The car is equipped with two braking systems - service and parking
The service braking system is designed to reduce the speed of the car, up to its complete stop and to hold the car stationary for a short time
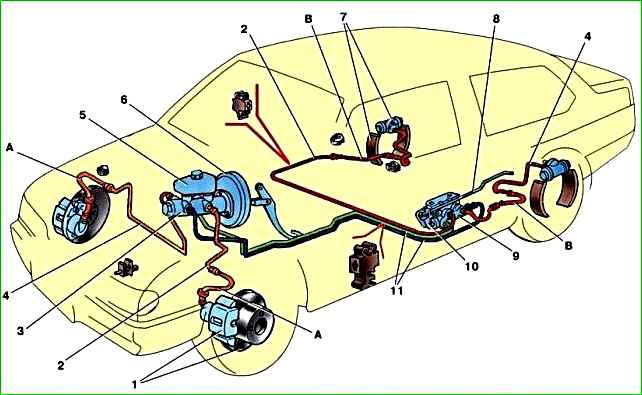
Brake hydraulic drive diagram: 1 - front wheel brake mechanism; 2-pipeline of the circuit "left front - right rear brake"; 3 - master cylinder of the brake hydraulic drive; 4 - pipeline of the circuit "right front - left rear brake"; 5 - reservoir of the master cylinder; 6 - vacuum booster; 7 - rear wheel brake mechanism; 8 - elastic lever of the pressure regulator drive; 9 - pressure regulator; 10 - lever of the pressure regulator drive; 11 - brake pedal; A - flexible hose of the front brake; B - flexible hose of the rear brake
The working brake system is dual-circuit, diagonal, with a hydraulic drive, consists of a master brake cylinder with a vacuum booster, four wheel brake mechanisms and a fluid pressure regulator in the rear brake mechanisms.
The front wheel brake mechanisms are disc, ventilated, the rear ones are drum.
Each of the circuits The vehicle includes the brake mechanisms of two wheels: one front and one rear, located diagonally on the vehicle.
One circuit includes the brake mechanisms of the front right and rear left tracks, and the second circuit includes the brake mechanisms of the front left and rear right tracks.
If one of the circuits fails, the second circuit, although less efficiently, will ensure that the vehicle stops.
The fluid pressure regulator limits the flow of fluid to the rear brake mechanisms when the load on the rear axle is insufficient, thereby preventing the rear wheels from locking and the rear axle of the vehicle from skidding during sudden braking.
The regulator body has an inspection hole closed with a plastic plug.
Fluid leaking from this hole indicates that the regulator rings are not tight.
To reduce the force applied by the driver to the brake pedal, a vacuum booster is installed in the brake system drive, which operates due to vacuum formed in the intake manifold of a running engine.
A brake fluid reservoir is installed on the body of the main brake cylinder.
A low brake fluid level sensor is built into the reservoir cap.
When the fluid level in the reservoir drops dangerously, the sensor turns on a warning light on the instrument panel.
Some cars are equipped with a brake system with ABS (anti-lock braking system).
Possible brake malfunctions and troubleshooting methods
- Cause of malfunction
Troubleshooting method
Increased brake pedal travel:
- Brake fluid leaking from wheel cylinders
Replace the failed wheel cylinder parts, flush and dry the pads, discs and drums, bleed the system hydraulic drive
- Air in the brake system
Bleed the system, article - "Replacing the brake fluid"
- Damaged rubber sealing rings in the master brake cylinder
Replace the rings and bleed the system
- Damaged rubber hoses of the brake hydraulic drive
Replace the hoses and bleed the system, article - "Replacing brake hoses and tubes"
- Increased runout of the brake disc (more than 0.15 mm)
Grind the disc; if the disc thickness is less than 10.8 mm, replace it
- Fluid leaking through the pressure regulator tappet seals
Replace the seals
Insufficient braking efficiency:
- Oily brake pads
Clean the pads with a wire brush, using warm water and detergents. Eliminate the cause of fluid or grease getting on the brake pads
- Pistons jammed in the wheel cylinders
Eliminate the causes of jamming, replace damaged parts, bleed the system
- Complete wear of the brake pad linings
Replace the brake pads, articles - "Repair of the front wheel brake mechanism", "Repair of the rear wheel brake mechanisms"
- Overheating of the brake mechanisms
Immediately stop and let the brake mechanisms cool down
- Use of pads with inappropriate linings
Use pads only recommended by the manufacturer
- Incorrect adjustment of the pressure regulator
Adjust the pressure regulator drive
- Loss of tightness of one of the circuits (accompanied by partial failure of the brake pedal)
Replace damaged parts, bleed the system
Incomplete release of all wheels:
- No free travel of the brake pedal
Adjust the free travel of the pedal
- The protrusion of the adjusting bolt of the vacuum booster rod relative to the mounting plane of the master cylinder is disturbed
Adjust the protrusion (1.25-0.2 mm) of the adjusting bolt
- Swelling of the rubber seals of the master cylinder due to gasoline, mineral oils, etc. getting into the fluid.
Thoroughly flush the entire system with brake fluid, replace the rubber parts, bleed the hydraulic drive system
- Jamming of the piston of the master cylinder
Check and, if necessary, replace the master cylinder, bleed the system
Braking of one wheel with the brake pedal released:
- The tension spring of the rear brake pads is broken or weakened brakes
Replace the spring
- The piston is stuck in the wheel cylinder due to contamination or corrosion of the cylinder body
Disassemble the cylinder, clean and wash the parts, replace the damaged ones, bleed the system
- Swelling of the wheel cylinder sealing rings due to gasoline, mineral oils, etc. getting into the fluid
Replace the rings, flush the brake hydraulic system with brake fluid, bleed the system
- Violation of the position of the caliper relative to the brake disc when the bolts securing the shoe guide to the steering knuckle are loose
Tighten the bolts, replace the damaged parts if necessary
- Incorrect adjustment of the parking brake system
Adjust the parking brake system
Skidding or pulling the car to the side when braking:
- Wheel cylinder piston jamming
Check and eliminate piston jamming in the cylinder, replace damaged parts if necessary, bleed the system
- Any steel tube is clogged due to a dent or blockage
Replace the tube or clean it and bleed the system
- Discs, drums and linings are dirty or oily
Clean brake mechanism parts
- Incorrect adjustment of the pressure regulator drive
Adjust the drive
- The pressure regulator is faulty
Repair or replace the regulator, article - "Brake pressure regulator"
- Wheel alignment angles are broken
Adjust the alignment angles wheels
- Different tire pressure
Set normal pressure
- One of the brake system circuits does not work (accompanied by deterioration in braking efficiency and increased pedal travel)
Replace damaged parts and bleed the system
Increased force on the brake pedal when braking:
- The vacuum booster is faulty
Replace the booster, article - "How to check and replace the vacuum booster"
- The hose connecting the vacuum booster and the engine intake pipe is damaged, or its fastening on the fittings has loosened
Replace the hose or tighten the clamps of its fastening
- Swelling of the cylinder seals due to gasoline, mineral oils and etc.
Flush the entire system thoroughly, replace rubber parts, bleed the system
Squeaking or vibration of the brakes:
- Weakening of the rear brake shoe tension spring
Check the tension spring, replace with a new one if necessary
- Ovality of the brake drums
Bore the drum
- Oiling of the friction linings
Clean the linings with a wire brush, using warm water with detergents.
Eliminate the cause of liquid or grease getting on the brake pads
- Wear of the linings or inclusion of foreign bodies in them
Replace the pads
- Excessive runout of the brake disc or its uneven wear (felt by vibration of the brake pedal)
Grind the disc, if the thickness is less than 10.8 mm, replace it
Basic system data:
- Brake fluid type DOT 4
- Filling volume of the brake system hydraulic drive 0.45 l
- Free travel of the brake pedal 3-5 mm
- Number of clicks of the parking brake ratchet device 2-4
- Minimum thickness of the friction linings of the front brake pads 1.5 mm
- Minimum thickness of the brake disc 17.8 mm
- Maximum runout of the brake disc 0.15 mm
- Maximum diameter of the working surface of the brake drum 201.5 mm
- Minimum thickness of the friction linings of the rear brake shoes 1.5 mm
Tightening torques of threaded connections:
Name of units - Thread - Tightening torque, Nm (kgf-m)
- Wheel mounting bolts М12х1.25 - 65.2-92.6 (6.7-9.5)
- Nut for mounting the brake booster bracket to the body М8 - 31-38 (3.2-3.9)
- Nuts for mounting the brake booster to the bracket М10 - 26.5-32.3 (2.7-3.3)
- Nuts for mounting the brake master cylinder to the vacuum M10 - 26.5-32.3 (2.7-3.3)
- Front wheel brake hose end M10x1.25 - 29.4-33.4 (3.0-3.4)
- Front wheel brake mechanism mounting bolts to steering knuckle M10x1.25 - 29.1-36 (3.0-3.7)
- Front brake mechanism working cylinder mounting bolts to guide pins M8 - 31-38 (3.2-3.9)
- Front brake mechanism working cylinder mounting bolts to caliper M12x1.25 - 95.9-118.4 (9.8-12.1)
- Brake pipe fittings M10 - 14.7-18.2 (1.5-1.9)
- Rear brake mechanism slave cylinder mounting bolt М6 - 3.3-7.7 (0.3-0.8)
- Pressure regulator bracket mounting nut М8 - 10.4-24.2 (1.1-2.5)
- Pressure regulator to bracket mounting bolt М8 - 10.4-24.2 (1.1-2.5)






