The main dimensions of the cylinder block are shown in Figure 1
The cylinder block is cast from special low-alloy cast iron
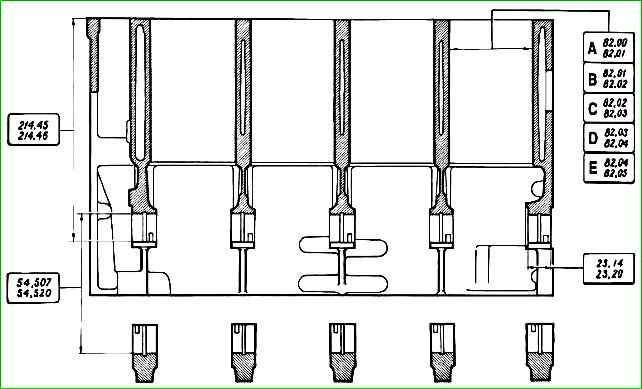
The cylinder diameters are divided into five classes, each 0.01 mm, designated by the letters A, B, C, D, E.
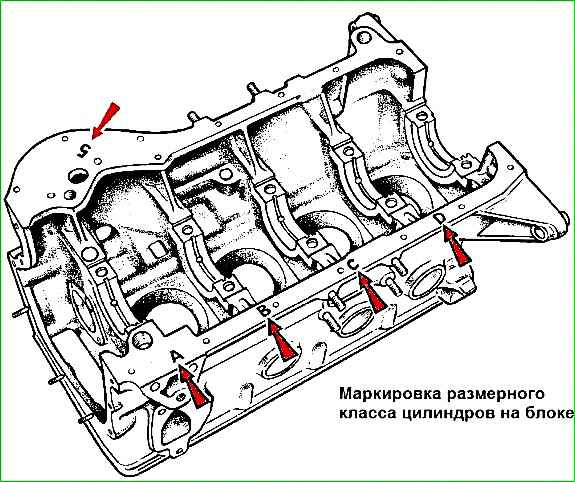
The cylinder class is stamped on the lower plane of the cylinder block
It is possible to bore the cylinders for repair pistons, increased in diameter by 0.4 and 0.8 mm.
The main bearing caps are machined together with the cylinder block.
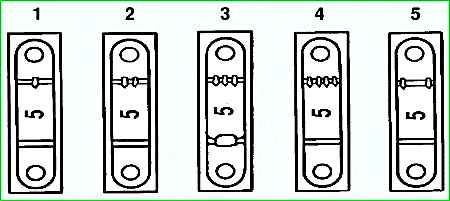
Therefore, they are not interchangeable and have marks on the outer surface to distinguish them (see Fig. 2-18).
Checking the technical condition and repairing the cylinder block
Thoroughly wash the cylinder block and clean the oil channels.
Blow it out and dry it with compressed air, then inspect the cylinder block. Cracks in the bearings or other places of the cylinder block are not allowed.
If there is a suspicion of coolant getting into the crankcase, then check the tightness of the cylinder block on a special stand.
To do this, having plugged the openings of the cooling jacket of the cylinder block, pump water at room temperature into it under a pressure of 0.3 MPa (3 kgf / cm 2).
There should be no water leakage from the cylinder block for two minutes.
If oil gets into the coolant, then without completely disassembling the engine, check for cracks in the cylinder block in the areas of the oil channels.
To do this, drain the coolant from the cooling system, remove the cylinder head, fill the cooling jacket of the cylinder block with water and supply compressed air to the vertical oil channel of the cylinder block.
If air bubbles appear in the water filling the jacket, cooling, replace the cylinder block.
Check the plane of the cylinder block joint with the head using a ruler and a set of feeler gauges.
The ruler is installed along the diagonals of the plane and in the middle in the longitudinal direction and across. The flatness tolerance should not be more than 0.1 mm.
Cylinder repair
Check whether the cylinder wear exceeds the maximum permissible value of 0.15 mm.
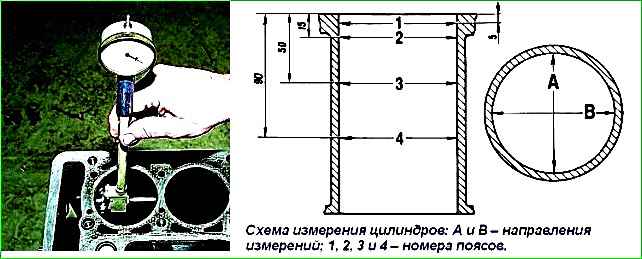
The cylinder diameter is measured with a bore gauge (Fig. 2-32) in four belts, both in the longitudinal and transverse directions of the engine. A micrometer is used to set the bore gauge to zero.
In the zone of belt 1, the cylinders are practically not worn out. Therefore, the difference in measurements in the first and other belts can be used to judge the amount of wear on the cylinders.
If the maximum wear is greater than 0.15 mm, bore the cylinders to the nearest repair size, leaving an allowance of 0.03 mm on the diameter for honing.
Then hone the cylinders, maintaining a diameter such that when installing the selected repair piston, the calculated gap between it and the cylinder is 0.025–0.045 mm.
Replacing the plugs
Replacing the oil channel plugs:
- - drill a hole with a diameter of 4-5 mm in the center of plug 1, Figures 5 and 6;
- - remove the plug from block 2;
- - remove burrs, clean and degrease the seating surface under the plug;
- - degrease the new plug;
- - apply anaerobic glue to the seating surface of the cylinder block under the plug (anaerobic glue AN-112);
when installing the plug 1/01586/01:
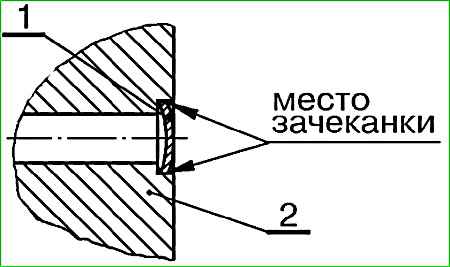
- - install plug 1, (Fig. 5), into the hole of the oil channel and settle;
- - calk the seat of the plug;
when installing the plug 21083-1002046:
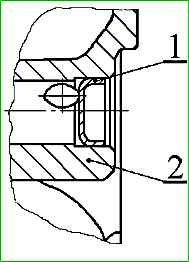
- - install plug 1, (Fig. 6), into the oil channel hole and press it in using a mandrel. The pressing depth is provided technologically (mandrel 67.7853-9631).
Replacing the cooling system plugs:
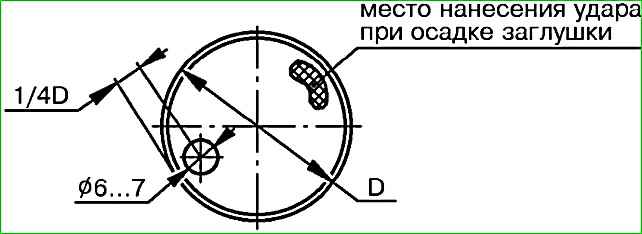
- - drill a hole in the plug with a diameter of 6-7 mm at a distance of 1/4 of its diameter from the edge, as shown in the figure 7;
- - seat the plug on the side diametrically opposite the hole until a gap appears between the inner wall of the cylinder block and the edge of the plug;
- - insert a firmware or a technological rod into the hole and remove the plug from the cylinder block;
- - remove burrs, clean and degrease the seating surface under the plug;
- - degrease the new plug;
- - apply anaerobic glue to the seating surface of the cylinder block under the plug (anaerobic glue AN-112);
- - install a new plug (mandrel 67.7853-9590 for plugs 00001-0043299-01-0 with a diameter of 40 mm, mandrel 67.7853-9591 for plugs 00001-0043289-01-0 diameter 25 mm, hammer).





