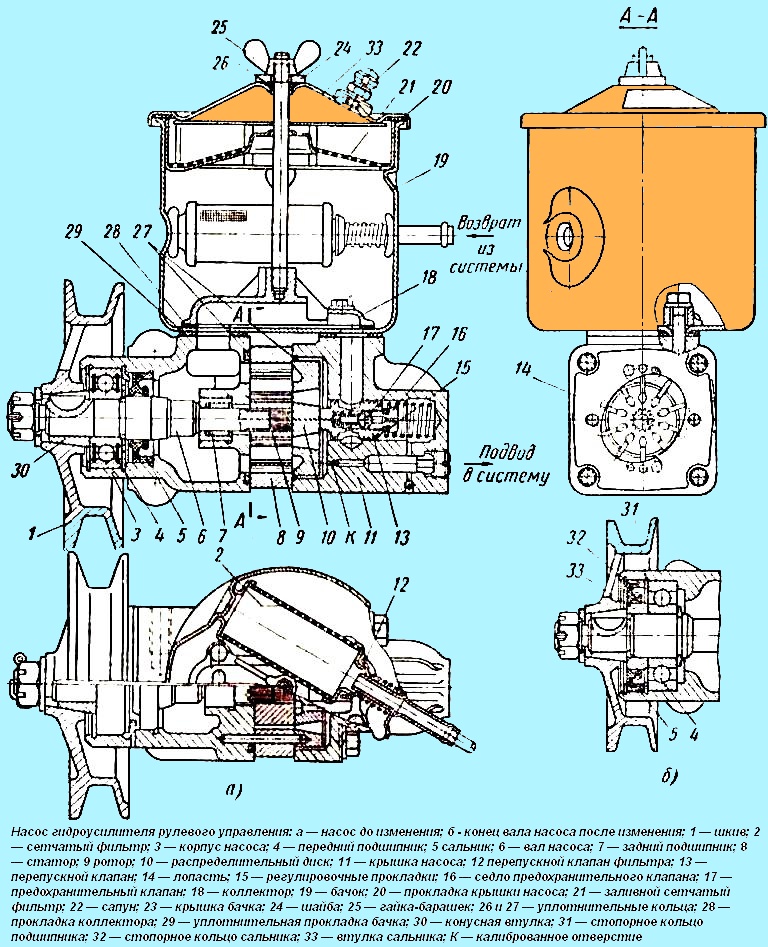
During operation, it is necessary to regularly check the oil level in the hydraulic booster system and wash the pump filters within the time specified in the lubrication map
Check the tightness of the connections and hoses of the power steering system daily.
The pump belt tension should also be checked daily.
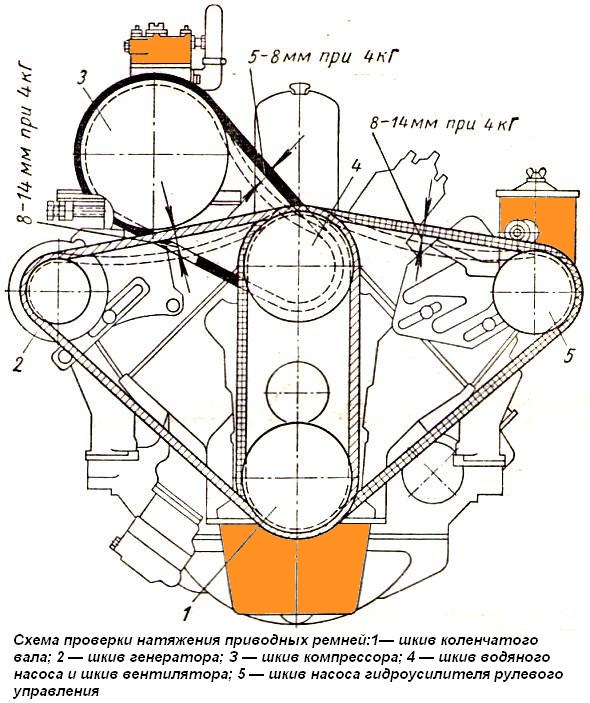
The belt is tensioned by moving the power steering pump.
With normal tension, the deflection of the belt between the fan pulleys and the power steering pump under a force of 4 kg should be within 8-14 mm (see Fig. 1).
Only clean, filtered oil specified in the lubrication chart should be used for the power steering system.
Oil must be filled through a funnel with a double mesh and a filler filter installed in the power steering pump reservoir.
The use of contaminated oil causes rapid wear of pump and hydraulic booster parts.
When checking the oil level in the power steering system, which must be carried out at every service, the front wheels of the car must be installed straight.
Before removing the reservoir cap to check the oil level, add it or change it, the cap must be thoroughly cleaned of dirt and rinsed with gasoline.
Oil must be added when the engine is idling until oil appears above the inlet filter mesh 21 (see Fig. 2). Full mesh coverage is not required.
For TO-2, both filters of the power steering pump must be washed in gasoline.
In case of significant clogging of the filters with tarry deposits, additional washing of the filters with a solvent used when painting a car should be carried out.
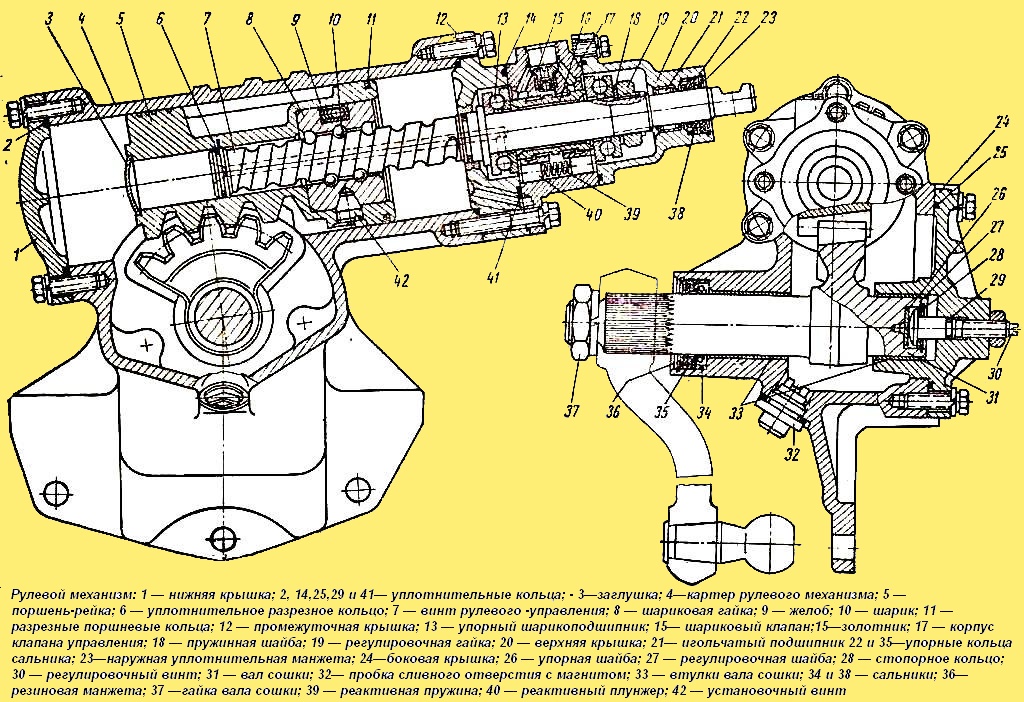
During maintenance, it is necessary to check the fastening of the steering gear housing to the frame, the steering column to the cab bracket, the steering wheel on the steering shaft, the tightening of the bipod, the tightening of the lock nut of the adjusting screw and the propeller shaft fastening nuts.
The tightening torque of the steering gear bipod nut should be 25-30 kgm, the adjusting screw locknuts 4-4.5 kgm, the propeller shaft wedge nuts 1.4-1.7 kgm.
When installing hoses, their twisting and sharp bends are not allowed.
Changing the steering gear oil
When changing the oil, disconnect the longitudinal link of the car and open the reservoir cap of the power steering pump.
To drain the oil you need:
- 1) turn the steering wheel all the way to the left;
- 2) open the drain hole by unscrewing the plug with the magnet from the steering gear housing.
The oil drain is considered complete when the oil flow from the steering gear housing drain hole has stopped.
After draining, you need to flush the hydraulic booster system, which requires:
- - remove the residue of contaminated oil from the reservoir of the hydraulic booster pump; the presence of residues of cleaning material in the tank is unacceptable;
- - wash the washer 24 (see Fig. 2), the rubber sealing ring 26 of the pump cover and the drain plug 32 (see Fig. 3) with the steering gear housing magnet, having cleaned them of dirt; remove and wash the pump filter screens and put them back in place;
- - pour 1 liter of fresh oil into the pump reservoir through a double-mesh funnel and drain this oil through the drain hole of the steering gear housing, while turning the steering wheel from lock to lock.
To pour fresh oil you need:
- 1. Screw the plug with a magnet into the drain hole of the steering gear case.
- 2. With the steering wheel turned all the way to the left, pour fresh oil into the pump reservoir until oil appears above the inlet filter screen.
Then, turning the steering wheel from lock to lock and without applying force on the stops, add oil until at least 2.5 liters of oil are poured into the system.
Start the engine, then add fresh oil and, when the engine is idling, turn the steering wheel from lock to lock, holding it briefly on the stops for 2-3 seconds with a force of about 10 kg and adding oil as necessary until it above the grid (no need to completely cover the grid).
Filling oil is considered complete when air stops flowing out of the system in the form of bubbles through the oil in the pump reservoir.
- 3. Stop the engine, install the tank cap with gasket, rubber sealing ring, cover studs and washer and secure with a wing nut. Tighten the wing nut by hand.
In case of oil leakage from under the tank cap, check the correct installation of the cap gasket and, if it is damaged, replace it.
- 4. Connect the trailing link and lubricate the joint.
Driving with the hydraulic booster not working
If the hydraulic booster fails to work due to damage to the pump or hydraulic booster, damage to the pump drive hose or belt, or engine stop, you can only use the steering mechanism for a short time, until the malfunction is corrected.
Prolonged work on a car with a non-working hydraulic booster leads to rapid wear of the steering mechanism or its breakdown.
In the event of a rupture in the hydraulic booster pump hoses, you should:
- 1) connect the pump outlet to the nozzle on the pump reservoir;
- 2) close the discharge and return openings on the hydraulic booster with wooden plugs or in another way that provides protection against the ingress of dirt or foreign bodies;
- 3) add oil to the pump tank to the level indicated above; it is allowed to fill the oil used for the engine, with its replacement at the base;
- 4) drive to the base while the engine is running at the lowest possible number of revolutions of the crankshaft, observing the temperature of the oil in the reservoir.
If the oil is heated, stop and let the oil cool down.
Tie Rods
The steering drive consists of a longitudinal and transverse steering rods.
Tubular tie rod with adjustable ball joints.
Each hinge has a spring and two spherical crackers, between which there is a ball head of the finger, clamped by an adjusting plug.
Longitudinal steering rod connects the ball pins of the lower end of the steering arm with the lever of the front axle left ball joint housing.
It is necessary that the rod with a shorter arm along the bend be put on the bipod ball pin.
When assembling the hinge, the adjusting plug is tightened to the stop, and then released to the first possible position for cotter pins, but not less than ¼ turn, and cottered.
It should be remembered that the complete elimination of gaps in the hinges is not allowed, as this can lead to breakage of the ball pin or rod.
To keep grease in the hinges and protect them from dirt, the grooves for the ball pins in the thrust head are covered with felt pads.
The tie rod has right-hand threads with different pitches at the ends, for screwing heads with ball joints, with which you can change the length of the rod and thereby adjust the toe-in.
The hinge heads are made with upper and lower bushings and a spring pressing the bushing.
Hinges do not need to be adjusted.
When assembling, make sure that the ball pins turn by hand without jamming.
Every day you should check and tighten all fasteners, check the condition of the swivel joints of the longitudinal and transverse steering rods, and if necessary, adjust the clearance of the hinges and lubricate the articulated steering rods according to the lubrication map.