The engine is in-line four-cylinder, equipped with an integrated microprocessor-based fuel injection and ignition control system (KMSUD).
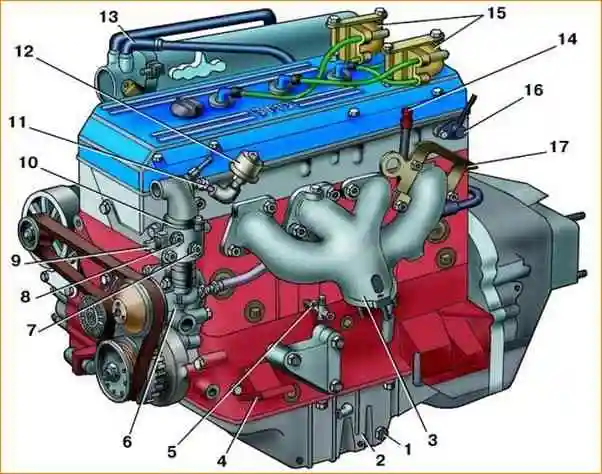
View of the ZMZ-4062 engine from the left side: 1 - drain plug; 2 - oil sump; 3 - exhaust manifold; 4 - engine support bracket; 5 - coolant drain valve; 6 - water pump; 7 - coolant overheat lamp sensor; 8 - coolant temperature indicator sensor; 9 - temperature sensor; 10 - thermostat; 11 - emergency oil pressure lamp sensor; 12 - oil pressure indicator sensor; 13 - crankcase ventilation hose; 14 - oil level indicator (dipstick); 15 - ignition coil; 16 - phase sensor; 17 - heat shield
The cylinder block is cast in gray cast iron.
There are channels for coolant between the cylinders.
Cylinders are made without insert sleeves.
There are five crankshaft main bearings at the bottom of the block.
The main bearing caps are made of ductile iron and are attached to the block with two bolts.
The bearing caps are bored together with the block, so they cannot be interchanged.
On all covers, except for the third bearing cover, their serial numbers are stamped.
The cover of the third bearing, together with the block, is machined at the ends to install thrust bearing half washers.
The chain cover and stuffing box with crankshaft seals are bolted to the ends of the block.
The oil sump is attached to the block from below.
At the top of the block is a cylinder head cast from an aluminum alloy. It has intake and exhaust valves.
There are four valves per cylinder, two intake and two exhaust.
The intake valves are on the right side of the head, and the exhaust valves are on the left.
The valves are driven by two camshafts through hydraulic tappets.
The use of hydraulic pushers eliminates the need to adjust valve clearances, as they automatically compensate for the gap between the camshaft lobes and valve stems.
Outside, on the body of the hydraulic pusher there is a groove and a hole for supplying oil into the hydraulic pusher from the oil line.
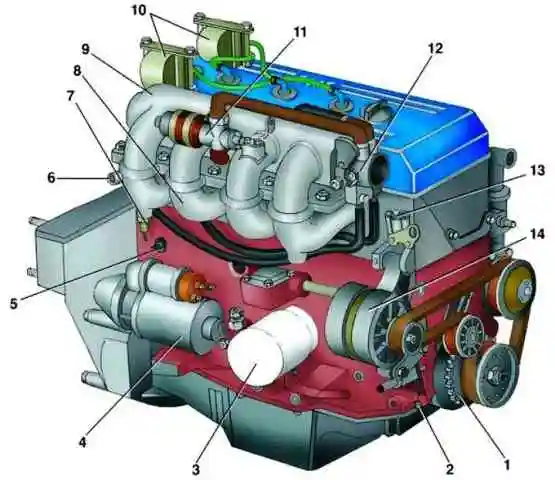
View of the ZMZ-4062 engine on the right side: 1 - synchronization disk; 2 - speed and synchronization sensor; 3 - oil filter; 4 - starter; 5 - knock sensor; 6 - coolant drain pipe; 7 - air temperature sensor; 8 - inlet pipe; 9 - receiver; 10 - ignition coil; 11 - idle speed regulator; 12 - throttle; 13 - hydraulic chain tensioner; 14 - generator
The piston rests against the bottom of the hydraulic pusher housing.
At the same time, the hydraulic pusher has a steel body, inside of which a guide sleeve is welded.
A compensator with a piston is installed in the sleeve. The compensator is held in the sleeve by a retaining ring.
An expanding spring is installed between the compensator and the piston, which compresses the body of the check ball valve.
When the camshaft cam does not press the hydraulic pusher, the spring presses the hydraulic pusher housing through the piston to the cylindrical part of the camshaft cam, and the compensator to the valve stem, while choosing the gaps in the valve drive.
The ball valve is open in this position, and oil enters the hydraulic pusher.
Once the camshaft cam turns and presses against the pushrod housing, the housing will drop down and the ball valve will close.
The oil between the piston and compensator begins to work as a solid body.
The hydraulic pusher moves down under the action of the camshaft cam and opens the valve.
When the cam, turning, stops pressing on the body of the hydraulic pusher, it moves up under the action of the spring, opening the ball valve, and the whole cycle repeats again.
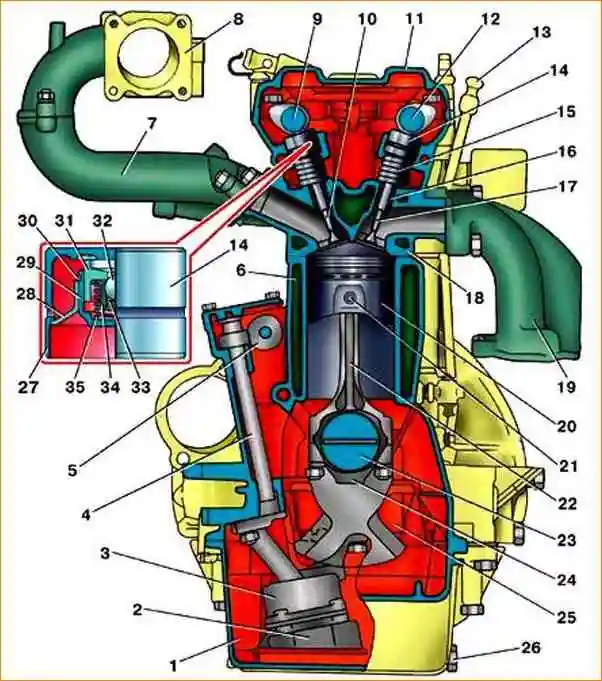
Cross section of the ZMZ-4062 engine: 1 - oil sump; 2 - oil pump receiver; 3 - oil pump; 4 - oil pump drive; 5 - intermediate shaft gear; 6 - cylinder block; 7 - inlet pipe; 8 - receiver; 9 - intake camshaft; 10 - inlet valve; 11 - valve cover; 12-camshaft exhaust valves; 13 - oil level indicator; 14 - hydraulic valve tappet; 15 - outer spring of the valve; 16 - valve guide 17 - exhaust valve; 18 - cylinder head; 19 - exhaust manifold; 20 - piston; 21 - piston pin; 22 - connecting rod; 23 - crankshaft; 24 - connecting rod cover; 25 - main bearing cap; 26 - drain plug; 27 - pusher body; 28 - guide sleeve; 29 - compensator body; 30 - retaining ring; 31 - compensator piston; 32 - ball valve; 33 - ball valve spring; 34 - body of the ball valve; 35 - expanding spring
Saddles and valve guides are installed in the head of the block with a large interference fit.
Combustion chambers are made in the lower part of the block head, and camshaft bearings are located in the upper part. Aluminum covers are installed on the supports.
The front cover is common to the intake and exhaust camshaft bearings.
This cover has plastic thrust flanges that fit into the grooves on the camshaft journals.
The covers are bored together with the head of the block, so they cannot be interchanged. On all covers, except for the front one, serial numbers are embossed.
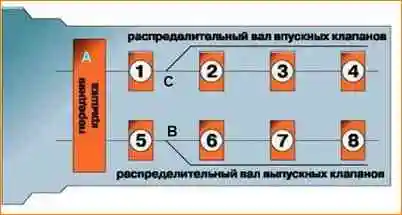
Camshafts are cast iron.
The cam profiles of the intake and exhaust shafts are the same.
The cams are offset by 1.0 mm relative to the axis of the hydraulic pushers, which makes them rotate when the engine is running.
This reduces wear on the surface of the hydraulic tappet and makes it even.
The top of the block head is closed with a cover cast from an aluminum alloy.
The pistons are also cast aluminum alloy. On the bottom of the piston there are four recesses for the valves, which prevent the piston from hitting the valves when the valve timing is disturbed.
For the correct installation of the piston in the cylinder, the inscription "Front" is cast on the side wall near the boss under the piston pin.
The piston is installed in the cylinder so that this inscription is up to the piston bottom.
The oil scraper ring consists of three elements: two facing the front of the engine.
Each piston has two compression rings and one oil scraper ring.
Compression rings are cast iron.
The barrel-shaped working surface of the upper ring is covered with a layer of porous chromium, which improves the running-in of the ring.
The working surface of the lower ring is coated with a layer of tin.
There is a groove on the inner surface of the lower ring.
The ring must be installed on the piston with this groove of steel discs and expander.
The piston is attached to the connecting rod using a "floating type" piston pin, i.e. the pin is not fixed either in the piston or in the connecting rod.
The finger is kept from moving by two spring retaining rings, which are installed in the grooves of the piston bosses.
Forged steel connecting rods with I-section shank.
A bronze bushing is pressed into the upper head of the connecting rod. The lower head of the connecting rod with a cover that is attached with two bolts.
The nuts of the connecting rod bolts have self-locking threads and therefore do not additionally lock.
The connecting rod caps are machined together with the connecting rod and therefore cannot be moved from one connecting rod to another.
Cylinder numbers are stamped on the connecting rods and connecting rod caps.
To cool the piston bottom with oil, holes are made in the rod of the connecting rod and the upper head.
The mass of pistons assembled with connecting rods should not differ by more than 10 g for different cylinders.
Thin-walled connecting rod bearings are installed in the lower head of the connecting rod.
The crankshaft is cast from ductile iron.
The shaft has eight counterweights. It is kept from axial movement by thrust washers mounted on the middle neck.
A flywheel is attached to the rear end of the crankshaft.
A spacer sleeve and a gearbox input shaft bearing are inserted into the flywheel bore.
Cylinder numbers are stamped on the connecting rods and connecting rod caps.
To cool the piston bottom with oil, holes are made in the rod of the connecting rod and the upper head.
The mass of pistons assembled with connecting rods should not differ by more than 10 grams for different cylinders.
Thin-walled connecting rod bearings are installed in the lower head of the connecting rod. The crankshaft is cast from ductile iron.
The shaft has eight counterweights. It is kept from axial movement by thrust washers mounted on the middle neck.
A flywheel is attached to the rear end of the crankshaft. A spacer sleeve and gearbox input shaft bearing are inserted into the flywheel bore.






