The engine ignition system uses one ignition coil. It consists of two two-terminal ignition coils, made in a single housing
Sparking occurs in two cylinders simultaneously (1-4 or 2-3).
The ignition coil is connected to the spark plugs by four high-voltage wires with permanent tips.

Turn off the ignition.

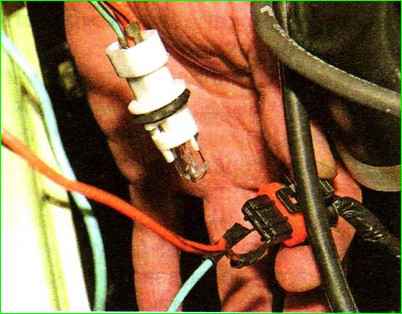
Having released the latch, disconnect the wiring harness block 1 from the terminals of the ignition module 2, Figure 1 and 2.

Disconnect the high-voltage wires from the spark plugs.

Use a five-point hexagon to unscrew the four screws securing the ignition module to the bracket

Location of the ignition module mounting screws

Removing the ignition module
Installing the ignition coil in reverse order
The procedure for checking the ignition module is described below
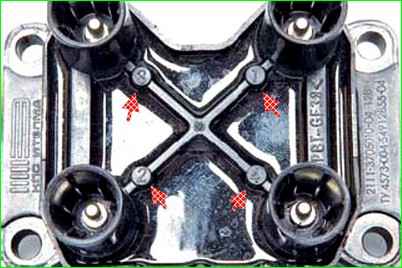
In order not to confuse the connection order, the serial numbers of the ignition wires are marked on the module
Checking the ignition module
Turn off the ignition and disconnect the engine control system wiring harness block from the coil.
To check the coil power circuit, connect the tester to the middle terminal of the harness block and the engine ground.
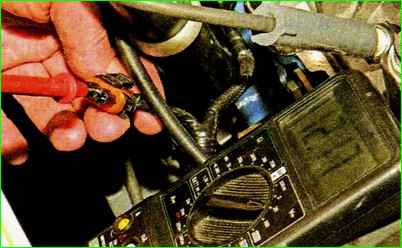
When the ignition is turned on, the device should record a voltage approximately equal to the battery voltage.
If there is no voltage at the middle terminal of the wiring harness block, then the wire connecting the block to the ignition switch or the lock contact group is probably faulty.
To check the coil control circuits, you can use a probe with a 1-2 W lamp.
Relieve the pressure in the engine power supply system and do not replace the fuel pump fuse.
Connect the probe probes to the middle and one of the outer terminals of the wiring harness block.
If the control (and power) circuit is working properly, the probe light should blink frequently when cranking the crankshaft with the starter.
Otherwise, check the wire connecting the outer terminal of the block to the controller terminal for open circuit and short to ground.
Similarly, by connecting the probe probes to the middle and other extreme terminals of the block, we check the other ignition coil control circuit.
You can check the serviceability of the ignition coil itself on the engine by disconnecting the wiring harness block and high-voltage wires from it; for clarity, we show the test on a dismantled coil.

To check one of the primary windings of the coil, connect the tester probes to the middle and one of the outer terminals of the ignition coil.
In ohmmeter mode, we check the circuit for an open circuit.
If the tester shows infinity, it means there is a break in the circuit.
Similarly, by connecting the tester probes to the middle and other extreme terminals of the coil, we check the other primary winding of the coil for an open circuit.
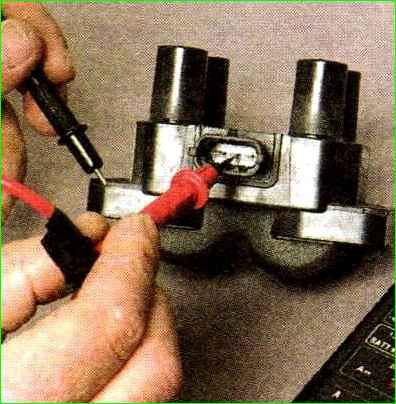
To check for breakdown (short to ground) of the primary windings, connect the tester probes to the middle terminal of the coil and to the metal part of the coil body.
If the circuit of the primary windings is working properly, the tester should record the value infinity.

To check for a break in the secondary winding of the ignition coil, connect the tester probes to the paired high-voltage terminals of the coil (terminals 1-4 or 2-3 cylinders).
For a working ignition coil, the tester should record a resistance of about 4.0 kOhm.
If the secondary winding breaks, the tester will show “infinity”. Similarly, we check the other secondary winding of the ignition coil.

We check the secondary windings of the ignition coil for breakdown on the engine.
Relieve the pressure in the engine power supply system and do not replace the fuel pump fuse.
Two known good spark plugs will be required for testing.
We tie the spark plug bodies together with a piece of bare wire (“massage”).
We connect the paired terminals of the ignition coil with the spark plugs using serviceable high-voltage wires and place the spark plugs on the cylinder head cover.
Crank the crankshaft with the starter
Do not touch spark plugs or high-voltage wire tips, otherwise you may receive an electric shock.
If the ignition coil is working properly, sparks should regularly jump between the electrodes of the spark plugs.
Similarly, by connecting the high-voltage wires to the other two paired terminals of the coil, we check the other secondary winding for breakdown.





