Clutch — single-plate, dry, with a central diaphragm-type spring
Located in an aluminum housing, structurally integrated with the gearbox and attached to the engine cylinder block
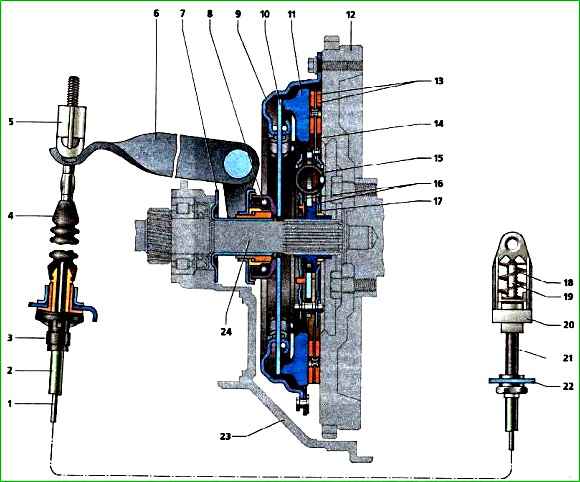
Clutch and its drive: 1 - clutch drive cable; 2 - cable casing; 3 - lower end of the cable casing; 4 - protective cover; 5 - linkage; 6 - fork lever; 7 - bearing guide sleeve; 8 - clutch release bearing; 9 - clutch housing; 10 - pressure spring; 11 - clutch pressure (leading) disc; 12 - flywheel; 13 - friction linings of the driven disc; 14 - driven disc; 15 - damper spring; 16 - torsional vibration damper; 17 - driven disc hub; 18 - spring; 19 - toothed tip of the cable; 20 - housing of the automatic cable length adjustment mechanism; 21 - spacer sleeve; 22 - cable casing bracket; 23 - clutch housing; 24 - primary shaft of the gearbox
The clutch housing is connected with six bolts to the engine flywheel.
The flywheel has three pins that enter the corresponding holes in the housing when installing the clutch, centering it.
The housing is connected to the pressure (leading) disk by three pairs of elastic steel plates.
The basket assembly is balanced on a stand, so it is replaced as a whole.
The basket must be replaced if the annular wear of the pressure spring petals is more than 0.8 mm deep, as well as if the surface of the pressure disk is heavily worn or the spring is "settled".

The driven disk with a spring torsional vibration damper is located on the splines of the primary shaft of the gearbox between the flywheel and the pressure plate.
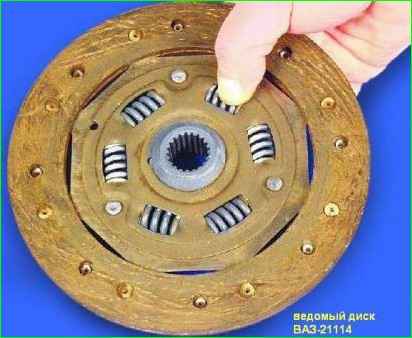
The driven disk is replaced when its axial runout is in the zone friction linings, loosening of riveted joints, and also if the rivet heads are recessed from the lining surface by less than 0.2 mm.
The clutch drive is cable-type, gap-free with automatic cable length adjustment.
A plastic leash is screwed onto the threaded end of the cable, which is inserted into the clutch release fork lever.
During vehicle operation, the linings of the driven disk wear out, causing the clutch release fork lever to move forward (in the direction of the vehicle).
Since the cable is connected to the fork lever, the length of the cable must be increased when the linings wear out to maintain normal clutch pedal travel.
The cable length is changed automatically using a regulator located in the upper end of the cable and connected to the clutch pedal.
Therefore, during operation, the adjustment There is no clutch cable.

The mechanism for automatic cable length adjustment consists of a plastic housing into which a toothed cable tip is inserted, held in the housing by two spring-loaded clamps.
The mechanism also includes a spacer sleeve put on the cable, one end of which enters the mechanism housing.
When the pedal is pressed, the spacer sleeve moves away from the cable casing bracket and does not press on the mechanism clamps.
In this case, the mechanism housing is rigidly connected with a cable.
If the driven disk linings are not worn, then when the pedal is released, the sleeve only touches the bracket and does not release the locks - the toothed end of the cable does not move relative to the housing.
As the linings wear out, the clutch release fork lever with the threaded end of the cable moves forward (in the direction of vehicle movement), tightening the cable.
In this case, the spacer sleeve, resting against the bracket, releases the spring-loaded locks, and the toothed end of the cable extends from the housing by the amount necessary to compensate for the wear of the linings.
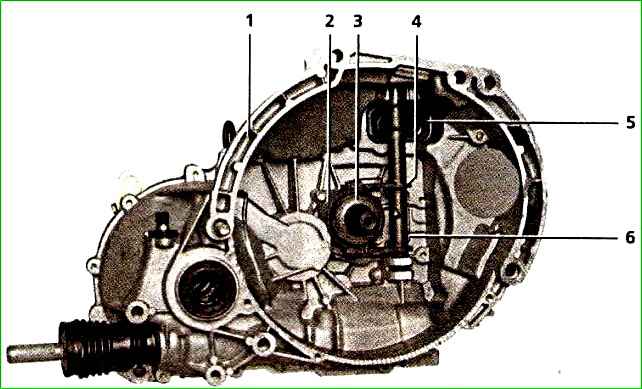
Clutch drive mechanism components: 1 - clutch housing; 2 - clutch release bearing guide sleeve; 3 - clutch release bearing with housing in assembly; 4 - clutch release fork; 5 - mud guard; 6 - bearing spring bracket
The clutch pedal is mounted on the axle in the pedal assembly bracket.
The clutch release bearing with the housing assembly is installed between the clutch release fork and the pressure spring petals.
The bearing housing is pressed against the fork tabs by the spring bracket.
The bearing moves freely along the guide sleeve secured to the clutch housing.
When the clutch pedal is pressed, the cable acts on the clutch release fork lever, which moves the bearing.
The bearing presses on the petals of the pressure spring of the clutch basket, while the pressure plate moves away from the flywheel, as a result of which the engine crankshaft and the input shaft of the gearbox can rotate independently of each other.
Possible malfunctions clutch and troubleshooting methods
Cause of malfunction - Troubleshooting methods
Clutch slips
(When you sharply press the accelerator pedal, the engine picks up speed, but the car barely accelerates.)
Oily contaminated flywheel, pressure plate, friction linings of the driven disk - Thoroughly wash the oiled surfaces with white spirit or gasoline and wipe them dry.
Replace a heavily oiled driven disk. Eliminate the cause of oiling (oil leak through engine or gearbox seals)
Loss of diaphragm spring force - Replace the pressure plate assembly ("basket")
Severe wear or burning of the friction linings of the driven disk - Replace the driven disk, article - "Replacing clutch parts"
Damaged or jammed clutch drive - Eliminate jamming. Replace drive parts if necessary
The clutch drags (forward gear shifting is difficult, reverse gear engages noisily, the gearbox is in good condition)
Incorrect clutch drive adjustment (insufficient pedal travel) - Adjust the drive. Replace a deformed clutch fork
Jammed clutch drive cable - Lubricate the cable with engine oil. If this does not help (cable wires are frayed, the sheath is damaged), replace the cable
Loose rivets or breakage of friction linings, warping of the driven disk (end runout more than 0.5 mm) - Replace the disk
Severe and uneven wear, scoring on the working surfaces of the flywheel or pressure plate - Replace the flywheel.
If the surface of the pressure plate is damaged, replace the housing with the pressure plate assembly (the "basket" of the clutch)
Jamming of the driven disk hub on the splines of the primary shaft of the gearbox - Clean the splines from dirt, eliminate minor damage with a file.
If the splines are significantly worn or damaged, replace the disk and / or the primary shaft of the gearbox.
Apply splines fresh grease SHRUS-4
Disc warping or warping - Replace the housing with the pressure plate assembly (clutch "basket")
Jerking when starting off
Clutch drive cable sticking - Lubricate the cable with engine oil. If this does not help, replace the cable
The driven disk hub is jammed on the splines of the gearbox input shaft - Clean the splines from dirt, remove minor damage with a file.
In case of significant wear or damage to the splines, replace the disk and / or the gearbox input shaft.
Before assembly, apply fresh SHRUS-4 grease to the splines
Deformation of the driven disk - Replace the driven disk
Loose fastening of the friction linings of the driven disk, severe wear or cracks on the linings - Replace the driven disk
Loss of elasticity of the spring plates of the driven disk - Replace the driven disk
Significant subsidence or breakage of the torsional vibration damper springs, wear of the windows under the springs - Replace driven disk
Scuffs on the working surfaces of the flywheel or pressure plate - Replace the flywheel or clutch housing with the pressure plate assembly (clutch "basket")
Oily contaminated working surfaces of the friction linings of the driven disk - Thoroughly wash the oiled surfaces with white spirit or gasoline and wipe them dry.
Replace a heavily oiled driven disk. Eliminate causes of oiling
Rattling, knocking or noise when engaging the clutch
Significant settling or breakage of the torsional vibration damper springs, wear of the windows under the springs - Replace the driven disk
Deformation of the driven disk - Replace the driven disk
Loose fastening of the friction linings of the driven disk, severe wear or cracks on the linings - Replace the driven disk
Increased noise when disengaging the clutch
Worn, damaged or leaking grease from the clutch release bearing - Replace the bearing





