low oil quality. Water got into the oil (when water gets into the oil, a white emulsion is formed, it can be seen on the dipstick)
Change the oil. Drive carefully through fords and deep puddles.
Install the engine splash guard, put the tube on the gearbox breather and bring it up to a place protected from splashes
- Wear or damage to bearings, gear teeth
Replace worn bearings, gears
Gears are difficult to engage, there are no extraneous noises:
- The gearshift drive rod is deformed
Straighten or replace the rod
- The bolts securing the hinge or gear selector lever have loosened
Tighten the bolts (apply to their threaded part ь anaerobic sealant)
- Failure of plastic parts of the control drive
Replace the parts
- Incorrect drive adjustment
Adjust the drive
- Broken gearshift mechanism springs, deformed parts
Replace the springs, straighten the deformed parts or replace the mechanism as a whole
- Loose fit of the gearshift forks on the rods
Tighten the fork clamps on the rods
- Gearbox shaft nuts are not tightened
Tighten the nuts
- The clutch does not disengage completely
See the malfunction "Clutch drags"
The gears disengage spontaneously:
- Damage or wear of splines on the clutch, gear or synchronizer hub
Replace defective parts
- Incorrect drive adjustment
Adjust the drive
- Weak springs in the gear shift mechanism, worn rods
Replace worn parts
- Loose gearbox shaft nuts
Tighten the nuts
- Lost elasticity or damaged powertrain mounts
Replace the mounts
Noise, crackling, squealing of gears when shifting into gear:
- The clutch does not disengage completely
See clutch fault diagnostics
- No oil in gearbox housing
Add oil. Check for leaks. Blow out breather
- Damaged bearings, gear teeth
Replace bearings, gears
- Wear of synchronizer ring of engaged gear
Replace ring
Noise of final drive (Noise from gearbox side only when vehicle is moving):
- Wear or destruction of bearings
Replace destroyed and worn bearings of secondary shaft and differential (even with minimal wear). Adjust the differential box bearing preload
Reverse gear does not engage:
- Solenoid is faulty
Replace the solenoid or remove it and plug the hole in the gearbox
- Solenoid activation circuit is faulty
You can supply power to the solenoid directly from the battery
Oil leak
- Worn seals: primary shaft, drives, gear selection rod, worn speed sensor seal
Replace the seals. Blow out the gearbox breather
- Severe wear, nicks on the surface of the shafts on which the seals operate
Sand small damage with fine-grained sandpaper and polish.
When installing a new seal, you can slightly under-press it so that the edge of the seal operates on the unworn part of the shaft (in this case, to avoid distortion, you can put spacers up to 1 mm thick under the seal). In case of significant damage, replace the shafts and seals
- Large play in the primary shaft of the gearbox
Check the condition of the shaft bearings, their seating surfaces, and the tightening of the nut. Replace worn parts
- Loose clutch housing and gearbox cover fastenings
Tighten threaded connections
- Drain plug, reverse light switch, reverse gear lock solenoid, fork rod lock plugs are not tightly tightened
Tighten drain plug, light switch, solenoid, lock plugs






